Revision Notes: Public Revenue | Financial Accounting for SSS 3 PDF Download
Meaning of Public Revenue
Public revenue is the money that a government earns, which is essential for funding various developmental projects like building roads, railways, schools, and hospitals. A significant amount of money is also needed to keep the government's administrative structure running. Therefore, it is crucial for the government to plan its revenue carefully to promote the economic growth of the country.
Sources of Public Revenue
Tax Revenue
- This is the primary source of income for the government.
- Taxes are mandatory payments imposed on individuals or businesses to cover government expenditures.
Non-Tax Revenue
- This revenue comes from sources other than taxes.
- Non-tax revenue is collected to provide administrative services to the public.
Taxes
A tax is a mandatory payment that the government imposes on individuals or businesses to cover the costs of providing common benefits to the public.
Characteristics of Tax
- Compulsory Payment: Taxes are mandatory payments that citizens must make to the government. Only the government can impose taxes, and refusal to pay can lead to legal action.
- General Welfare: The money collected from taxes is used by the government for the common good of the taxpayers and the welfare of the nation.
Commercial Revenues
Commercial revenues refer to the income generated by the government through public enterprises by selling their goods and services.
Differences between Tax and Price:
- Tax: A tax is a mandatory payment made by citizens to the government. Only the government can impose taxes.
- Price: A price is paid only by those who purchase goods and services provided by the government.
- Benefit: When people pay taxes, they are not guaranteed any specific benefit in return. In contrast, a price is paid directly for goods consumed in the market.
Administrative Revenues
- Fees: A fee is charged for a specific purpose, such as a school admission fee. Unlike taxes, fees are not compulsory payments to the government, and there is no legal penalty for not paying a fee.
- Forfeiture: Forfeiture is a penalty imposed by the court when an individual fails to appear in court.
- Right of Escheat: The Right of Escheat allows the government to acquire the bank balance or property of a person who dies without a will or legal heirs.
Objectives and Significance of Taxes
Taxes play a crucial role in generating revenue for the government to finance developmental programs. Tax relief provided to entrepreneurs helps them manage the production of goods, and such tax policies can lead to the expansion of certain industries and trade. Custom duties are also an important tool for reducing the import of goods that are available domestically, thereby promoting economic growth.
Furthermore, taxation policy is instrumental in regulating the production and consumption of goods and services within a country. For instance, heavy taxes can be imposed on nonessential goods like wines and cigarettes, which helps in reducing their production and consumption. This policy also aids in allocating scarce resources to more desirable lines of production. Differential commodity taxation is therefore an effective means of regulating the production and consumption patterns of goods in the economy.
Direct and Indirect Taxes
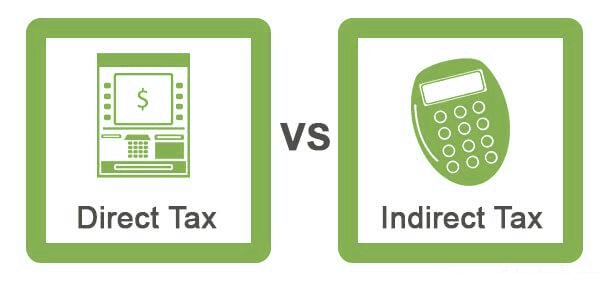
Differences between direct taxes and indirect taxes
Direct Taxes:
- Direct taxes are levied on individuals or entities and cannot be shifted to others.
- These taxes are progressive, meaning the tax rate increases with higher income levels.
- The impact and incidence of direct taxes fall on the same person, making them accountable for the tax burden.
Indirect Taxes:
- Indirect taxes are imposed on individuals but can be passed on to others, either partially or fully.
- These taxes are regressive, as they often burden common people regardless of their income levels.
- The producer bears the impact and incidence of indirect taxes, passing the cost onto consumers.
Merits of Direct Tax
- Equity: Direct taxes are based on the principle of ability to pay, ensuring that the tax burden is distributed more on the rich than on the poor. This promotes fairness in the tax system.
- Certainty: Direct taxes provide certainty to both individuals and the government. Taxpayers know how much tax is due and when, while the government can predict tax revenue, allowing for better budget management.
- Elasticity: Direct taxes are elastic, meaning the government can increase tax rates during crises to generate more revenue. This flexibility helps during economic downturns.
Demerits of Direct Tax
- Tax evasion: Direct taxes are vulnerable to evasion as they rely on the honesty of taxpayers. Businesses may misrepresent their income to evade taxes, making enforcement challenging.
- Narrow in scope: Direct taxes primarily target the wealthy, limiting the government's ability to collect from low-income groups. This narrow scope restricts the overall tax base.
Merits of Indirect Tax
- Convenient: Indirect taxes are paid in small portions at regular intervals, making them convenient for taxpayers. Since these taxes are included in the price of the commodity, they do not feel like a burden to the taxpayer.
Demerits of Indirect Tax
- Uncertain: Indirect taxes on goods with elastic demand are uncertain. When a commodity is taxed, its price increases, which can reduce the demand for that commodity in the market. This makes the revenue from indirect taxes unpredictable.
- Discourage savings: Since a large portion of income is spent on the consumption of goods that include indirect taxes in their price, it leaves little room for savings.
Understanding Impact and Incidence of Taxation
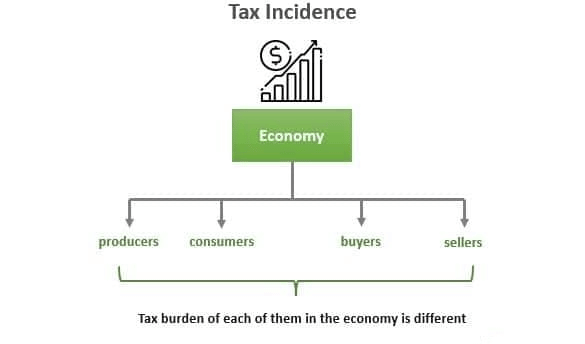
When the government imposes a tax, it creates a burden on the taxpayer. However, the person who bears the burden of the tax may not always be the same as the person from whom the government collects it. Impact of Taxation Incidence of Taxation Example: Income Tax Example: Sales Tax
- The tax burden is shifted to the consumer, who pays a higher price for the commodity.
Other Kinds of Taxes
Progressive Tax: This type of tax means that as a person's income increases, the percentage of income paid as tax also increases.
For example:
- If the monthly income is Rs 2000, the tax rate is 10%, and the tax collection is Rs 200.
- If the monthly income is Rs 4000, the tax rate is 5%, and the tax collection is Rs 200.
Proportional Tax: In a proportional tax system, the tax rate remains the same no matter how much the income increases. Everyone pays the same percentage of their income as tax.
For example:
- If the monthly income is Rs 2000, the tax rate is 10%, and the tax collection is Rs 200.
- If the monthly income is Rs 4000, the tax rate is 10%, and the tax collection is Rs 400.
Regressive Tax: In a regressive tax system, the tax rate decreases as income increases. Although the total amount of tax increases with higher income, the average tax rate decreases.
For example:
- If the monthly income is Rs 2000, the tax rate is 10%, and the tax collection is Rs 200.
- If the monthly income is Rs 4000, the tax rate is 7.5%, and the tax collection is Rs 300.
Degressive Tax: This system combines both progressive and proportional taxes. The tax rate increases up to a certain level, after which a uniform rate is charged. As income increases, the total tax amount may decrease.
For example:
- If the monthly income is Rs 2000, the tax rate is 10%, and the tax collection is Rs 200.
- If the monthly income is Rs 4000, the tax rate is 2.5%, and the tax collection is Rs 100.
|
1 videos|18 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Public Revenue - Financial Accounting for SSS 3
| 1. What are the key characteristics of a tax? |  |
| 2. What are the merits of direct taxes? |  |
| 3. What are the demerits of direct taxes? |  |
| 4. What are the merits of indirect taxes? |  |
| 5. What are the demerits of indirect taxes? |  |














