Revision Notes: Consumer Awareness | Economics Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Consumer Awareness |

|
| Growth of Consumer Awareness |

|
| Rights and Duties of a Consumer |

|
| Consumer Protection Act |

|
Understanding Consumer Awareness
- Consumer awareness refers to the understanding and knowledge that consumers have about their rights and responsibilities when purchasing goods and services.
- It is essential for consumers to be aware of their rights to ensure that the products and services they buy meet proper standards.
- According to the Consumer Protection Act of 1986 in India, a consumer is defined as anyone who buys goods and services, either in full or part payment, without the intention of using them for commercial purposes.
Forms of Consumer Exploitation
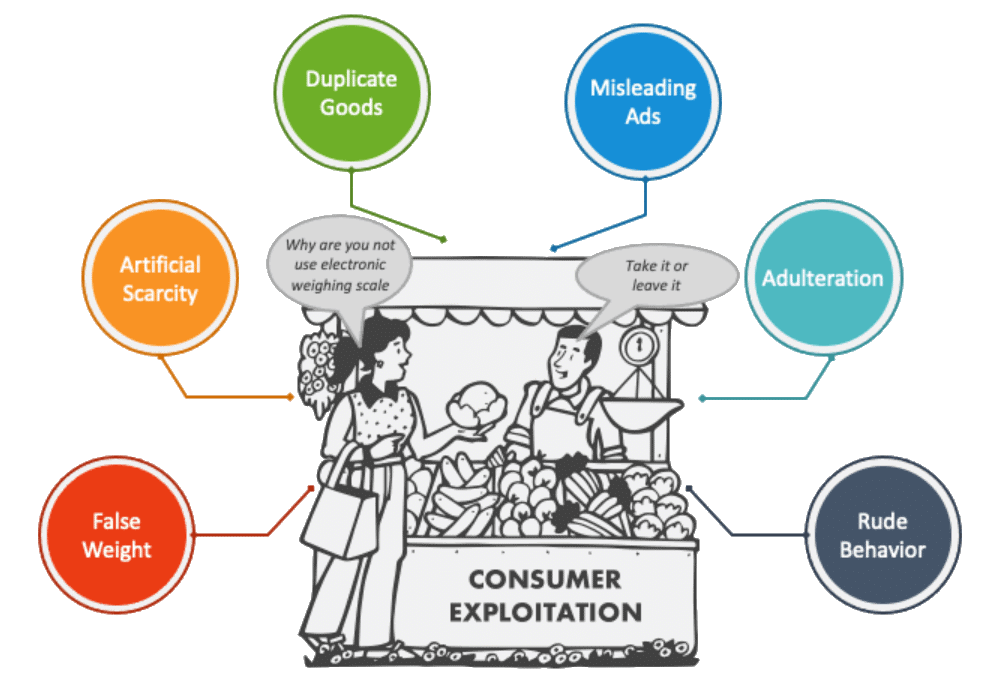
Common business malpractices in the market include:
- Sale of Adulterated Goods: This involves mixing inferior substances with the product being sold.
- Sale of Sub-Standard Goods: Selling products that do not meet the prescribed quality standards.
- Use of False Weights and Measures: Misleading consumers by using inaccurate weights and measures, resulting in losses.
- Supply of Defective Goods: Providing products that are faulty or damaged.
- Misleading Advertisements: Promoting a product or service with false claims about its quality, grade, or standard.
- Sale of Spurious Goods: Selling items of little value instead of the genuine product.
- Sale of Duplicate Goods: Offering counterfeit products as originals.
- Hoarding and Black-Marketing: Creating scarcity and inflating prices through unethical practices.
- Overcharging: Charging more than the maximum retail price (MRP) set for a product.
- Supply of Inferior Services: Providing services that do not meet the agreed-upon quality standards.
Reasons for Consumer Exploitation
- Many consumers purchase a wide range of goods without being adequately informed about their consumer rights.
- Due to illiteracy, some consumers do not question the quality and quantity of goods provided by sellers, even when they are unsatisfactory.
- Consumers are often lured by advertisements for products without verifying their quality.
Growth of Consumer Awareness
The consumer movement in India originated from social concerns, driven by the need to protect consumers from unfair practices by traders. Widespread issues such as food shortages, hoarding, black marketing, and the adulteration of food and edible oils led to increasing dissatisfaction among consumers with dishonest traders. This dissatisfaction sparked the consumer movement in an organized manner.
In response to these issues, the Government of India took steps to promote consumer protection, culminating in the enactment of the Consumer Protection Act in 1986. This legislation aimed to safeguard the interests of consumers and ensure fair practices in the marketplace.
Since 1962, March 15th of every year is celebrated as World Consumer Rights Day, further highlighting the importance of consumer rights and protection.
Consumer protection in India is crucial for:
- Improving market conditions to provide consumers with more choices at lower prices.
- Reducing instances of consumer exploitation by sellers in the marketplace.
- Empowering consumers to transition from being 'passive' to 'active' participants in the market.
Rights and Duties of a Consumer
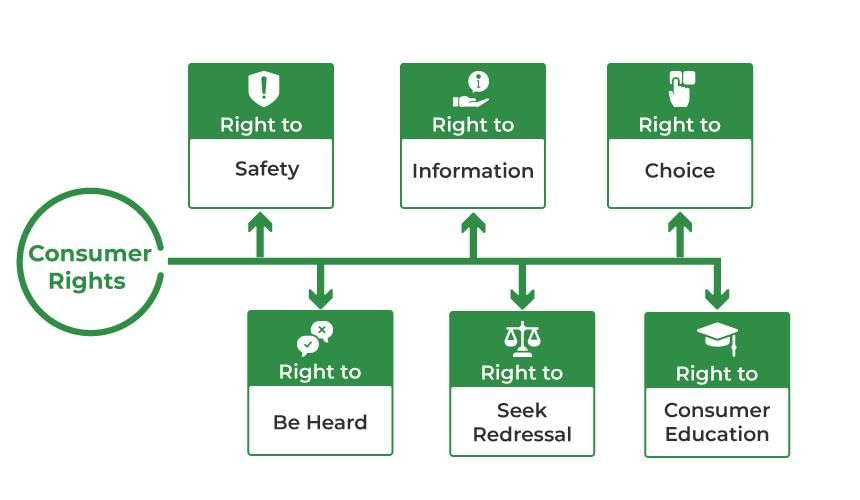
Rights of a Consumer
- Right to Safety: Consumers have the right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services that are hazardous to their health and property. The products and services they purchase should not only meet their immediate needs but also safeguard their long-term interests.
- Right to Choose: This right allows consumers to select from a variety of goods and services available at competitive prices. It is most meaningful in a competitive environment where multiple enterprises can offer different products and services with minimal government control.
- Right to be Heard: Consumers have the right to have their interests considered in appropriate forums. This means they can voice their concerns against unfair and restrictive trade practices.
- Right to Seek Redressal: Consumers are entitled to seek redress for grievances related to the performance, grade, and quality of goods and services. If a product is defective, it should be repaired or replaced by the seller. The Consumer Protection Act provides for a fair settlement of genuine complaints and establishes a mechanism for redressal at district, state, and national levels.
- Right to Consumer Education: Consumers have the right to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to become educated and informed throughout their lives.
- Right to be Informed: Consumers must be provided with adequate and accurate information about the quality, quantity, purity, standard, and price of goods and services. Manufacturers typically include detailed information on product labels and packaging, such as contents, quantity, manufacturing date, expiry date, maximum retail price, and precautions, to assist consumers in their buying decisions.
To acquire proper knowledge: It is a consumer’s duty to acquire knowledge and skills needed for taking action and to influence factors which affect consumer decisions.
To receive consumer education: Education is the most powerful tool for the promotion of consumer welfare. Consumers must educate themselves through programmes conducted by voluntary organisations with the help of mass media.
Consumer Protection Act

The Consumer Protection Act, 1986, made the provision for setting up a three-tier system of consumer courts at the national, state and district levels. This lead to the formation of the National Consumer Commission at the national level, the State Consumer Commission at the state level and the District Forum at the district level. Consumer grievances and complaints against traders are checked at these three levels. Also, they provide relief and compensation to the affected consumers. Currently, there are more than 500 district courts functioning in the three-tier system of India.
Right to Information (RTI)
The Right to Information (RTI) Act is a law in India that was passed on June 15, 2005, and came into effect on October 13, 2005. This Act gives people the right to access information held by public authorities. The RTI Act is based on the principle that transparency and accountability in government are essential for a healthy democracy.
Under the RTI Act, "right to information" means the right to access various types of information held by public authorities. This includes:
- Inspection of Work, Documents, and Records: Individuals have the right to physically inspect work, documents, and records maintained by public authorities.
- Making Notes and Certified Copies: People can make notes or request certified copies of documents or records.
- Making Certified Samples: The Act allows for the making of certified samples of materials held by public authorities.
- Receiving Information in Electronic Form: Individuals can receive information stored in computers or other devices in electronic form, such as CDs, or through printouts.
|
18 videos|101 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Consumer Awareness - Economics Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are the main reasons for consumer exploitation in the market? |  |
| 2. How can consumers protect themselves from exploitation? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Right to Information for consumers? |  |
| 4. How does consumer behavior influence market practices? |  |
| 5. What role do regulatory bodies play in consumer protection? |  |















