JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Mind Map: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
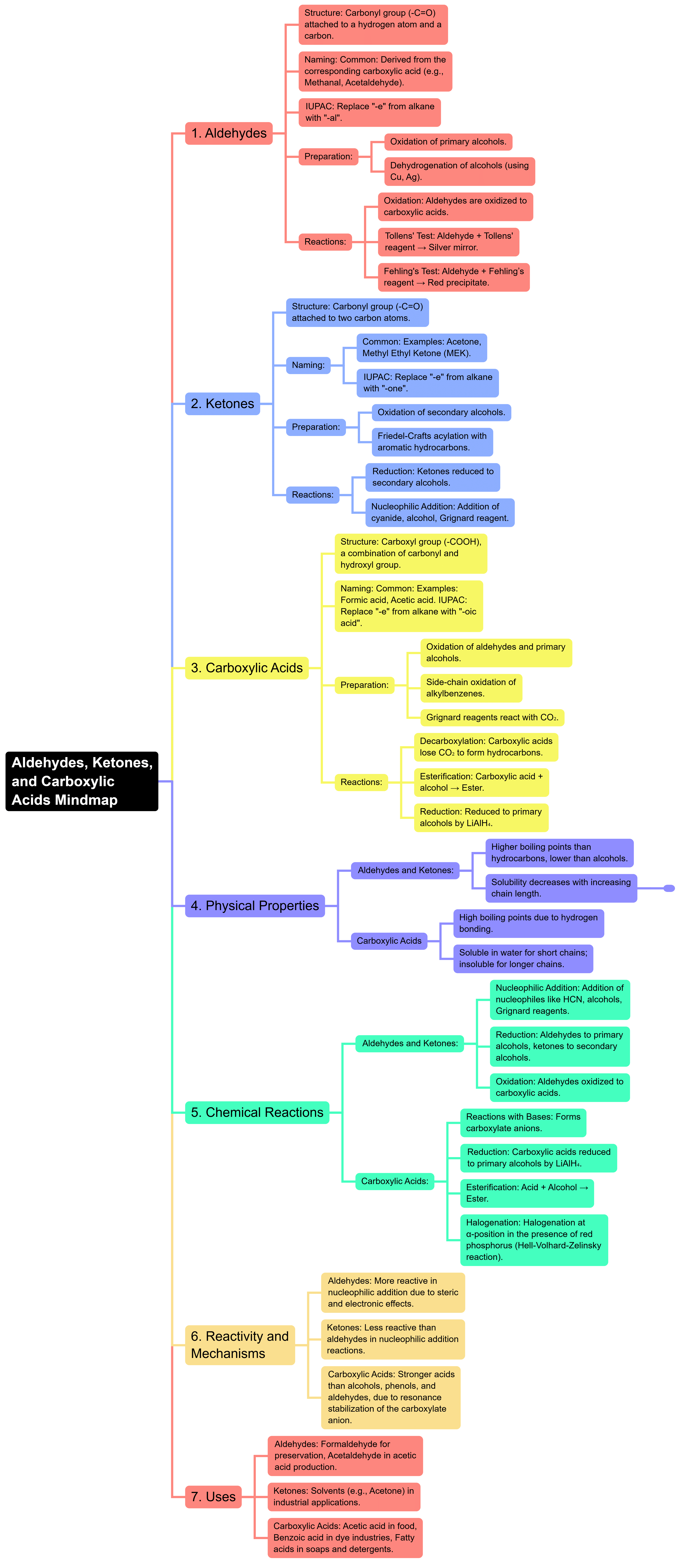
The document Mind Map: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
334 videos|656 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the key differences between aldehydes and ketones? |  |
Ans.Aldehydes and ketones are both types of carbonyl compounds, but they differ in their structure and properties. Aldehydes have the carbonyl group (C=O) at the end of the carbon chain, whereas ketones have the carbonyl group located within the chain. This structural difference leads to variations in their reactivity and physical properties, such as boiling points and solubility. For example, aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones due to the presence of the hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon, which makes them more prone to oxidation.
| 2. How can carboxylic acids be identified in a laboratory setting? |  |
Ans.Carboxylic acids can be identified using several methods. One common method is to perform a litmus test; carboxylic acids turn blue litmus paper red due to their acidic nature. Another method involves the reaction of carboxylic acids with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), which produces carbon dioxide gas (CO₂), indicated by bubbling or fizzing. Additionally, infrared spectroscopy (IR) can be used to identify the characteristic C=O (carbonyl) stretching vibrations around 1700 cm⁻¹ and O-H stretching around 2500-3300 cm⁻¹.
| 3. What are some common reactions that aldehydes undergo? |  |
Ans.Aldehydes undergo several important reactions. One of the most notable is oxidation, where aldehydes can be oxidized to form carboxylic acids in the presence of oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) or dichromate ions. They also undergo nucleophilic addition reactions, where nucleophiles such as alcohols or Grignard reagents attack the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of hemiacetals or alcohols. Aldehydes can also participate in condensation reactions, such as the aldol condensation.
| 4. What is the significance of the carboxyl group in carboxylic acids? |  |
Ans.The carboxyl group (-COOH) is significant in carboxylic acids as it is responsible for their acidic properties. The presence of the -COOH group allows carboxylic acids to donate a proton (H⁺) in solution, making them weak acids. This acidity is due to the resonance stabilization of the carboxylate ion (RCOO⁻) formed upon deprotonation. Additionally, the carboxyl group influences the solubility, boiling point, and reactivity of carboxylic acids, making them important in various biological and chemical processes.
| 5. How do aldehydes and ketones differ in their boiling points and solubility? |  |
Ans.Aldehydes and ketones exhibit different boiling points and solubility characteristics due to their molecular structure. Generally, aldehydes have lower boiling points than corresponding ketones of similar molecular weight because ketones have a more significant dipole moment due to the presence of two alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon, enhancing intermolecular forces. In terms of solubility, both aldehydes and ketones are polar and can dissolve in water, but aldehydes with shorter carbon chains tend to be more soluble compared to ketones, as longer carbon chains in ketones can reduce solubility.
Related Searches





















