JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Biomolecules
Mind Map: Biomolecules | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
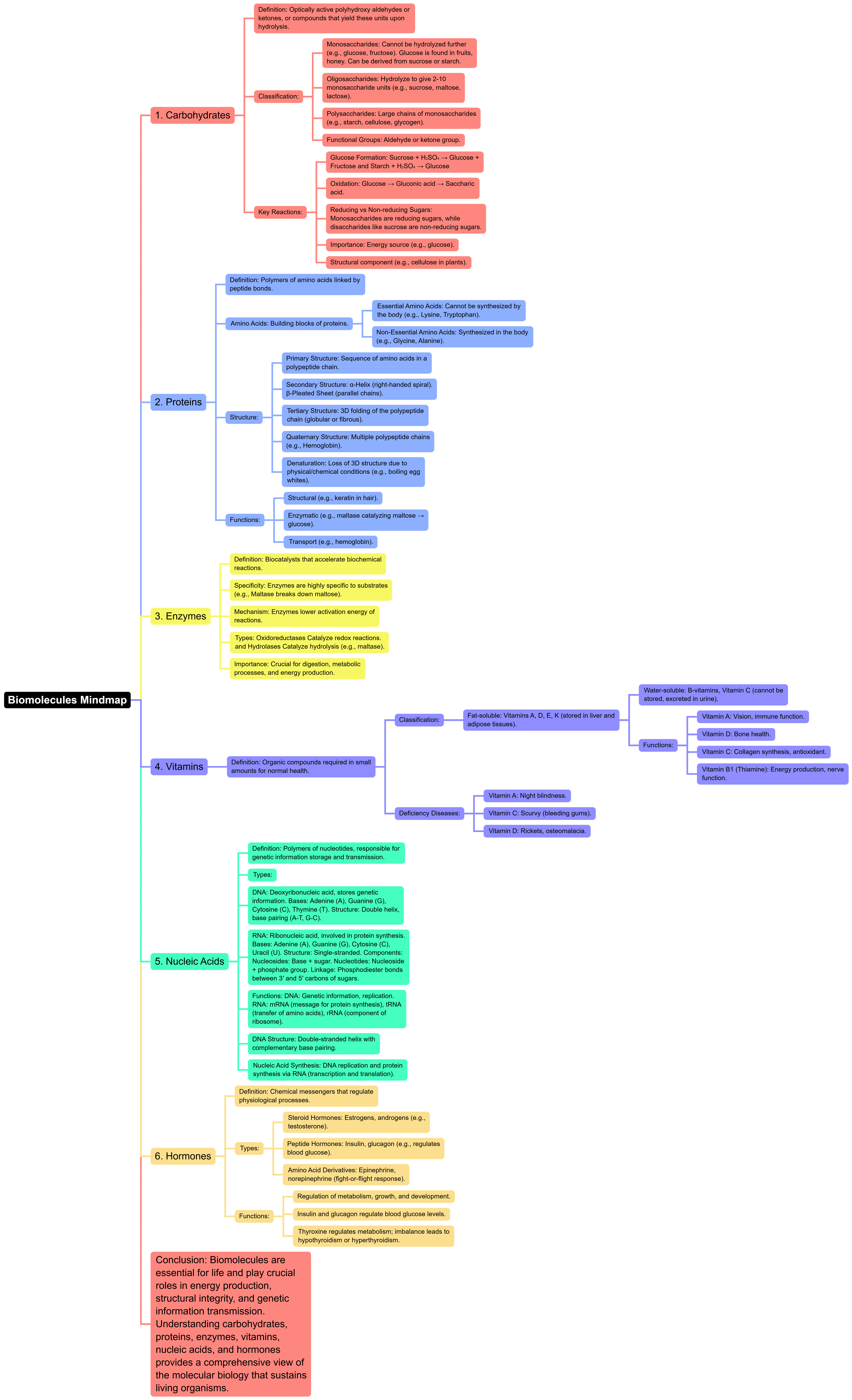
The document Mind Map: Biomolecules | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
334 videos|651 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Biomolecules - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the main types of biomolecules and their functions in living organisms? |  |
Ans. The main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates provide energy and structural support. Lipids serve as energy storage molecules and are key components of cell membranes. Proteins perform a wide range of functions including catalyzing biochemical reactions (enzymes), providing structure (collagen), and facilitating communication (hormones). Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, store and transfer genetic information.
| 2. How do enzymes, which are proteins, function as biological catalysts? |  |
Ans. Enzymes function as biological catalysts by lowering the activation energy required for chemical reactions to occur. They possess a specific active site that binds to substrates, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. This interaction facilitates the conversion of substrates into products, thereby speeding up the reaction without being consumed in the process. Factors such as temperature, pH, and substrate concentration can affect enzyme activity.
| 3. What is the significance of the structure of proteins in their function? |  |
Ans. The structure of proteins is crucial to their function, as it determines how they interact with other molecules. Proteins have four levels of structure: primary (amino acid sequence), secondary (alpha helices and beta sheets), tertiary (three-dimensional shape), and quaternary (multiple polypeptide chains). Any alteration in these structures can affect the protein's ability to bind to substrates or other molecules, impacting its overall function.
| 4. What roles do nucleic acids play in genetic information transfer? |  |
Ans. Nucleic acids, primarily DNA and RNA, play vital roles in the storage, transmission, and expression of genetic information. DNA contains the genetic blueprint for an organism and is responsible for inheritance. RNA is involved in protein synthesis, with messenger RNA (mRNA) conveying genetic information from DNA to ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. This process is essential for cellular function and organismal development.
| 5. How do lipids contribute to cell membrane structure and function? |  |
Ans. Lipids, particularly phospholipids, are fundamental components of cell membranes. They form a bilayer structure that provides a barrier between the internal and external environments of the cell. This bilayer allows for selective permeability, enabling the cell to maintain homeostasis by regulating what enters and exits. Additionally, lipids play roles in signaling and energy storage, contributing to the overall function of the cell.
Related Searches
















