JEE Exam > JEE Notes > Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced > Mind Map: Redox Reaction
Mind Map: Redox Reaction | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
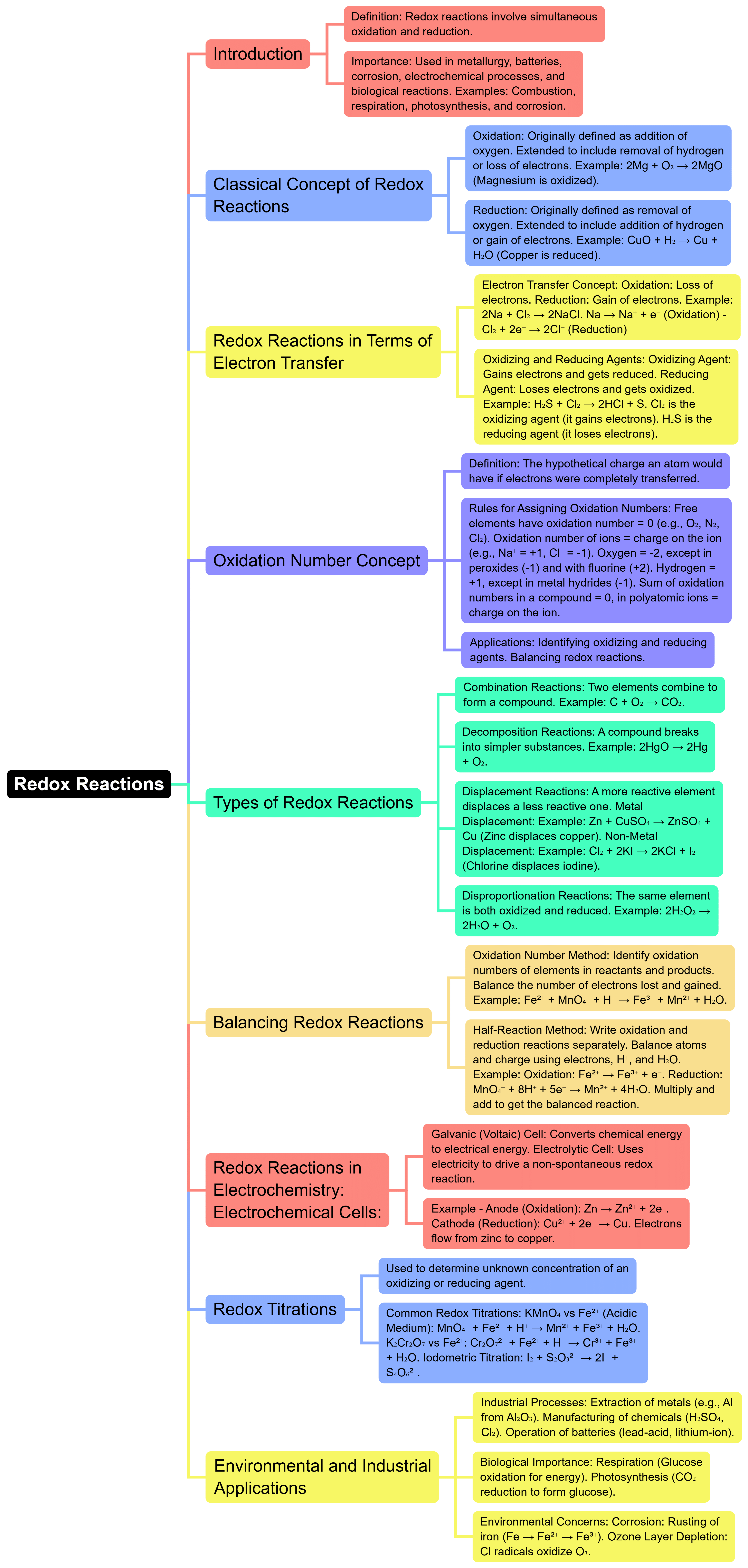
The document Mind Map: Redox Reaction | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced is a part of the JEE Course Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced.
All you need of JEE at this link: JEE
|
334 videos|651 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Redox Reaction - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are redox reactions and how do they work? |  |
Ans. Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between two substances. In these reactions, one substance gets oxidized (loses electrons) while the other gets reduced (gains electrons). This electron transfer results in a change in oxidation states of the involved species. Redox reactions are fundamental in various chemical processes, including combustion, respiration, and corrosion.
| 2. How can I identify oxidizing and reducing agents in a redox reaction? |  |
Ans. To identify oxidizing and reducing agents in a redox reaction, you need to look at the changes in oxidation states of the reactants. The substance that is oxidized (loses electrons) is the reducing agent, while the substance that is reduced (gains electrons) is the oxidizing agent. You can determine the oxidation states by assigning them based on certain rules (e.g., the oxidation state of elements in their standard state is zero).
| 3. What are some common examples of redox reactions in daily life? |  |
Ans. Common examples of redox reactions include the rusting of iron, where iron is oxidized to form iron oxide; combustion of fuels, where hydrocarbons are oxidized to produce carbon dioxide and water; and cellular respiration, where glucose is oxidized to produce energy. These reactions are essential in energy production, material degradation, and biological processes.
| 4. How do redox reactions relate to electrochemistry? |  |
Ans. Redox reactions are closely related to electrochemistry, which is the study of chemical processes that involve the movement of electrons. In electrochemical cells, redox reactions occur, resulting in the generation of electrical energy or the use of electrical energy to drive chemical reactions. For example, in galvanic cells, spontaneous redox reactions produce electricity, while in electrolytic cells, electrical energy is used to induce non-spontaneous redox reactions.
| 5. What are the key concepts I should focus on for JEE regarding redox reactions? |  |
Ans. For JEE, focus on understanding the concepts of oxidation states, identifying oxidizing and reducing agents, balancing redox reactions using the half-reaction method, and the applications of redox reactions in electrochemistry. Familiarize yourself with standard electrode potentials and how to use them to predict the spontaneity of redox reactions. Practice with various problem sets to strengthen your grasp of these concepts.
Related Searches





















