PIB Summary- 17th February, 2025 | PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC PDF Download
Casting Nets, Catching Success
Introduction
India ranks as the second-largest fish producer globally, contributing 8% to world fish production.
The fisheries sector has grown significantly from 2004 to 2024, marked by technological advancements and policy reforms.
The Union Budget 2025-26 allocated ₹2,703.67 crores, the highest ever, underscoring the sector’s importance.
Highlights of the Union Budget 2025-26
- Financial inclusion: Focus on reducing farmers‘ financial burden and increasing credit access.
- Marine Fisheries Development: Sustainable exploration of Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) & High Seas in Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Limit Raised: From ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh, boosting financial accessibility for fishers, processors, and other stakeholders.
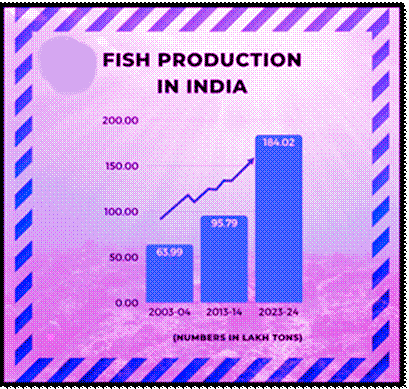
Growth in Fisheries Over Two Decades
Increase in Fish Production:
- 2023-24: 184.02 lakh tons
- 2013-14: 95.79 lakh tons
- 2003-04: 63.99 lakh tons
- Increase (2014-24): 88.23 lakh tons vs. 31.80 lakh tons (2004-14)
Inland and Aquaculture Production Growth:
- 2014-24: 77.71 lakh tons increase vs. 26.78 lakh tons (2004-14)
Marine Fish Production:
- Doubled from 5.02 lakh tons (2014-24) to 10.52 lakh tons (2004-14).
Seafood Exports (MPEDA Data, 2023-24):
- 17.81 lakh MT exported, worth ₹60,523.89 crores, a significant jump from ₹609.95 crores in 2003-04.
Policy Initiatives and Schemes
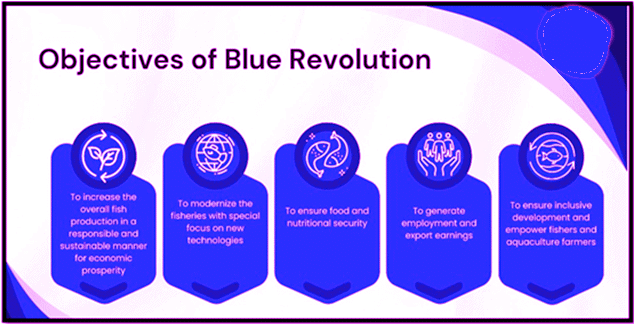
Blue Revolution (2015-16)
- First step towards enhancing fisheries productivity.
- Budget: ₹3,000 crores (5 years) for modernizing aquaculture.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) (2020-25)
- Investment of ₹20,050 crores for fisheries development, targeting:
- Inland fisheries & aquaculture
- Socio-economic welfare of fishers
Key Initiatives Under PMMSY
- Fish Farmers Producer Organisations (FFPOs)
- 2195 FFPOs approved at ₹544.85 crores to empower fishers.
- KCC extended to fisheries (4.5 lakh KCC cards sanctioned).
Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF)
- ₹7,522.48 crores fund, supporting 136 projects across states/UTs.
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Kisan Samridhi Sah-Yojana (PMMKSSY) (2024-27)
- ₹6,000 crores outlay for financial and technological reforms.
Integrated Aqua Parks
- 11 aqua parks sanctioned at ₹682.6 crores to develop aquaculture.
Artificial Reefs Deployment
- 937 artificial reefs installed at ₹291.37 crores across coastal states.
Nucleus Breeding Centres (NBCs)
- Focus on genetic improvement of shrimp & aquaculture species.
Technological Advancements
Satellite Technology for Fisheries
- Vessel Communication System, Oceansat & PFZ mapping for fishing zones.
GIS-Based Resource Mapping
- Helps in tracking marine fish landing centers & fishing grounds.
ICAR-Central Institute of Fisheries Education (CIFE)
- A leading institute training 4,000+ fisheries professionals.
Sustainable Fishing Policies & Regulations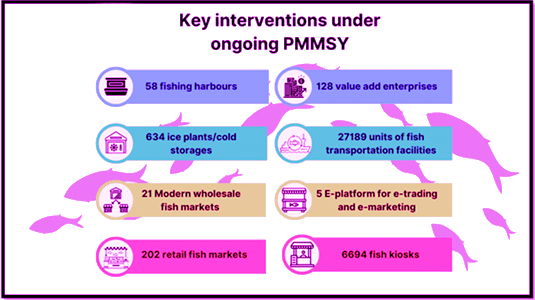
National Policy on Marine Fisheries (NPMF, 2017)
- Emphasizes sustainability & conservation of marine resources.
Conservation Measures
- Uniform Fishing Ban (61 days in monsoon for fish stock replenishment).
- Bans on Destructive Fishing (pair trawling, bull trawling, LED light use).
- Sustainable Practices: Sea ranching, artificial reefs, mariculture (seaweed cultivation, etc.).
- State-Level Regulations: Gear-mesh size rules, zonation of fishing areas, legal size restrictions.
Conclusion
- India’s fisheries sector has experienced transformative growth (2004-2024).
- Government initiatives, policy reforms, and technological advancements have made India a global leader in aquaculture and seafood exports.
- Sustainability & innovation will be key to maintaining this upward trajectory.
India and Sri Lanka Strengthen Ties in Critical Minerals, Exploration, and Mining
Context & Significance
India and Sri Lanka are strengthening bilateral ties in critical minerals, exploration, and mining.
Critical minerals like lithium, graphite, cobalt, and nickel are vital for renewable energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and high-tech industries.
Sri Lanka has rich deposits of graphite and beach sand minerals, crucial for battery technology and clean energy transition.
Discussions & Agreements
Mining & Exploration Opportunities:
- India seeks investment opportunities for Indian companies in Sri Lanka’s mineral sector.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) has shown interest in mineral assessments in Sri Lanka.
- Government-to-Government (G2G) cooperation was discussed for smoother exploration and mining ventures.
National Critical Mineral Mission:
- India is aiming to secure a steady supply of essential raw materials for energy security.
- Focus on international partnerships and overseas mineral asset acquisition.
- Encouraging Indian companies to expand operations in mineral-rich countries.
Memorandum of Understanding (MoU):
- MoU on Cooperation in Geology and Mineral Resources is in progress.
- It aims at capacity building, knowledge sharing, and technological collaboration.
- India to support Sri Lanka in modernizing its mining sector through financial & technological aid.
Economic & Strategic Implications
For India:
- Ensures supply chain security for critical minerals essential for EVs and renewable energy.
- Reduces dependency on China and other mineral-exporting nations.
- Strengthens India’s role in regional economic cooperation & strategic mineral diplomacy.
For Sri Lanka:
- Attracts Indian investment in mining and processing.
- Enhances mining sector efficiency through advanced technologies.
- Economic boost through resource monetization & industrial growth.
Geopolitical Relevance
- Strategic Cooperation: Strengthening economic ties aligns with India’s “Neighborhood First” policy.
- Countering Chinese Influence: Reducing Sri Lanka’s reliance on China’s mineral investments.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Diversifying sources of critical minerals to avoid monopolization risks.
Way Forward
- Fast-track MoU finalization for structured collaboration.
- Encourage Indian firms to participate in Sri Lanka’s mineral sector.
- Leverage advanced mining technologies for efficient resource extraction.
- Expand cooperation in rare earth minerals essential for future technologies.
FAQs on PIB Summary- 17th February, 2025 - PIB (Press Information Bureau) Summary - UPSC
| 1. What are the key areas of collaboration between India and Sri Lanka in the context of critical minerals? |  |
| 2. How does the partnership between India and Sri Lanka benefit their economies? |  |
| 3. What role do critical minerals play in India and Sri Lanka's development strategies? |  |
| 4. Are there any environmental considerations in the India-Sri Lanka partnership on mining? |  |
| 5. What impact does the collaboration have on regional security and geopolitical dynamics? |  |





















