Environment and Ecology: February 2025 UPSC Current Affairs | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
India’s Shift from Mitigation to Adaptation in Climate Action

Why in News?
India has indicated a strategic shift in its climate policy by emphasizing adaptation over emission reductions. This change stems from concerns regarding global inaction and insufficient financial commitments at the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties 29 (COP29). The delay in India's submission of the 2035 Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) further highlights this shift.
Key Takeaways
- India prioritizes adaptation due to global failures in emission targets.
- Developed nations have not met their climate finance obligations, impacting developing countries.
- Immediate local benefits from adaptation strategies are emphasized over global cooperation.
- India seeks flexibility in its energy transition, balancing growth and sustainability.
Additional Details
- Global Climate Commitments: The global community is falling short on emissions reduction targets, which stipulate a 42% reduction by 2030 and 57% by 2035. Developed nations have not fulfilled their financial responsibilities, securing only USD 300 billion annually instead of the USD 1 trillion sought by developing nations.
- Immediate and Local Benefits: Unlike mitigation efforts that require global coordination, adaptation measures such as developing climate-resilient infrastructure provide direct, immediate benefits and support local economies.
- Economic Growth: The Economic Survey 2024-25 indicates that achieving developed country status by 2047 is paramount, enabling a sustainable transition to clean energy.
- Flexibility in Energy Transition: India aims for a bottom-up approach to energy transition, prioritizing economic growth over strict adherence to international targets.
- In balancing growth with clean energy transition, India is expanding its renewable energy sector while resisting stringent coal phase-down commitments. The nation is on track to meet its 2030 NDC targets by aiming for 50% of installed electricity capacity from non-fossil sources.
India’s Key Climate Adaptation Initiatives
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP): Created by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), the NAP aligns with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and focuses on enhancing climate resilience across various sectors.
- Adaptation in Agriculture: To address heat and water stress, India is implementing measures such as climate-resilient seeds and improved soil health practices.
- Urban Climate Resilience: Initiatives like the National Mission on Sustainable Habitat (NMSH) promote waste management and green buildings to tackle urban flooding.
- Coastal Adaptation Measures: Programs like the Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI) aim to restore mangroves and create jobs while sequestering significant amounts of carbon.
- India's approach to climate adaptation signifies a pragmatic response to both local needs and global climate challenges, ensuring a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability.
International Big Cat Alliance

Why in News?
The International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) officially became a treaty-based intergovernmental organization and international legal entity on 23rd January 2025, with its headquarters located in India.
Key Takeaways
- IBCA was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2023 during the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- The organization was formally approved by the Union Cabinet in February 2024.
- It operates under the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) within the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC).
Additional Details
- Objective:The primary aim of the IBCA is the conservation of seven major big cat species, including:
- Lion
- Leopard
- Snow Leopard
- Cheetah
- Jaguar
- Puma
- Membership: Countries such as the Republic of Nicaragua, Kingdom of Eswatini, Republic of India, Federal Republic of Somalia, and Republic of Liberia have ratified the IBCA framework agreement. Membership is open to all United Nations member states, including both range countries where these species naturally occur and non-range countries interested in supporting big cat conservation.
- Need for IBCA:Big cats face numerous threats, including:
- Habitat loss
- Poaching
- Climate change
- Human-wildlife conflicts
- Funding: India has committed Rs. 150 crore from 2023 to 2028 to support IBCA initiatives, with plans to seek additional funding through various bilateral, multilateral, and donor organizations.
- The IBCA serves as a collaborative conservation platform that brings together conservationists, policymakers, researchers, and governments from around the world, facilitating the sharing of best practices in habitat management, anti-poaching strategies, and ecological restoration.
- The alliance acts as a financial and technical resource, providing support to under-resourced nations and reinforcing existing wildlife protection treaties like CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) and CMS (Convention on Migratory Species).
- By focusing on the conservation of apex predators, the IBCA contributes to maintaining healthy ecosystems, preserving biodiversity, and enhancing climate resilience through forestry and grassland restoration initiatives.
World Wetlands Day 2025

Why in News?
The Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) organised the World Wetlands Day 2025 celebrations at the Parvati Arga Ramsar Site, Gonda, Uttar Pradesh (UP) on 2nd February 2025.
What are the Key Facts Regarding World Wetlands Day 2025?
- About: It is observed annually to raise awareness about the importance of wetlands and marks the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971 in Ramsar, Iran.
- Theme for 2025: Protecting Wetlands for our Common Future.
- New Ramsar Sites: Udhwa Lake in Jharkhand, Theerthangal and Sakkarakottai in Tamil Nadu and Khecheopalri in Sikkim are included in the list of Ramsar sites.
- These are the first Ramsar Sites of Sikkim and Jharkhand.
- With this, Ramsar sites (Wetlands of International Importance) in India increased to 89.
- Tamil Nadu continues to have the maximum number of Ramsar Sites (20 sites) followed by Uttar Pradesh (10 sites).
- New Corridor: The government announced a new nature-culture tourism corridor will be developed between Ayodhya and Devi Patan in UP.
- Amrit Dharohar Initiative: Amrit Dharohar was launched in June 2023 to conserve Ramsar Sites that focuses on four key components i.e., Species and Habitat Conservation, Nature Tourism, Wetlands Livelihood and Wetlands Carbon.
- Threat: The biggest threat to wetlands is pollution from industrial and human effluents, which degrade these ecosystems.
What are Key Facts About Parvati Arga Ramsar Site?
- About: It is a permanent freshwater environment, consisting of two oxbow lakes i.e., Parvati and Arga, which are rain-fed and located in the terai region (Gangetic plains).
- The nearby Tikri Forest is also being developed as an eco-tourism site.
- Oxbow lakes are U-shaped lakes formed when a meander of a river is cut off, creating a standalone water body.
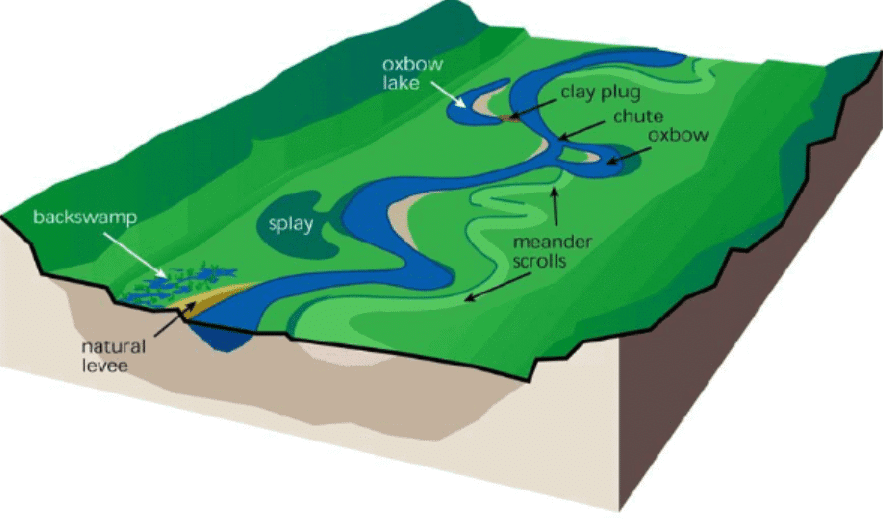
- Ecological Significance: It is a refuge for critically endangered white-rumped vulture, Indian vulture, and endangered Egyptian vulture.
- Migratory birds like Eurasian coots, mallards, greylag geese, northern pintails, and red-crested pochards visit the site in the winter months.
- Invasive Species: It faces threats from invasive species, notably the common water hyacinth.
- Cultural Landmarks: The region is home to cultural landmarks such as the birthplaces of Maharishi Patanjali and Goswami Tulsidas, boosting religious and cultural tourism.
|
95 videos|234 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Environment and Ecology: February 2025 UPSC Current Affairs - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of India's shift from mitigation to adaptation in climate action? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of India's adaptation strategies in climate action? |  |
| 3. How does the International Big Cat Alliance relate to India's climate action efforts? |  |
| 4. What role does World Wetlands Day play in promoting climate adaptation in India? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to India's climate adaptation efforts? |  |
















