Calendars | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Fundamental Concepts |

|
| Finding the Day of the Week for Any Date |

|
| Repetition of Calendars |

|
| Types of Calendar Questions |

|
| Some More Examples |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
A calendar is a system used to measure time based on days, weeks, months, and years. It helps in organizing and keeping track of dates. In Logical Reasoning, calendar-related questions involve determining the day of the week for a given date, counting odd days, identifying leap years, recognizing patterns in the repetition of calendars, and solving complex date-based problems. These questions require mathematical reasoning, understanding of date progression, and quick calculations.

Fundamental Concepts
1. Leap Year vs. Non-Leap Year
A Leap Year has 366 days (extra day in February - 29 days).
A Non-Leap Year has 365 days (February has 28 days).
Leap Year Rule:
A year is a leap year if divisible by 4 (e.g., 2020, 2024).
If a year is divisible by 100, it must also be divisible by 400 to be a leap year (e.g., 2000 is a leap year, but 1900 is not).

2. Odd Days and Their Role
Odd days help in determining the day of the week for any date.
1 Non-Leap Year = 365 days = 1 odd day
1 Leap Year = 366 days = 2 odd days
100 Years = 5 odd days
200 Years = 3 odd days
300 Years = 1 odd day
400 Years = 0 odd days (full weeks complete)
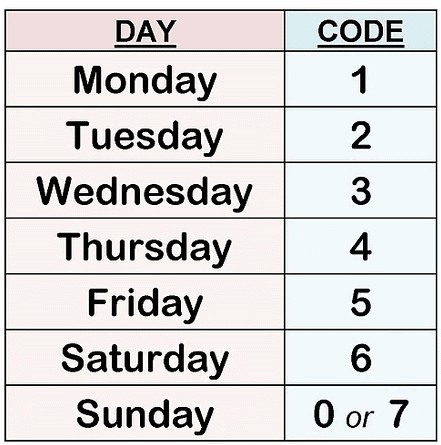
3. Day Mapping for Odd Days
The remainder obtained when dividing odd days by 7 helps in finding the day of the week:
0 → Sunday
1 → Monday
2 → Tuesday
3 → Wednesday
4 → Thursday
5 → Friday
6 → Saturday
4. Century Codes for Quick Calculation
To determine the day of the week quickly for a given date, century codes can be used:
1700s → 4
1800s → 2
1900s → 0
2000s → 6
2100s → 4
Finding the Day of the Week for Any Date
To determine the day for a given date:
Find the number of odd days (from a base year to the required date).
Divide by 7 and take the remainder.
Use the day mapping above.
Example 1: Find the day on 15th August 1947
Step 1: Reference Date: 1st Jan 1900 (Monday)
Step 2: Compute Odd Days:
1900 to 1946 = 47 years
Leap years = 11 × 2 = 22 odd days
Normal years = 36 × 1 = 36 odd days
Total odd days = 22 + 36 = 58 → 58 ÷ 7 = 2 remainder (Tuesday)
Jan to August 1947:
Jan to July = 16 odd days
Aug 15 = 15 odd days
Total = (16+15) = 31 → 31 ÷ 7 = 3 remainder (Wednesday)
Answer: Friday
Repetition of Calendars
A year repeats when it has the same odd days and starts on the same weekday.
Leap Year repeats after 28 years.
Non-Leap Year follows a cycle where odd days match.
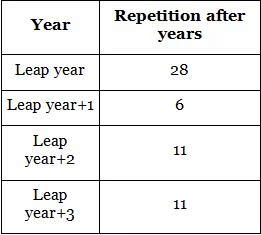
Example 2: When will the calendar of 2024 repeat?
2024 is a Leap Year → Repeats after 28 years.
Answer: 2052
Types of Calendar Questions
1. Finding the Day of the Week
Example 3: What was the day on 26th January 1950?
Reference Date: 1st Jan 1900 (Monday)
Compute Odd Days:
50 years (1900–1949) → 62 odd days → 6 (Saturday)
Jan 1950 = 26 ÷ 7 = 5 odd days (Thursday)
Final Day = Saturday + 5 days = Thursday
Answer: Thursday
2. Calendar Matching and Year Repeats
Example 4: Which year will have the same calendar as 2025?
2025 is a Normal Year (1 odd day).
Find the next year with the same odd days.
Answer: 2031
3. Counting Days Between Two Dates
Example 5: Find the number of days between 15th August 2023 and 10th February 2024
Aug 15 - Aug 31 = 16 days
Sept = 30, Oct = 31, Nov = 30, Dec = 31, Jan = 31, Feb 10 = 10
Total = 16 + 30 + 31 + 30 + 31 + 31 + 10 = 179 days
4. Clock & Calendar Combined Questions
Example 6: A clock gains 3 minutes per day. How many minutes will it gain in 2 years?
1 year = 365 days
2 years = 730 days
730 × 3 = 2190 minutes
Answer: 2190 minutes (or 36 hours 30 minutes)
5. Validity of a Given Date
Example 7: Which of the following dates is incorrect?
29th Feb 2004
29th Feb 1900
31st April 2021
Answer: 2 & 3 (1900 is not a leap year, April has only 30 days).
Some More Examples
Example 8 : If 5th October 1972 was a Thursday, what day of the week was 5th October 1965?
Solution:
- The difference between 1972 and 1965 is 7 years.
- The number of leap years in this period: 1968, 1972 (2 leap years).
- The number of normal years: 1966, 1967, 1969, 1970, 1971 (5 normal years).
- Odd days contributed:
- Leap years → 2 × 2 = 4 odd days
- Normal years → 5 × 1 = 5 odd days
- Total odd days = 4 + 5 = 9 odd days.
- 9 ÷ 7 = 2 remainder, meaning the day shifts back 2 days from Thursday.
- Answer: Tuesday.
Example 9: Which of the following years will have the same calendar as 2029?
(a) 2035
(b) 2036
(c) 2037
(d) 2039
Solution:
- 2029 is a normal year (365 days, 1 odd day).
- Find the next year that has the same number of odd days.
- Checking odd days from 2030 onwards:
- 2030 → Normal year (+1 odd day).
- 2031 → Normal year (+1 odd day).
- 2032 → Leap year (+2 odd days).
- 2033 → Normal year (+1 odd day).
- 2034 → Normal year (+1 odd day).
- 2035 → Normal year (+1 odd day).
- Total odd days = 1+1+2+1+1+1 = 7 (full week).
- Calendar repeats in 2035.
Answer: (a) 2035.
Example 10: Which of the following dates is incorrect?
(a) 30th February 2020
(b) 29th February 2016
(c) 31st June 2019
(d) 15th August 2025
Solution:
- 30th February 2020 → Incorrect, as February has only 28 days in normal years and 29 in leap years.
- 29th February 2016 → Correct, as 2016 was a leap year.
- 31st June 2019 → Incorrect, as June has only 30 days.
- 15th August 2025 → Correct, as it is a valid date.
Answer: (a) and (c) are incorrect.
Example 11: Find the total number of days between 12th May 2023 and 27th October 2023.
Solution:
- Counting days from May 12 to October 27:
- May (after 12th) = 31 - 12 = 19 days
- June = 30 days
- July = 31 days
- August = 31 days
- September = 30 days
- October (till 27th) = 27 days
- Total days = 19 + 30 + 31 + 31 + 30 + 27 = 168 days.
Answer: 168 days.
Conclusion
Understanding calendar-related problems is essential for logical reasoning in CUET UG. The key concepts covered include leap years, odd days, day calculations, and repetition patterns. By practicing various types of calendar questions, one can efficiently determine the day of any date, count the number of days between two dates, analyze repeating calendar years, and verify the correctness of a given date. Mastering these techniques ensures accuracy and speed in solving CUET UG logical reasoning questions. With consistent practice, students can confidently solve any calendar-based problem in their examinations
|
164 videos|626 docs|1130 tests
|
FAQs on Calendars - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What are the fundamental concepts of calendars in logical reasoning? |  |
| 2. How can I find the day of the week for any given date? |  |
| 3. Why do calendars repeat, and how does this affect logical reasoning problems? |  |
| 4. What types of questions are commonly asked about calendars in logical reasoning exams? |  |
| 5. Can you provide some examples of calendar-related logical reasoning problems? |  |















