Unit Test (Solution): Exploring Magnets | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Attempt all questions. Time: 1 hour, M.M. 30
- Question numbers 1 to 7 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 8 to 12 carry 2 mark each.
- Question numbers 13 to 15 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 16 carries 4 marks each
Q1: Which of the following materials is attracted to a magnet?
A. Wood
B. Rubber
C. Iron
D. Glass
Ans: C) Iron
Iron is a material, which means it is attracted to magnets.
Q2: The materials that are attracted to a magnet are called __________ materials.
Ans: magnetic
Magnetic materials are those that exhibit magnetic properties, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, and are attracted to magnets.
Q3: The North pole of a magnet is attracted to which pole of another magnet.
Ans: South
Magnetic poles attract each other; therefore, the North pole of one magnet will attract the South pole of another magnet.
Q4: What is the shape of the magnetic field observed when iron filings are spread on paper near a bar magnet?
A. Circular
B. Straight
C. Linear
D. A pattern with two poles
Ans: D) A pattern with two poles
The magnetic field lines form a distinct pattern showing the two poles of the magnet.
Q5: What happens when two like poles of a magnet are brought close to each other?
A. They attract each other
B. They repel each other
C. They stay unaffected
D. They break apart
Ans: B) They repel each other
Like poles of a magnet (either north-north or south-south) repel each other.
Q6: A freely suspended magnet always aligns itself along the __________ direction.
Ans: north-south
Freely suspended magnets align themselves with the Earth's magnetic field, which runs from the geographic North to the geographic South.
Q7: Name a device that works using Earth's magnetic field?
Ans: Magnetic compass.
Q8: The two poles of a magnet are __________ and __________.
Ans: North and South
Every magnet has two poles: the North pole and the South pole, which exhibit opposite magnetic properties.
Q9: Give some examples of non-magnetic materials?
Ans: Yes, some examples of non-magnetic materials include wood, plastic, rubber, glass, and paper. These materials do not contain magnetic elements like iron, nickel, or cobalt, so they are not attracted to magnets.
Q10: What materials are needed to make a simple magnetic compass?
Ans: A simple magnetic compass can be made using a cork, an iron needle, and a permanent magnet. The iron needle is magnetized by stroking it with the permanent magnet, allowing it to align with Earth's magnetic field. The cork helps the needle float freely in water, enabling it to point towards the north-south direction.
Q11: What are the differences between magnetic and non-magnetic materials? Provide two examples of each.
Ans: Magnetic materials can attract or repel magnets, while non-magnetic materials do not interact with magnets. Examples of magnetic materials include iron and nickel; examples of non-magnetic materials are wood and plastic.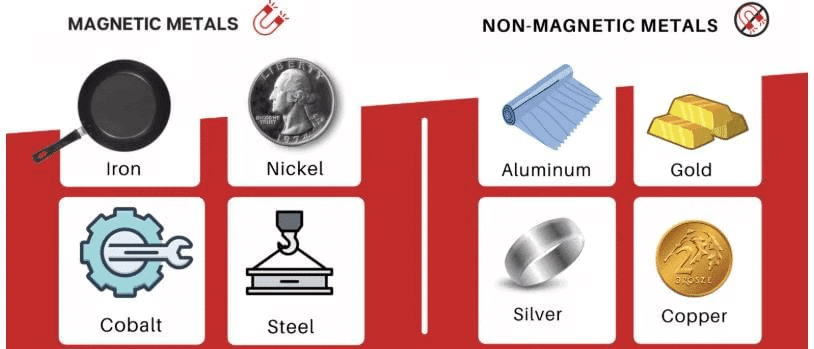
Q12: Explain how a magnetic compass helps in finding directions.
Ans: A magnetic compass helps in finding directions by using a magnetized needle that aligns itself with Earth's magnetic field. The needle's north pole points toward the Earth's magnetic north, allowing users to determine directions accurately. By aligning the compass with a map or using landmarks, travelers and navigators can find their way efficiently.
Q13: You have a bar magnet. How would you demonstrate that it has two poles?
Ans: To demonstrate that a bar magnet has two poles, you can use a compass. When you bring the compass near one end of the magnet, the compass needle will point in a certain direction, indicating attraction. When you bring the compass near the other end of the magnet, the needle will point in the opposite direction, indicating repulsion. This shows that one end of the magnet is the North pole and the other end is the South pole, confirming that a magnet has two poles: North and South.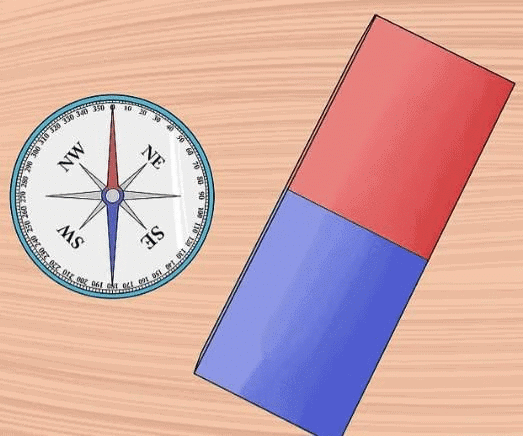
Q14: What happens when a magnet is broken into two pieces? What can you conclude from this experiment about the poles of a magnet?
Ans: When a magnet is broken, each piece forms its own new magnet, and both pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. This means that no matter how many times a magnet is broken, each smaller piece will still have two poles. This demonstrates that magnetic poles always exist in pairs, and it's impossible to isolate just one pole (like a single North or South pole) in nature.
Q15: Explain why a piece of wood does not affect the deflection of a magnetic compass needle. What does this suggest about the interaction between magnets and non-magnetic materials?
Ans: A piece of wood does not affect the deflection of a magnetic compass needle because wood is a non-magnetic material. Non-magnetic materials, like wood, do not interact with magnetic fields. This suggests that only magnetic materials (such as iron or steel) affect the behavior of magnetic fields, while non-magnetic materials do not influence a magnet's effects.
Q16: How does a magnetic compass work, and why does its needle always point in the north-south direction?
Ans: A magnetic compass works by using a small, freely rotating magnetized needle that aligns itself with Earth's magnetic field. The Earth behaves like a giant magnet with a magnetic north and south pole, which influences the needle’s movement.
The north end of the needle is attracted to the Earth's magnetic south pole, located near the geographic North Pole, while the south end of the needle is attracted to the Earth's magnetic north pole, near the geographic South Pole. This alignment causes the needle to always point in the north-south direction.
Magnetic compasses are widely used in navigation by travelers, sailors, and explorers to find directions accurately. Since Earth's magnetic field remains stable over time, compasses provide a reliable way to determine orientation even without modern technology like GPS.
|
67 videos|349 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solution): Exploring Magnets - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of magnets? |  |
| 2. How do magnets work? |  |
| 3. What materials can magnets attract? |  |
| 4. How can we demagnetize a magnet? |  |
| 5. What are some everyday uses of magnets? |  |
















