Class 6 Social Science : Sample Paper Solutions- 1 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 34 questions and is divided into four sections: A, B, C, and D.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section A comprises question numbers 1 to 15. These are multiple-choice questions carrying one mark each. You are to select one most appropriate response out of the four provided options.
- Section B comprises question numbers 16 to 22. These are short-answer questions carrying two marks each.
- Section C comprises question numbers 23 to 31. These are short-answer questions carrying four marks each.
- Section D comprises question numbers 32 to 34. These are short-answer questions carrying five marks each.
Section A
Q1: What distinguishes mountains from hills as landforms? (1 Mark)
(a) Mountains are always snow-capped, while hills are not
(b) Mountains have steep slopes and narrow summits, while hills are lower with rounded tops
(c) Hills are younger in geological terms than mountains
(d) Mountains are flat on top, while hills have steep slopes
Ans: b
Mountains are characterized by their height, steep slopes, and often pointed summits, while hills are generally lower, less steep, and have rounded tops. Snow cover or geological age isn’t a defining factor, and mountains aren’t typically flat-topped unless they’re plateaus.
Q2: What is the primary purpose of the Panchayati Raj system? (1 Mark)
(a) To provide entertainment
(b) To centralize governance
(c) To bring governance closer to the rural population
(d) To increase taxes
Ans: c
The Panchayati Raj system decentralizes governance by empowering rural communities to manage their own affairs through local bodies like Gram Panchayats, ensuring decisions reflect local needs rather than being centralized or tax-focused.
Q3: Which ancient Indian text uses "Bhāratavarșha" to encompass the entire Subcontinent, including rivers and peoples? (1 Mark)
(a) Rig Veda
(b) Viṣhṇu Purāna
(c) Mahābhārata
(d) Constitution of India
Ans: c
The Mahābhārata uses "Bhāratavarșha" to describe the entire Indian Subcontinent, detailing its rivers, regions, and peoples, reflecting a broad geographical and cultural identity. Other texts like the Rig Veda focus more narrowly, and the Constitution is modern.
Q4: If it is 12:00 pm (noon) at the Prime Meridian, what is the local time at a location with a longitude of 45° W? (1 Mark)
(a) 3:00 pm
(b) 9:00 am
(c) 12:00 am
(d) 6:00 pm
Ans: b
The Earth rotates 15° per hour. Moving west from the Prime Meridian (0°), each 15° subtracts 1 hour. At 45° W (3 intervals of 15°), subtract 3 hours from 12:00 pm, resulting in 9:00 am.
Q5: What concept is illustrated by the widespread use of staple grains like rice, wheat, and millets across India, despite the vast variety of regional dishes? (1 Mark)
(a) Cultural isolation
(b) Unity in diversity
(c) Economic disparity
(d) Linguistic uniformity
Ans: b
The common use of staple grains across India’s diverse cuisines shows a unifying element (shared ingredients) amidst varied regional practices, embodying "unity in diversity," not isolation, disparity, or linguistic sameness.
Q6: Why does the Earth appear mostly blue when viewed from space? (1 Mark)
(a) The atmosphere scatters blue light more than other colors
(b) Water covers nearly three-fourths of the surface, reflecting blue
(c) The landmasses are smaller and less visible from a distance
(d) Clouds over the oceans create a blue tint
Ans: b
Oceans cover about 71% of Earth’s surface and reflect blue light due to water’s properties, making the planet appear predominantly blue from space. Atmospheric scattering contributes but isn’t the primary reason.
Q7: What role does the secondary sector play in the economy? (1 Mark)
(a) It only sells goods produced by the primary sector
(b) It processes and manufactures goods from raw materials
(c) It provides educational services only
(d) It handles international trade exclusively
Ans: b
The secondary sector transforms raw materials (e.g., cotton into cloth) from the primary sector into finished goods through manufacturing and processing, unlike selling, services, or trade alone.
Q8: Which principle shared by Jainism and Buddhism emphasizes not just avoiding physical harm but also negative thoughts toward others? (1 Mark)
(a) Karma
(b) Ahimsa
(c) Dharma
(d) Rebirth
Ans: b
Ahimsa, or non-violence, in Jainism and Buddhism extends beyond physical actions to include avoiding harmful thoughts, distinguishing it from karma (actions’ consequences), dharma (duty), or rebirth.
Q9: What happens to the date when you cross the International Date Line traveling eastward? (1 Mark)
(a) It stays the same, but the time changes by 12 hours
(b) You subtract one day, moving back in time
(c) You add one day, moving forward in time
(d) The date doubles, skipping a full day ahead
Ans: b
Traveling east across the International Date Line (from +12 to -12 time zone) moves you back one day (e.g., Tuesday to Monday) due to the Earth’s rotation and the line’s design to standardize dates.
Q10: What did the Harappans build at Lothal for trade? (1 Mark)
(a) Reservoir
(b) Dockyard
(c) Bath
(d) Wall
Ans: b
The Harappans constructed a large dockyard at Lothal to facilitate maritime trade, connecting their civilization to distant regions, unlike reservoirs (water storage) or baths (hygiene).
Q11: What is the primary purpose of family relationships according to Indian traditions? (1 Mark)
(a) To provide financial support to each other
(b) To maintain traditions and practices
(c) To build relationships based on love, care, cooperation, and interdependence
(d) To create a formal structure within the household
Ans: c
In Indian tradition, family relationships prioritize emotional bonds—love, care, and cooperation—over mere financial or structural roles, fostering interdependence across generations.
Q12: Why are oceans considered the "planet’s lungs"? (1 Mark)
(a) They regulate global temperatures like lungs control breathing
(b) They produce over half of the world’s oxygen through marine plants
(c) They absorb carbon dioxide from human activity
(d) They circulate air currents across the globe
Ans: b
Marine plants like phytoplankton produce over 50% of Earth’s oxygen via photosynthesis, earning oceans the "lungs" metaphor, beyond temperature regulation or CO2 absorption.
Q13: What illustrates a direct application of grassroots democracy? (1 Mark)
(a) A president making a unilateral decision
(b) Citizens voting directly on specific issues
(c) Representatives voting on behalf of people
(d) Courts deciding laws without public input
Ans: b
Grassroots democracy involves direct citizen participation, like voting on local issues, rather than top-down decisions or representative proxies, empowering communities at the base level.
Q14: Why might excessive tourism pose a threat to mountain environments? (1 Mark)
(a) It depletes mineral resources through mining
(b) It disrupts the fragile balance of the ecosystem
(c) It lowers the altitude of mountain peaks
(d) It increases sediment deposits in rivers
Ans: b
Mountain ecosystems are delicate, and excessive tourism can disrupt wildlife, vegetation, and soil stability, unlike mining (resource extraction) or altering physical features like altitude.
Q15: What major shift occurred in human societies after the last Ice Age ended around 12,000 years ago? (1 Mark)
(a) They began using metals like copper and iron
(b) They settled near rivers, cultivating crops and domesticating animals
(c) They built the first cities in Mesopotamia
(d) They invented pottery for storing goods
Ans: b
Post-Ice Age warming enabled humans to settle near rivers, farm crops, and domesticate animals (Neolithic Revolution), predating metal use, city-building, or widespread pottery.
Section B
Q16:What is the difference between a map and a globe? (2 Marks)
Ans: 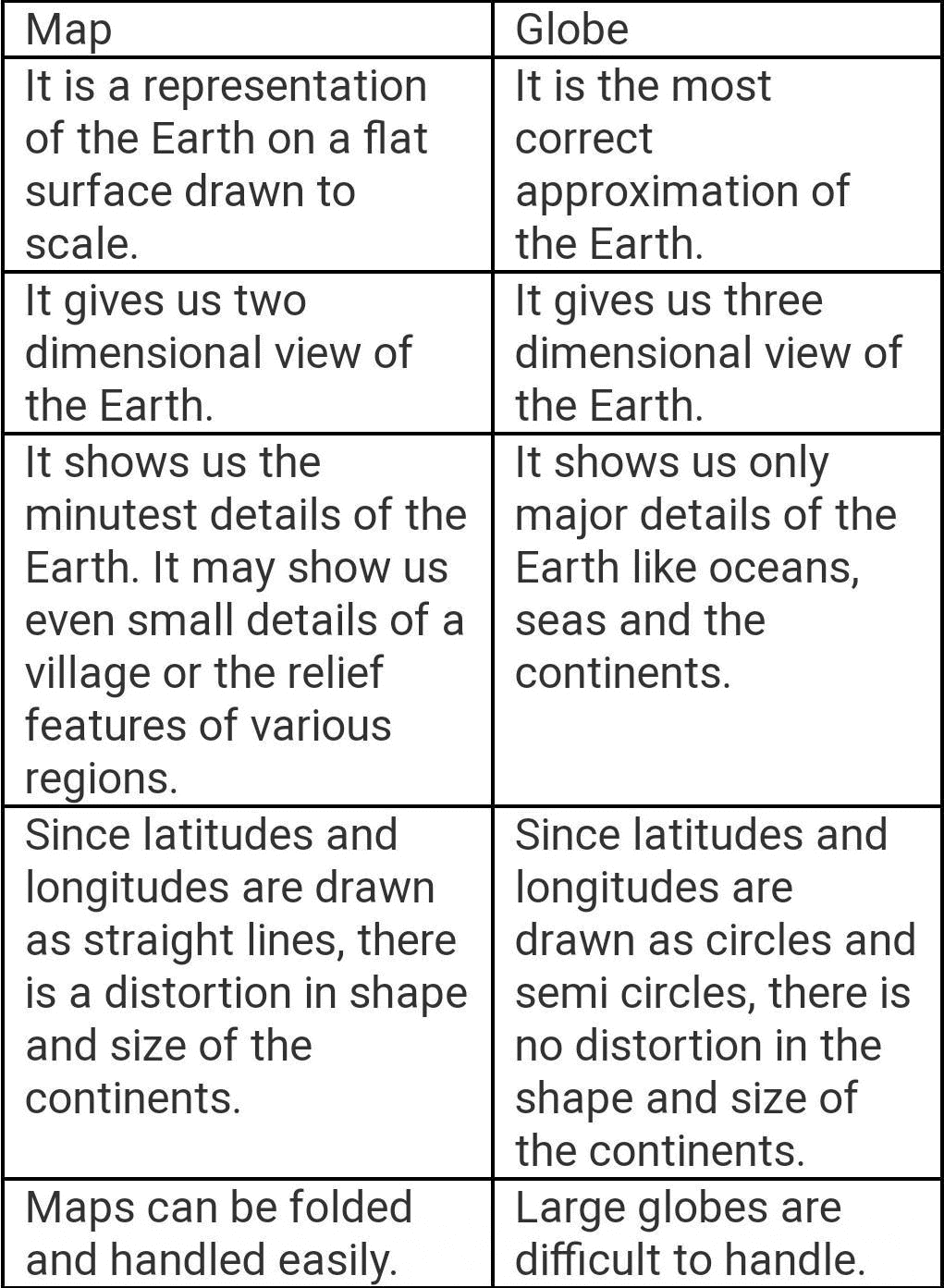
Q17: Name two continents that are entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. (2 Marks)
Ans: The two continents entirely in the Southern Hemisphere are Australia and Antarctica. Australia is a large landmass with deserts, forests, and cities, located south of the Equator. Antarctica is a cold, icy continent at the South Pole, also fully below the Equator. These continents are unique because they don’t cross into the Northern Hemisphere like others do.
Q18: How do plains support human life? (2 Marks)
Ans: Plains support human life by providing flat, fertile land that is perfect for growing crops like wheat, rice, and vegetables, which feed people. They also make it easy to build houses, roads, and villages because the land is level and stable. Many big rivers flow through plains, giving water for drinking and farming. This is why so many people live in plains areas around the world.
Q19: What are archaeological sources? Give one example. (2 Marks)
Ans: Archaeological sources are things left behind from the past that we dig up to learn about old times, like tools, pots, coins, or buildings. These objects tell us how people lived before writing was common. One example is Harappan seals, which are small stone pieces with carvings found in ancient Indian cities. They show us about trade and art from that time.
Q20: Why is India called a subcontinent? (2 Marks)
Ans: India is called a subcontinent because it’s a big, separate landmass that’s part of Asia but stands out due to its own special features. The tall Himalayas in the north cut it off from the rest of Asia, while the Arabian Sea, Bay of Bengal, and Indian Ocean surround it on other sides. It has its own climate, rivers like the Ganga, and a mix of cultures, making it unique.
Q21: What was the importance of seals in the Harappan civilization? (2 Marks)
Ans: Seals in the Harappan civilization were small stone objects with carvings of animals or symbols, and they were very important for daily life. They were used in trade to mark goods, showing who owned them or where they came from. Seals might also have been like a signature to prove something belonged to a person or family. They tell us the Harappans were smart traders with a system to organize things.
Q22: How do ancient stories like the Ramayana reflect India’s cultural roots? (2 Marks)
Ans: Ancient stories like the Ramayana reflect India’s cultural roots by teaching values like honesty, courage, and respect for family, which are still important today. The story of Rama, who fought to save Sita, shows ideas of duty (dharm(a) that come from the Vedas. These tales were told orally long ago and connect people to their past. They also mix fun with lessons, shaping how Indians think and live.
Section C
Q23: (i) What are latitudes and longitudes?
(ii) How do they help us locate places on Earth? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) Latitudes are imaginary lines that run horizontally around the Earth, measuring how far north or south a place is from the Equator, which is the 0° line. Longitudes are imaginary lines that run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring how far east or west a place is from the Prime Meridian, which is the 0° line through Greenwich, England. Together, they’re like a grid on the Earth’s surface.
(ii) Latitudes and longitudes help us locate places by giving exact coordinates, like a map address. For example, if a place is at 20°N latitude and 78°E longitude, we know it’s north of the Equator and east of the Prime Meridian—Delhi is near there! This grid system lets explorers, pilots, and even kids find any spot on Earth accurately, whether it’s a city or an island.
Q24: (i) Name two major oceans and two major continents.
(ii) How do oceans influence the climate of nearby land areas? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) Two major oceans are the Pacific Ocean, which is the biggest and deepest, and the Indian Ocean, which touches India’s southern coast. Two major continents are Asia, the largest with many countries including India, and Africa, known for its deserts and forests. These are some of the Earth’s biggest natural features.
(ii) Oceans influence climate by keeping nearby land areas cooler in summer and warmer in winter because water heats up and cools down slower than land. For example, places near the Indian Ocean, like southern India, get gentler weather than inland areas. Oceans also bring rain through winds that carry water vapor, helping crops grow in coastal regions. This makes life easier for people living close to them.
Q25: (i) What is a plateau?
(ii) Give an example of a plateau in India and explain its importance. (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) A plateau is a high piece of land that’s flat on top, like a table, with steep sides all around it. It’s higher than plains but not as pointy as mountains, formed long ago by Earth’s movements or lava flows. Plateaus can have rivers or forests and are found all over the world.
(ii) An example in India is the Deccan Plateau, which covers much of southern India. It’s important because it’s full of minerals like coal and iron, which people use to make things in factories. It also has fertile soil in some parts where farmers grow crops like cotton, and its height affects the weather, bringing rain to nearby areas.
Q26: (i) What is the difference between history and prehistory?
(ii) Name one source used to study each period. (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) History is the time when people wrote things down, like events or kings’ names, so we have records to read.
Prehistory is the time before writing was invented, when people didn’t keep written stories, so we only guess about their lives from objects. History starts when writing begins, but prehistory goes back much further.
(ii) For history, one source is Ashoka’s edicts, which are carvings on rocks telling us about his rule and ideas. For prehistory, stone tools are a source—simple rocks shaped by early humans to hunt or cut, found buried in the ground. These help us understand how people lived in each time.
Q27: (i) What is the significance of the term "Jambudvipa" in ancient texts?
(ii) How does it relate to India’s geography? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) "Jambudvipa" is an old name from Jain and Buddhist texts meaning "land of the rose-apple tree," used for the Indian subcontinent. It was special because it showed how ancient people saw India as a central, fertile land in their world, full of life and importance. It’s tied to stories about nature and human values from long ago.
(ii) It relates to India’s geography because India is a big land surrounded by the Himalayas in the north and seas on three sides, making it stand out. It describes it as a place with rivers like the Ganga and plains for farming, matching India’s real features that made it a unique home for people and cultures.
Q28: (i) What was the Great Bath in the Harappan civilization?
(ii) What does it tell us about their society? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) The Great Bath was a big, rectangular water tank in Mohenjo-Daro, made of baked bricks and sealed to hold water without leaking. It had steps leading down into it and rooms nearby, suggesting it was built carefully for a special purpose, maybe washing or ceremonies, about 4,500 years ago.
(ii) It tells us the Harappans were clever builders who knew how to manage water, showing advanced skills in engineering. It also hints they cared about staying clean or had religious rituals, as such a big public bath wasn’t just for fun. Their society was organized, with people working together to make and use it.
Q29: (i) How did the Vedas influence India’s cultural roots?
(ii) What is one example of a value they teach? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) The Vedas influenced India’s cultural roots by being some of the oldest texts, written in Sanskrit thousands of years ago, guiding how people prayed, lived, and thought. They gave rules for society, like respecting elders, and shaped ideas about gods, nature, and rituals that Indians still follow in festivals or daily life. Priests passed them down by memorizing them, keeping the culture alive.
(ii) One value they teach is truthfulness, which means always speaking the truth and being honest in actions. This is seen in hymns that praise truth as a way to live righteously, influencing stories like the Ramayana where Rama stays true to his word, showing its lasting impact on Indian values.
Q30: A and B are two levels of local government. Level A operates in rural areas and is led by a Sarpanch. Level B operates in urban areas and is responsible for services like water supply and roads.
(i) Name Level A.What is the role of the Sarpanch in Level A?
(ii) Name Level B.
(iii) Give one example of a service provided by Level B.
(iv) Why is local government important for democracy? (4 Marks)
Ans: (i) Level A is the Gram Panchayat, which is the local government for villages all over India, handling everyday rural needs. The Sarpanch in Level A is the leader who runs meetings, listens to villagers’ problems, and makes sure plans like building a school or repairing a pump happen. They also speak for the village to higher officials, acting like a bridge between people and the government, keeping everything fair and organized.
(ii) Level B is the Municipal Corporation, which takes care of cities and towns, managing bigger areas with more people.
(iii) One service provided by Level B is garbage collection, where they send workers to pick up trash from streets and homes, keeping the city clean and healthy for everyone living there.
(iv) Local government is important for democracy because it lets people choose their own leaders and decide what’s best for their area, like fixing a park or adding lights. It makes sure power isn’t just with far-off rulers but stays with the community, so everyone feels included and heard in how things are run.
Q31: (4 Marks)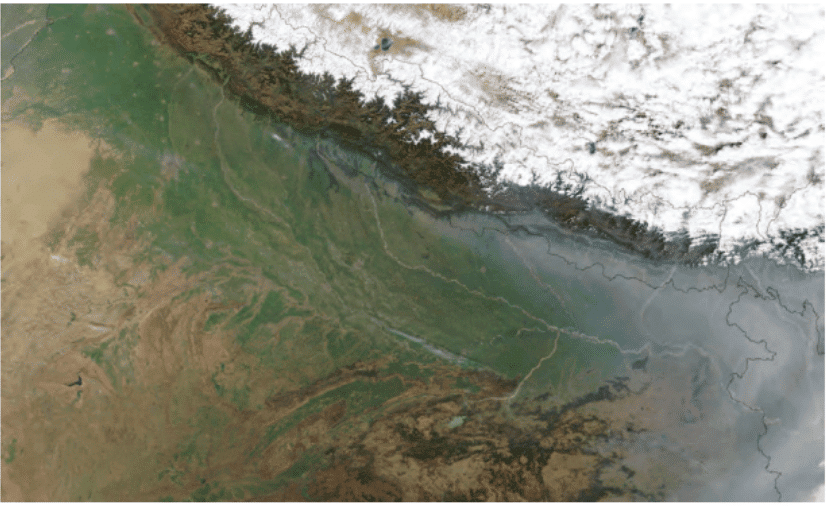
(i) Which colour is the Ganga plain?
Ans: Ganga plain is blue in colour.
(ii) What does the white expanse represent?
Ans: The white expanse represent the snow or ice sleets in the mountains (Himalayan range).
Ans: Plains
(iv) Can you give examples of river sources or confluences from your region that are regarded sacred by any community?
Ans: Rivers are the main source of fresh water. I am impressed by that region where I am living. River Ganga passes from nearby place. Cool air blows in the morning birds are chirping. The water is flowing with great speed with full enthusiasm. Fisherman catch hold of the fishes. Children are enjoy near the bank of the river. They have their Pet animals also with them.
Section D
Q32: Explain the structure and functions of a Gram Panchayat. How does it help in rural governance? (5 Marks)
Ans: The Gram Panchayat is a village-level government made up of elected members called Panchs, led by a Sarpanch chosen by the villagers.
Structure of Gram Panchayat
Its structure includes regular meetings where everyone discusses village needs, like fixing wells or building schools. The Panchs and Sarpanch work together to make decisions and talk to higher officials if more help is needed. It’s small but powerful because it’s close to the people it serves.
Functions of Gram Panchayat
- Its functions are to look after basic things like clean water, roads, and streetlights, and to settle small fights between neighbors so everyone gets along.
- It also runs government programs, like giving jobs or food to the poor.
- The Gram Panchayat helps rural governance by letting villagers solve their own problems instead of waiting for faraway leaders.
- For example, if a road breaks, they fix it fast, making life better and showing people their voice matters in democracy.
Q33: Label the Continents in the Following Map. (5 Marks)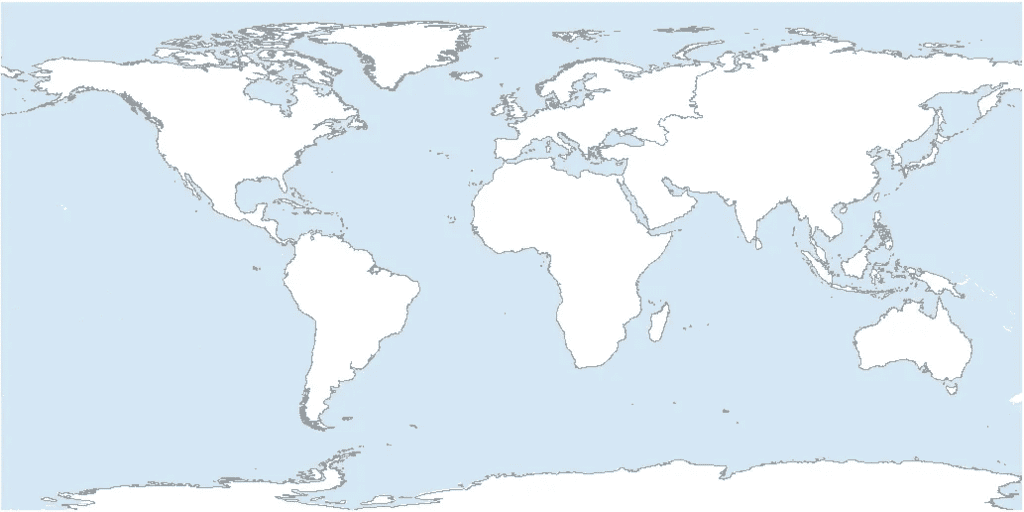
Ans:
Q34: Describe the different types of economic activities around us. Give one example of each type and explain how they contribute to society. (5 Marks)
Ans: Economic activities are the ways people work to meet their needs and make life better, and there are four main types around us.
First, agriculture is growing plants or raising animals; an example is growing rice, which gives us food to eat every day, keeping us healthy and strong—it’s the base of life in many villages.
Second, manufacturing is making things in factories; for example, making clothes provides shirts and pants we wear, protecting us and creating jobs for workers.
Third, trade is buying and selling goods; an example is selling vegetables in a market, which makes food available to everyone, even those who don’t farm, linking producers and buyers.
Fourth, services are jobs that help people directly; teaching is an example, where teachers educate kids so they can grow up smart and help society later, building a brighter future.
Together, these activities provide food, goods, and knowledge, making society run smoothly by meeting different needs and keeping people connected and cared for.
FAQs on Class 6 Social Science : Sample Paper Solutions- 1 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What topics are typically covered in Class 6 Social Science exams? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 6 Social Science exam? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of Social Science in the curriculum? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific study materials recommended for Class 6 Social Science? |  |
| 5. How can parents support their children in studying Social Science? |  |