Class 6 Social Science : Sample Paper - 3 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
Time: 3 hrs
Total Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of 34 questions and is divided into four sections: A, B, C, and D.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section A comprises question numbers 1 to 15. These are multiple-choice questions carrying one mark each. You are to select one most appropriate response out of the four provided options.
- Section B comprises question numbers 16 to 22. These are short-answer questions carrying two marks each.
- Section C comprises question numbers 23 to 31. These are short-answer questions carrying four marks each.
- Section D comprises question numbers 32 to 34. These are short-answer questions carrying five marks each.
SECTION A
Q1: Which statement about the Ujjayini meridian is incorrect? (1 Mark)
a) It served as a reference for ancient Indian astronomical calculations
b) It passed through Ujjain, a key center for astronomy
c) It was internationally adopted in 1884, replacing Greenwich
d) It was called the "madhya rekha" or "middle line"
Q2: What is a common feature of festivals like Makara Sankrānti, celebrated across India under different names? (1 Mark)
a) They mark the end of the monsoon season
b) They are linked to the harvest season
c) They celebrate military victories
d) They occur only in northern India
Q3: What is the primary purpose of urban local bodies? (1 Mark)
a) To provide national security
b) To decentralize governance in urban areas
c) To enforce religious practices
d) To centralize economic power
Q4: Why are some mountains still growing in height today? (1 Mark)
a) Erosion keeps reshaping their peaks upward
b) Snow accumulation adds to their elevation
c) Upliftment processes continue to push them higher
d) Volcanic activity deposits new layers on them
Q5: Which crop did the Harappans grow first in Eurasia? (1 Mark)
a) Wheat
b) Rice
c) Cotton
d) Barley
Q6: What does the concept "separation of powers" ensure in a democracy?(1 Mark)
a) That all powers are held by the judiciary
b) That no branch of government has excessive power
c) That the legislature can make decisions alone
d) That the executive branch controls the judiciary
Q7: Which hemisphere contains a greater proportion of water compared to land? (1 Mark)
a) Northern Hemisphere, due to its larger oceans
b) Southern Hemisphere, as it has more ocean coverage
c) Both hemispheres have equal water and land distribution
d) Northern Hemisphere, because of its larger continents
Q8: Why is there no "year zero" in the Gregorian calendar, and how does this affect calculating time between BCE and CE dates? (1 Mark)
a) It simplifies counting centuries; subtract 1 when adding BCE and CE years
b) It aligns with lunar cycles; add 1 to all calculations
c) It marks a leap year; no adjustment is needed
d) It reflects ancient traditions; multiply years by 2
Q9: What defines a joint family? (1 Mark)
a) Parents and children living alone
b) Grandparents living with their children’s families
c) A single adult living with children
d) Unrelated individuals sharing a house
Q10: Which concept from the Upaniṣhads connects the individual self to the universal divine essence, suggesting everything is interdependent? (1 Mark)
a) Ahimsa
b) Ātman
c) Anekāntavāda
d) Aparigraha
Q11: How can the number of continents vary between four and seven? (1 Mark)
a) Some continents are too small to count consistently
b) North and South America, and Europe and Asia, can be combined or separated based on perspective
c) Islands are sometimes included as continents
d) Oceans occasionally submerge parts of continents
Q12: What role does the Gram Sabha play in the Panchayati Raj system? (1 Mark)
a) It handles foreign policies
b) It is a gathering where villagers discuss and make decisions
c) It only supports financial decisions
d) It is a ceremonial body without real power
Q13: Why are non-economic activities considered valuable? (1 Mark)
a) They generate large profits
b) They contribute to personal and community well-being
c) They require less time and effort
d) They are mandated by law
Q14: Which traditional Indian garment exemplifies both a shared cultural practice and a range of regional styles and materials? (1 Mark)
a) Dhoti
b) Sari
c) Kurta
d) Sherwani
Q15: What mechanism allows citizens in urban areas to participate in governance? (1 Mark)
a) Mandatory military service
b) Compulsory voting
c) Committees and public meetings
d) State-level elections only
SECTION B
Q16: How do families share work? (2 Marks)
Q17: What is the Equator’s role on Earth? (2 Marks)
Q18: What was unique about Harappan streets? (2 Marks)
Q19: Why are deserts dry despite rivers nearby? (2 Marks)
Q20: Why are Jataka Tales important? (2 Marks)
Q21: How does the Bay of Bengal affect India? (2 Marks)
Q22: Why is it 5:30 pm in India when it is 12 pm or noon. in London? (2 Marks)
SECTION C
Q23:
(i) What is the Rigveda about?
(ii) How does it shape rituals? (4 Marks)
Q24:
(i) What is a meridian?
(ii) How is it different from a parallel? (4 Marks)
Q25:
(i) How are plains formed by rivers?
(ii) Name one such plain in India. (4 Marks)
Q26:
(i) What were Harappan docks?
(ii) Why were they built? (4 Marks)
Q27:
(i) What is Asia’s largest desert?
(ii) How does it affect the continent? (4 Marks)
Q28:
(i) How do dances show India’s diversity?
(ii) Name one dance from the northeast. (4 Marks)
Q29:
(i) What is the Western Ghats’ role?
(ii) How does it influence rain? (4 Marks)
Q30:
(i) What are monuments as sources?
(ii) Give an example from India. (4 Marks)
Q31:
(i) What does the Municipal Corporation do?
(ii) Give one example of its work. (4 Marks)
 |
Download the notes
Class 6 Social Science : Sample Paper - 3
|
Download as PDF |
SECTION D
Q32: Match the Following (5 Marks)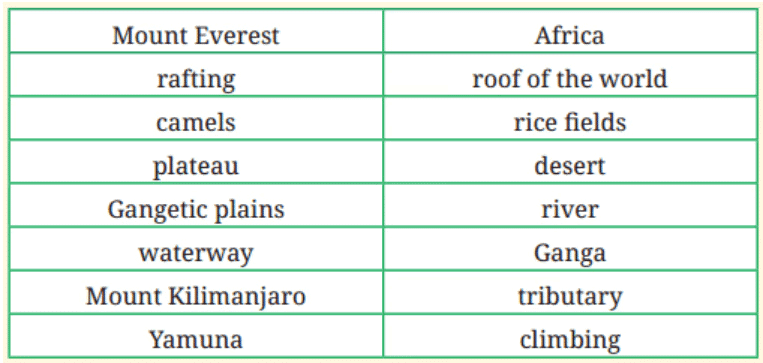
Q33: What is grassroots democracy? How does it empower people? (5 Marks)
Q34: P and Q are urban bodies. P covers a whole city, Q is a smaller city unit.
(i) Name P.
(ii) What does P do?
(iii) Name Q.
(iv) Give one task of Q.
(v) How do P and Q make cities better? (5 Marks)
The Solutions of the Sample Paper -3 Here
FAQs on Class 6 Social Science : Sample Paper - 3 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What are the main topics covered in Class 6 Social Science? |  |
| 2. How can students prepare effectively for the Class 6 Social Science exam? |  |
| 3. What types of questions are commonly found in Class 6 Social Science exams? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to study Social Science in Class 6? |  |
| 5. What resources can students use to enhance their understanding of Social Science topics? |  |





















