UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Science & Technology for UPSC CSE > Mnemonics: Motion and Laws of Motion
Mnemonics: Motion and Laws of Motion | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Types of Motion |

|
| 2. Types of Speed |

|
| 3. Types of Velocity |

|
| 4. Types of Acceleration |

|
| 5. Four Fundamental Forces in Nature |

|
This document will help you remember important concepts about Motion and the Laws of Motion in a fun and easy way. Inside, you'll find mnemonics—memory tricks—that will make it simpler for you to recall key principles, formulas, and laws related to motion.

Whether you're preparing for the SSC CGL exam, a quiz, or simply enhancing your understanding of physics, these mnemonics will serve as valuable memory aids. Use them alongside your regular study routine to strengthen your grasp of motion and improve your recall.
1. Types of Motion
Mnemonic: Run And Rest
Mnemonic Explanation:
- Run: Rectilinear Motion
- And: Angular Motion
- Rest: Rotational Motion
2. Types of Speed
Mnemonic: I Use New App
Mnemonic Explanation:
- I: Instantaneous Speed
- Use: Uniform Speed
- New: Non-Uniform Speed
- App: Average Speed
3. Types of Velocity
Mnemonic: I Use New App
Mnemonic Explanation:
- I: Instantaneous Velocity
- Use: Uniform Velocity
- New: Non-Uniform Velocity
- App: Average Velocity
4. Types of Acceleration
Mnemonic: I Play New Chess
Mnemonic Explanation:
- I: Instantaneous Acceleration
- Play: Positive Acceleration
- New: Negative Acceleration
- Chess: Constant Acceleration
5. Four Fundamental Forces in Nature
Mnemonic: Go Eat Warm Soup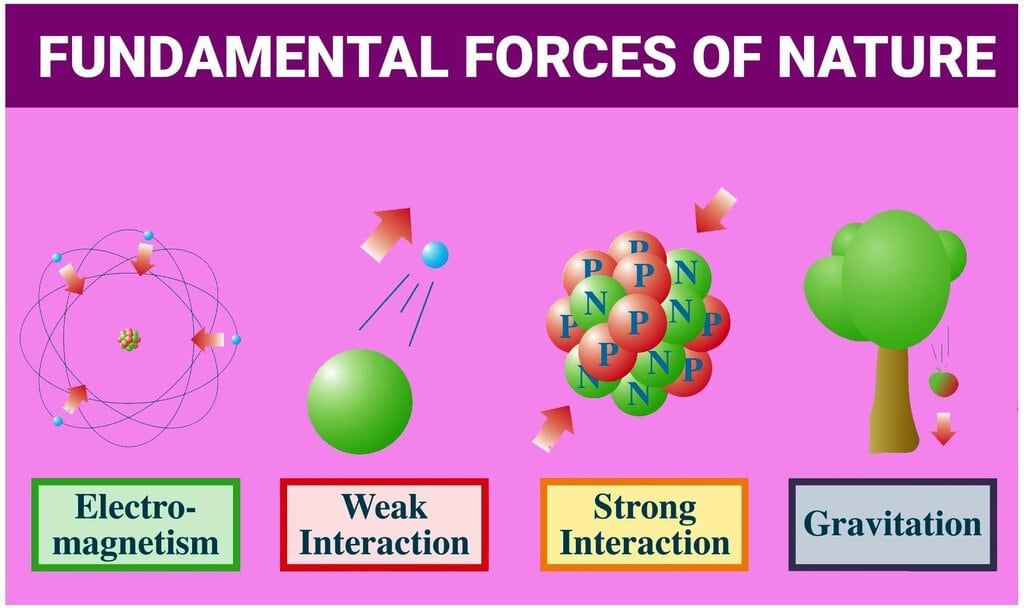
Mnemonic Explanation:
- Go: Gravitational force
- Eat: Electromagnetic force
- Warm: Weak nuclear force
- Soup: Strong nuclear force (the strongest of the four)
The document Mnemonics: Motion and Laws of Motion | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Science & Technology for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Motion and Laws of Motion - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the different types of motion in physics? |  |
Ans. In physics, motion can be categorized into several types, including:
1. <b>Translational Motion</b>: Movement from one location to another, such as a car driving down a road.
2. <b>Rotational Motion</b>: Motion around an axis, like a spinning top or the Earth rotating on its axis.
3. <b>Oscillatory Motion</b>: Back-and-forth movement around a central position, such as a pendulum swinging.
4. <b>Periodic Motion</b>: Motion that repeats at regular intervals, like a heartbeat or the motion of a clock.
5. <b>Linear Motion</b>: Movement along a straight line, which can be uniform (constant speed) or non-uniform (varying speed).
| 2. What are the various types of speed? |  |
Ans. Speed can be classified into several types:
1. <b>Uniform Speed</b>: When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, e.g., a train moving at a constant speed.
2. <b>Variable Speed</b>: When an object's speed changes over time, such as a car accelerating or decelerating.
3. <b>Average Speed</b>: Calculated as the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken.
4. <b>Instantaneous Speed</b>: The speed of an object at a specific moment in time, often measured using speedometers in vehicles.
| 3. How is velocity different from speed? |  |
Ans. Velocity differs from speed in that it is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. Speed is a scalar quantity, indicating only how fast an object is moving regardless of its direction. For example, if a car is traveling at 60 km/h north, its speed is 60 km/h, but its velocity is 60 km/h north.
| 4. What are the different types of acceleration? |  |
Ans. Acceleration can be categorized as follows:
1. <b>Uniform Acceleration</b>: When an object's acceleration remains constant over time, such as a freely falling object under gravity.
2. <b>Non-uniform Acceleration</b>: When an object's acceleration changes over time, like a car that speeds up and slows down in traffic.
3. <b>Centripetal Acceleration</b>: Acceleration directed towards the center of a circular path, experienced by objects moving in circular motion, such as a satellite orbiting Earth.
4. <b>Tangential Acceleration</b>: This occurs when there is a change in the speed of an object moving along a curved path.
| 5. What are the four fundamental forces in nature? |  |
Ans. The four fundamental forces in nature are:
1. <b>Gravitational Force</b>: The attraction between two masses, such as the Earth and an object falling towards it.
2. <b>Electromagnetic Force</b>: This force acts between charged particles, responsible for electricity, magnetism, and light.
3. <b>Weak Nuclear Force</b>: A force that is responsible for radioactive decay and certain types of particle interactions.
4. <b>Strong Nuclear Force</b>: The force that holds protons and neutrons together in an atomic nucleus, overcoming the repulsive electromagnetic force between positively charged protons.
Related Searches















