Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th March 2025) - 1 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Budgetary Dependence of CPSEs |

|
| Need for Balanced Cryptocurrency Regulation |

|
| International Women’s Day 2025 |

|
| India’s Energy Strategy |

|
| India as the 2nd Largest Arms Importer |

|
Budgetary Dependence of CPSEs
 Why in News?
Why in News?
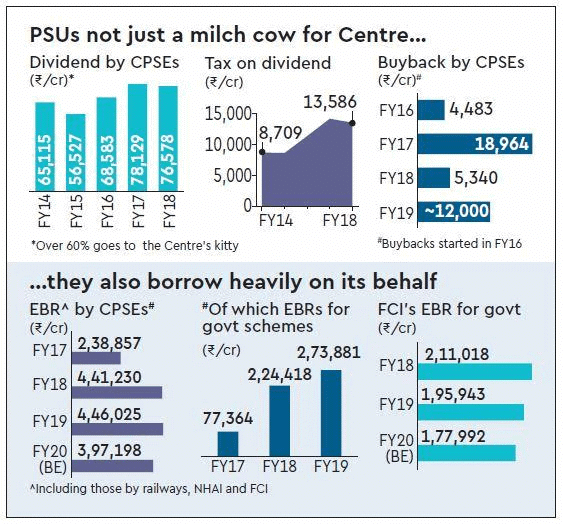
- Concerns have emerged as Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) adjust their capital expenditure (capex) strategy, increasingly relying on budgetary support instead of self-financing or private investment. This trend raises questions about the long-term financial sustainability and autonomy of these enterprises.
Key Takeaways
- CPSEs are increasingly dependent on budgetary support, which has surged by over 150% in five years.
- The Internal and Extra Budgetary Resources (IEBR) have significantly declined, limiting financial flexibility.
- High government debt and policy instability are deterring private investment in CPSEs.
Additional Details
- Overdependence on Budgetary Support: CPSEs are relying more on funding from the government. Budgetary support increased from Rs 2.1 lakh crore in FY20 to Rs 5.48 lakh crore in FY25 (Revised Estimate).
- Decline in IEBR: The IEBR used for financing capex has dropped from Rs 6.42 lakh crore in FY20 to Rs 3.63 lakh crore in FY23, and is estimated at Rs 3.82 lakh crore in FY25, limiting CPSEs' financial flexibility.
- Reduced Private Sector Participation: The reliance on budgetary support has discouraged private investment, as seen with the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) where expected private funding fell to nil in FY23-FY24.
- Policy Concerns: The Standing Committee on Transport (FY22) emphasized that reliance on budgetary support may not meet investment needs, urging for increased private sector engagement.
- High Dividends: Government pressure on CPSEs to prioritize dividend payments over reinvestment restricts their ability to modernize and grow independently.
- Limited Financial Autonomy: CPSEs lack the flexibility to respond rapidly to market changes, which can slow down decision-making processes.
In summary, the financial health of CPSEs is under scrutiny due to rising debt burdens and a lack of private investment. Addressing these issues through policy reforms, encouraging independent capital raising, and balancing dividend payments with reinvestment is crucial for ensuring fiscal sustainability.
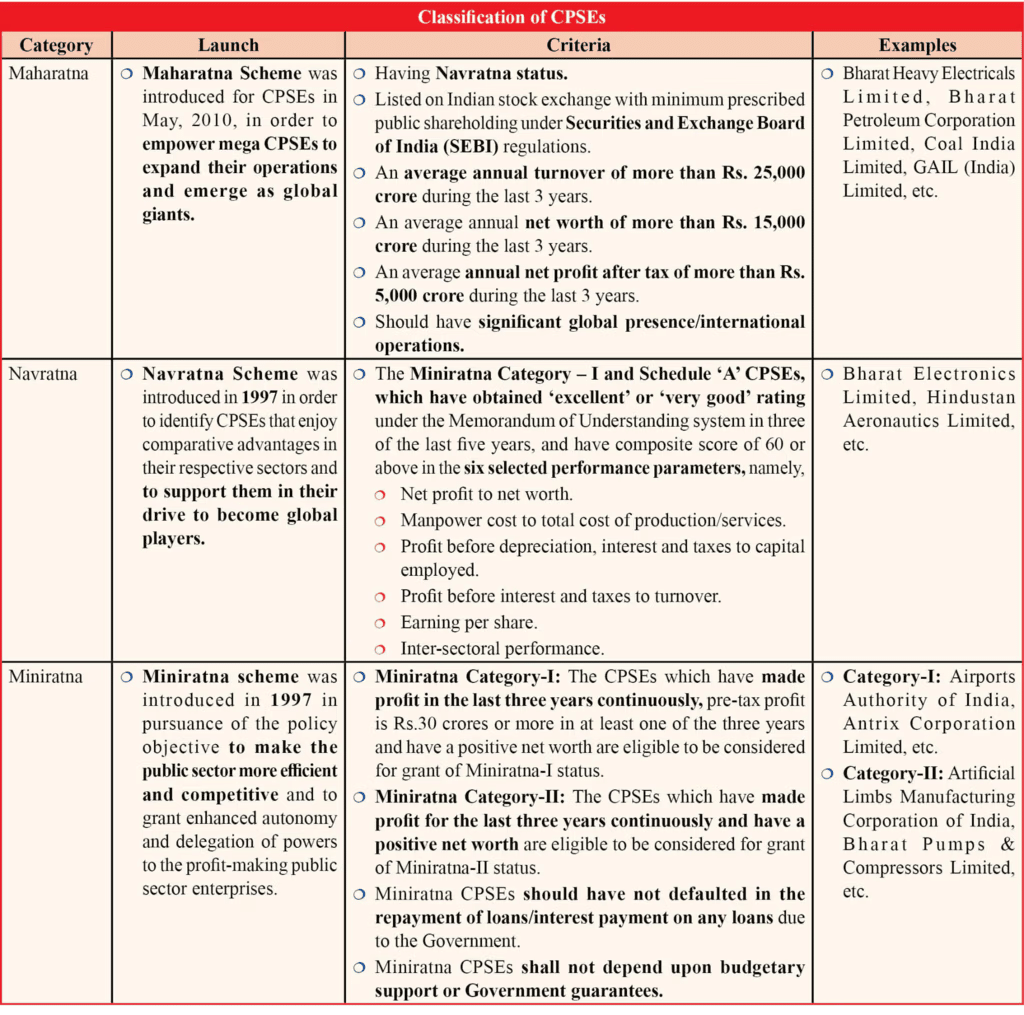
What are the Key Facts About CPSEs?
- About: CPSEs are companies in which the Central Government or other CPSEs hold at least a 51% stake.
- Department Oversight: The performance, finance, and policies of CPSEs are overseen by the Department of Public Enterprises (DPE).
- Historical Context: Post-independence, India's socialist model led to the establishment of CPSEs in key industries, which saw a shift towards corporatization and efficiency post-1991 economic reforms.
- Significance: CPSEs are vital for India's economic development, infrastructure creation, and employment generation.
- Classification: CPSEs are classified into Miniratna, Navratna, and Maharatna based on size, financial performance, and strategic importance.
As of March 2024, there are 448 CPSEs, with only 272 operating in FY24. The gross revenue of these enterprises declined by 4.7% to Rs 36.08 lakh crore in FY24. They contributed Rs 4.85 lakh crore to the central exchequer in FY 2023-24, marking a 5.96% increase from the previous year. Additionally, CPSEs spent around Rs 4,900 crore on CSR activities, reflecting a significant increase from the prior year.
What Measures Can Address CPSEs’ Concerns?
- Disinvestment: The Department of Investment and Public Asset Management (DIPAM) suggests prioritizing the privatization of non-strategic CPSEs to attract private investment.
- Raise Capital Independently: Encourage CPSEs to enhance IEBR financing through bonds and partnerships to reduce reliance on budgetary support.
- Digital Transformation: CPSEs should improve operational efficiency by adopting advanced digital infrastructures.
- Limiting High Dividend Payout: CPSEs should balance dividend payments with necessary reinvestments for growth.
- CPSE Performance Reviews: Limit performance reviews to twice a year for better efficiency.
In conclusion, critically evaluating the financial health of CPSEs, especially in light of their increasing debt, indicates a need for strategic reforms and measures to ensure their fiscal sustainability.
Need for Balanced Cryptocurrency Regulation

Why in News?
- The US administration has recognized the significance of crypto assets, firmly establishing their role in global finance. In contrast, countries such as Vietnam are advocating for clear regulations, while the EU is setting global standards with the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework. Meanwhile, India is still awaiting the release of a discussion paper on this matter.
Key Takeaways
- The US embraces crypto assets, while India lags in regulatory discussions.
- Countries are moving towards clearer regulations to enhance investor protection.
- Cryptocurrencies are decentralized digital currencies secured by cryptography.
Additional Details
- What is Cryptocurrency? A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that employs cryptography for secure transactions. It operates independently of any government or institution and is recorded on a public digital ledger known as the blockchain, which is maintained by a worldwide network of computers.
- Examples of cryptocurrencies include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
- The difference between cryptocurrency, e-money, and physical currency includes aspects such as accessibility, value determination, customer identification, issuer, and regulatory oversight.
Regulations
- Globally, most cryptocurrencies function outside the purview of national government regulations, serving as alternative currencies.
- Countries like Switzerland have established clear regulatory frameworks to protect investors while promoting blockchain innovation.
- In September 2021, El Salvador became the first nation to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
- In India, cryptocurrency remains unregulated but is not explicitly banned.
Why Does India Need a Policy for Cryptocurrency?
- Preventing Talent Exodus: A comprehensive ban could result in a significant brain drain, as blockchain experts may relocate to more crypto-friendly nations.
- Integrating into the Global Financial Ecosystem: By adopting cryptocurrency regulations, India can enhance its position in the global financial landscape, attracting investments and nurturing crypto startups.
- Leveraging New Technology and Services: The demand for blockchain applications presents an opportunity for India to develop a skilled workforce in crypto technologies.
- Encouraging Financial Innovation: The dynamic nature of blockchain technology can lead to innovative business models and applications across various sectors.
- Enhancing Investor Protections: Robust education and guidelines are essential to safeguard investors and regulate crypto assets as commodities.
What are the Challenges Cryptocurrency Poses?
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are highly speculative, leading to drastic price changes and potential losses.
- Risk of Misuse: The ease of transferring cryptocurrencies across borders raises concerns about money laundering and terror financing.
- Scalability Issues: The growing size of blockchain data can limit the capacity for rapid transactions, especially in emergencies.
- Economic Imbalance: The rise of cryptocurrencies can disrupt traditional money flow in the economy.
- Lack of Regulatory Oversight: Without a dedicated regulatory framework, consumers face risks related to transactions and information.
Way Forward
- Regulatory Clarity: A comprehensive regulation bill must clarify the distinctions between various crypto assets based on their use cases.
- Investor Protection: Mechanisms for dispute resolution and fraud prevention should be established to protect retail investors.
- Stablecoin and CBDC Integration: India's digital rupee initiative can coexist with crypto assets if clear regulatory guidelines are established.
- Taxation Reform: Adjusting the tax regime for cryptocurrencies could encourage domestic innovation.
- Public-private Collaboration: Engaging with industry leaders and international regulatory bodies will aid in crafting effective policies.
In conclusion, the establishment of a balanced regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies in India is crucial to foster innovation while protecting investors. A clear policy can help integrate the country into the global financial system and leverage the potential of blockchain technology.
International Women’s Day 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- International Women's Day is celebrated globally on the 8th of March to recognize women’s achievements across cultural, economic, and political spheres. Additionally, the year 2025 is significant as it marks the 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (BPfA), a landmark commitment to women's rights.
Key Takeaways
- International Women's Day is observed on March 8.
- 2025 marks the 30th anniversary of the BPfA.
- The theme for 2025 is “For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.”
Additional Details
- What is International Women’s Day: It is a special day dedicated to honoring women's achievements and advocating for their rights in politics, society, and the economy.
- History: Proposed by German activist Clara Zetkin, the first celebrations took place in 1911 in the USA and Europe. In 1975, the United Nations officially recognized it as International Women's Day.
- Purpose: It serves as a platform to discuss crucial issues such as workplace equality, reproductive rights, and leadership representation. Governments and organizations promote policies for women's empowerment and ending discrimination.
What is the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action?
- Overview: Adopted at the 4th World Conference on Women in Beijing, China, in 1995, it is a key blueprint for women's and girls' rights, promoting legal protection, service access, youth engagement, and social change.
- India's Role: India is a signatory to this declaration.
- Areas for Action: It identifies 12 key areas for urgent action on gender equality and strategies for ensuring equal opportunities for all.
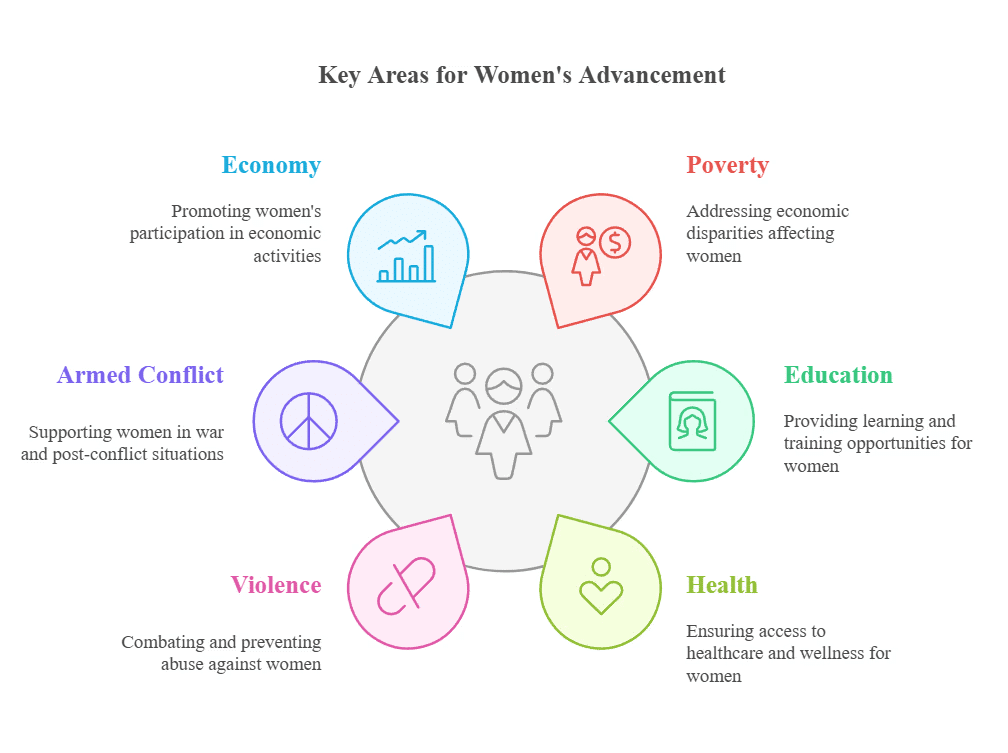
Beijing+30 Action Agenda
- Marks the period from 1995 to 2025 for reviewing and appraising the implementation of the BPfA.
- Focuses on six key areas to enhance progress towards gender equality.
What is the Current Status of Women in India?
- Maternal Health: Institutional deliveries have increased to 95%, leading to a decline in maternal mortality from 130 to 97 per 100,000 births (2014-2020). Modern contraceptive use among married women is at 56.5%, enhancing reproductive health choices.
- Education & Skills: Initiatives like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao have improved the sex ratio (1020 females per 1000 males as per NFHS - 5) and increased female higher school enrollment by 28% since 2014-15. The Vigyan Jyoti initiative encourages girls' participation in STEM education.
- Financial Inclusion: 100 million women have gained financial access through Self-Help Groups (SHGs), while PMGDISHA has trained 35 million rural women in digital literacy.
- Addressing Gender-Based Violence: 770 One Stop Centres provide medical, legal, and psychological support to women victims. For example, Odisha's blockchain system enables swift, confidential support for survivors.
- Political Representation: The Women’s Reservation Act, 2023, ensures 33% legislative representation for women, and India has 1.4 million women in local governance, leading globally.
- Women in Science & Technology: Programs like Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI) support women in STEM fields, and the G20 TechEquity platform trains thousands of young women in emerging technologies.
What are the Challenges to Women Empowerment?
- Political Underrepresentation: Women hold only 27% of parliamentary seats, 36% of local government positions, and 28% of management roles, which hinders inclusive policy-making.
- Workplace Discrimination: Women comprise 61% of the prime working-age workforce, earning only 51% of men's income, deepening inequality.
- Unpaid Care Work: Women spend 2.3 times more daily on unpaid care work than men, limiting their education and job opportunities.
- Barriers in Education & Food: By 2030, 110 million girls and young women may remain out of school, and 24% may face food insecurity.
- Legal Barriers: In 28 countries, women lack equal rights in marriage and divorce, while 67 nations have no legal protections against gender-based discrimination (UN Women Report).
Way Forward
- Gender-Responsive Budgeting: Increase funding for women’s education, health, finance, and social security, ensuring accountability and impact.
- Strengthening Legal Protection: Eliminate discriminatory laws related to marriage, divorce, and labor while strengthening enforcement of laws against gender violence.
- Economic Empowerment: Ensure women farmers have equal access to land, credit, and resources for food security, and support SHGs and women entrepreneurs.
- Bridging Workplace Inequality: Promote flexible work arrangements, parental leave, and workplace childcare to enhance women's labor force participation.
In conclusion, while significant strides have been made towards women’s empowerment in India, continued efforts are necessary to address the challenges and ensure equality across all sectors. The upcoming International Women’s Day serves as a crucial reminder of these ongoing efforts and the need for collective action.
India’s Energy Strategy
Why in News?
- India has made a commitment to increase its oil and natural gas imports from the United States, with expectations for energy trade to grow from USD 15 billion to USD 25 billion in the near future. This initiative is part of a broader objective to double bilateral trade to USD 500 billion. The decision is aimed at enhancing India’s energy security while also strengthening economic ties amid significant global geopolitical changes.
Key Takeaways
- Energy Security: India is the world’s third-largest oil importer, relying on imports for over 85% of its crude needs.
- Bilateral Trade Growth: Energy imports help balance India’s USD 45.7 billion trade surplus with the US as part of the 'Mission 500' initiative.
- Infrastructure Boost: US crude and LNG are competitively priced, aiming to support India’s industrial growth.
- Geopolitical Benefits: Stronger energy ties with the US can help India counterbalance China's influence in global markets.
Additional Details
- Crude Oil Consumption:
- Total Imports (2023-24): 234.26 million tonnes.
- Import Dependence: Increased to 87.8% in 2023-24.
- Future Projection: Expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.59% to 500 million tonnes by FY40.
- Natural Gas and Cleaner Fuels:
- Target to increase natural gas’s share in the energy mix to 15% by 2030 from ~6%.
- Total LNG Imports (2023-24): 31.80 billion cubic meters worth USD 13.405 billion.
- Ethanol Blending Target: Increased to 20% by 2025-26, which has contributed to a reduction of CO₂ emissions significantly.
- Increasing Domestic Production: India aims to double its oil & gas exploration area from 0.5 million sq. km by 2025 to 1 million sq. km by 2030.
- Global Energy Partnerships: Diversifying imports from various countries to ensure supply security amidst geopolitical challenges.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR): Acts as a buffer against disruptions and aims to commercialize 50% of its SPR.
- Clean & Renewable Energy: Targeting 500 GW of renewable energy capacity, focusing on solar, wind, and hydro projects.
In conclusion, India’s strategy for oil and gas is driven by economic growth and an increasing demand for energy while addressing high import dependence. The country is focusing on expanding refining capacity, investing in natural gas, and diversifying its sources of energy imports while transitioning to cleaner energy solutions.
Mains Question:
- How does India's strategy of diversifying its oil and gas imports impact its energy security?
India as the 2nd Largest Arms Importer
Why in News?
- According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) report, India's share of global arms imports decreased to 8.3% during the period of 2020-2024, making it the second-largest arms importer, following Ukraine.
Key Takeaways
- India's arms imports saw a decline of 9.3% when compared to the period from 2015-2019.
- Russia has been India's primary supplier, although its share of India's imports fell from 72% (2010-2014) to 36% (2020-2024).
- France emerged as the second-largest supplier to India, accounting for 28% of India's total arms imports.
Additional Details
- Regional Developments: Pakistan's arms imports increased by 61%, with China supplying 81% of Pakistan's total arms imports.
- For the first time since 1990-94, China dropped out of the top 10 arms importers, experiencing a 64% decline in imports attributed to a stronger domestic defense industry.
- In Asia and Oceania, India, Pakistan, Japan, and Australia were identified as among the top 10 largest arms importers globally during 2020-2024.
- US Arms Exports: The United States maintained its position as the largest arms exporter, providing weapons to Ukraine, NATO allies, and nations in the Asia-Pacific region.
- European Arms Imports: European countries increased their arms imports by 155% as a response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine, with France surpassing Russia to become the second-largest arms exporter.
- Russia's Exports: Russia's global arms exports fell to 7.8% of total exports, placing it in third due to Western sanctions and production issues. However, India, China, and Kazakhstan remained its key buyers.
- In the Middle East, arms imports decreased by 20%, yet the region continues to be a major importer, with Qatar now the third-largest globally.
- Global Overview: Global arms transfers remained stable compared to previous years but saw an 18% increase from 2005-2009, with rising imports in Europe and the Americas offsetting declines in other regions like China.
India is actively working to reduce its reliance on arms imports through various initiatives aimed at fostering domestic manufacturing capabilities. The government has set ambitious production targets and policies to promote indigenization in defense.
India’s Initiatives to Reduce Arms Imports
- Budget Allocation: Rs 6.21 lakh crore allocated for defense in Budget 2024-25, with 75% of capital procurement reserved for domestic manufacturers.
- Self-Reliant Initiatives: The SRIJAN portal has been launched to facilitate procurement from Indian vendors.
- Defense Production Growth: India's defense production reached a record Rs 1.27 lakh crore in 2023-24, representing a 174% increase from 2014-15.
- Positive Indigenization Lists: Five lists of defense items have been released, which place an embargo on the import of these items, ensuring they are produced within India.
- Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020: This policy prioritizes domestic procurement over foreign purchases and promotes initiatives for private-sector participation in defense manufacturing.
- Defence Industrial Corridors: Two corridors established in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu to enhance defense manufacturing capabilities.
- Private Sector & FDI Participation: 100% FDI is allowed via the Government Route, contributing to 21% of India’s total defense production.
- Defence Public Sector Units: India has 16 DPSUs, including Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL), undertaking major indigenization projects like INS Vikrant and LCA Tejas.
- R&D & Innovation: The iDEX initiative supports startups and MSMEs in developing advanced military technologies.
- Future Goals: India aims for a defense production target of Rs 1.75 lakh crore by 2025 and Rs 3 lakh crore by 2029.
Mains Question:
- India’s defense production has seen significant growth in recent years. Critically examine the government’s initiatives to boost domestic defense manufacturing.
|
287 docs|142 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th March 2025) - 1 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of budgetary dependence for Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) in India? |  |
| 2. Why is there a need for balanced cryptocurrency regulation in India? |  |
| 3. How does India plan to enhance its energy strategy in the coming years? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of India being the second-largest arms importer globally? |  |
| 5. How is International Women’s Day observed in India, and what are its goals? |  |















