Difference Between SRAM and DRAM | Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is RAM? |

|
| Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) |

|
| Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) |

|
| Difference Between SRAM and DRAM |

|
| Key Differences Between SRAM and DRAM |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
SRAM and DRAM are two kinds of RAM (Random Access Memory) used in computers. SRAM, or Static Random Access Memory, stores data using transistors and keeps it as voltage. DRAM, or Dynamic Random Access Memory, stores data in capacitors as electric charges. SRAM is faster and costs more, while DRAM is slower and cheaper. You’ll usually find SRAM in cache memory (super-fast storage near the CPU), and DRAM as the main memory (the bigger storage for everything else). Let’s break down the differences.
What is RAM?
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. It’s the computer’s short-term memory that the CPU can grab data from quickly. It holds stuff the CPU is working on right now—like a game you’re playing or a file you’re editing. But if the power goes off, poof, the data’s gone. RAM comes in two types: SRAM and DRAM.
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)
SRAM stores data in transistors, kind of like tiny switches that stay on or off using voltage. As long as the power’s flowing, it remembers the data without needing a refresh. That’s why it’s called “static”—it just sits there holding the data steady. It’s super fast, so it’s used in cache memory, which is like a small, speedy helper for the CPU.
Characteristics of SRAM
- It’s a lot faster than DRAM.
- It uses less power to do its job.
Advantages of SRAM
- It doesn’t need much power.
- It’s quick at getting data to the CPU.
- It’s perfect for making fast cache memory.
Disadvantages of SRAM
- It can’t hold as much data as DRAM.
- It’s expensive to make.
- It’s trickier to build because it’s more complicated.
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
DRAM stores data in capacitors, which are like tiny buckets holding electric charges. But these buckets leak over time, so the data fades unless it gets refreshed with a new charge every few milliseconds. That’s why it’s called “dynamic”—it’s always changing and needs action to keep the data alive. It’s used for the main memory in computers because it can hold a lot more data cheaply.
Characteristics of DRAM
- It’s slower than SRAM.
- It’s cheaper than SRAM.
- It uses more power because of the refreshing.
Advantages of DRAM
- It’s not expensive to make.
- It can store tons of data.
Disadvantages of DRAM
- It’s slower at giving data to the CPU.
- It uses more power than SRAM.
- If the power cuts out, the data disappears.
Difference Between SRAM and DRAM
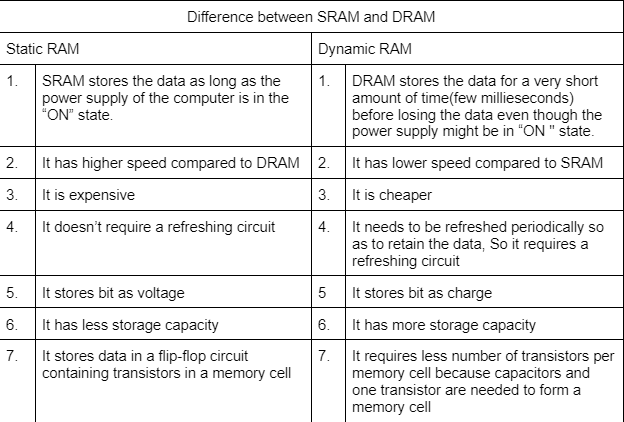
Key Differences Between SRAM and DRAM
SRAM and DRAM are two types of RAM (Random Access Memory) that work differently. SRAM is super fast and used for cache memory near the CPU, while DRAM is cheaper and used as the main memory in computers. Knowing how they’re different helps pick the right one for what a device needs.
- Speed: SRAM (Static RAM) is faster than DRAM (Dynamic RAM). It can grab data quicker, so the CPU doesn’t have to wait long.
- Design Complexity: SRAM uses six transistors for each bit of data, which makes it more complicated. DRAM uses just one transistor and one capacitor per bit, so it’s simpler to build.
- Cost: SRAM costs more because it’s trickier to make with all those transistors. DRAM is cheaper since it’s simpler and uses fewer parts.
- Power Consumption: SRAM uses less power when it’s just sitting there, but it takes more power when reading or writing data. DRAM uses a steady amount of power all the time because it needs to keep refreshing its data.
- Data Volatility: Both lose data when the power’s off (they’re volatile), but SRAM holds onto data without any extra work as long as it has power. DRAM needs to refresh its data constantly or it forgets everything.
- Usage: SRAM’s speed makes it perfect for cache memory—the small, fast storage the CPU uses a lot. DRAM is used for main memory, where the computer keeps bigger stuff like programs and files, since it’s affordable and can store more.
Conclusion
SRAM is fast, pricey, and takes up more space per bit, so it’s great for cache memory where speed matters most. DRAM is slower, cheaper, and can pack in more data, making it the go-to choice for a computer’s main memory. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, so we use both depending on what a device needs—SRAM for quick jobs and DRAM for bigger, budget-friendly storage.
|
76 videos|175 docs|70 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between SRAM and DRAM - Digital Circuits - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE)
| 1. What is the primary function of RAM in a computer system? |  |
| 2. What are the main differences between Static RAM (SRAM) and Dynamic RAM (DRAM)? |  |
| 3. Why is SRAM typically used for cache memory in processors? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using DRAM over SRAM in applications? |  |
| 5. In what scenarios would one choose to use SRAM instead of DRAM? |  |















