Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st March 2025) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Habitual Offender Laws
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Supreme Court of India has raised significant concerns regarding laws that classify habitual offenders. As of March 2025, 14 States and Union Territories continue to enforce these classifications, which have been deemed constitutionally questionable, particularly regarding their impact on denotified tribes.
Key Takeaways
- The classification of habitual offenders has historical roots in colonial-era laws.
- Recent Supreme Court observations highlight the discriminatory nature of these laws against denotified tribes.
- Responses from state governments vary, with some repealing the laws while others maintain them.
Additional Details
- Origin of Habitual Offender Classification: The concept dates back to the late 18th century, with Regulation XXII of 1793 allowing magistrates to imprison certain communities based on suspicion. The Criminal Tribes Act of 1871 formally classified entire tribes as criminal, a classification that persisted despite the repeal of these laws in 1952. Many states subsequently enacted their own laws focusing on individual convictions.
- Post-Independence Developments: Following the repeal of the Criminal Tribes Act, states continued to enact habitual offender laws (e.g., Madras in 1948, Rajasthan in 1953). The 1965 Lokur Committee still regarded denotified tribes as possessing an “anti-social heritage.” Major incidents such as the custodial death of Budhan Sabar in 1998 led to national outrage and calls for reform.
- The Supreme Court’s stance in October 2024 emphasized the problematic application of these laws, noting their tendency to target members of denotified tribes and perpetuate criminalization.
- Current Status: The debate over habitual offender laws is ongoing, with some states like Punjab and Odisha ceasing their implementation, while others, such as Gujarat, continue to apply them for preventive reasons.
The discussion surrounding habitual offender laws encapsulates broader themes of social justice and the need for legal reforms that promote inclusivity and fairness. The Supreme Court's observations may catalyze further legislative changes in the near future.
Glacier Thinning in Hindu Kush Himalaya
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The alarming rates of glacier thinning in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region have gained significant attention. A recent United Nations report highlights that glaciers in this area are retreating 65% faster from 2011 to 2020 compared to the previous decade. This report coincided with World Day for Glaciers, underscoring the urgent need to address the impacts of climate change.
Key Takeaways
- The HKH region, referred to as the "Third Pole," is crucial for global water supply.
- Projected glacier volume loss could threaten water security for nearly two billion people by 2100.
- Melting glaciers increase the risk of hazardous events like Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
- Weak water governance and mistrust among countries hinder effective cooperation for resource management.
Additional Details
- Importance of HKH Glaciers: The HKH spans five million square kilometers and contains approximately 100,000 square kilometers of glaciers. These glaciers nourish ten major river systems, providing water for nearly two billion individuals.
- Projected Glacier Losses: If global temperatures rise by 1.5 to 2°C, glacier volume in the HKH could decrease by 30-50% by 2100. A rise exceeding 2°C could lead to a loss of 45% of the 2020 glacier volume.
- Hazards from Glacier Melts: Melting glaciers contribute to Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), which have caused over 12,000 fatalities in the past 200 years, with a significant number occurring in the HKH region.
- Impact on Local Communities: Communities in mountainous areas depend on glaciers for freshwater and agricultural needs. Climate change is disrupting hydropower generation and water availability, with industries such as lithium mining intensifying the strain on water resources.
- Governance and Cooperation Challenges: Effective water governance is often lacking in mountainous regions, and inadequate transboundary cooperation complicates data sharing, which is essential for disaster risk reduction.
The report concludes with six key actions for the HKH region, emphasizing the importance of sustainable cooperation, recognizing local populations' unique needs, and undertaking concerted climate action to mitigate global warming. Enhancing ecosystem resilience and engaging in data-sharing initiatives are critical for effectively addressing the challenges posed by climate change.
What is Hawala?
Why in News?
- The use of hawala networks has significantly increased in recent years, especially for illicit activities such as poaching and money laundering. A recent investigation uncovered that a poaching network in central India has taken advantage of these informal money transfer systems to facilitate the illegal killing of tigers.
Key Takeaways
- Hawala Definition: An informal method for transferring money without the movement of physical cash.
- Trust-Based System: Operates on trust, utilizing a network of brokers known as hawaladars.
- Widespread Use: Despite a lack of regulation, hawala is favored for its convenience.
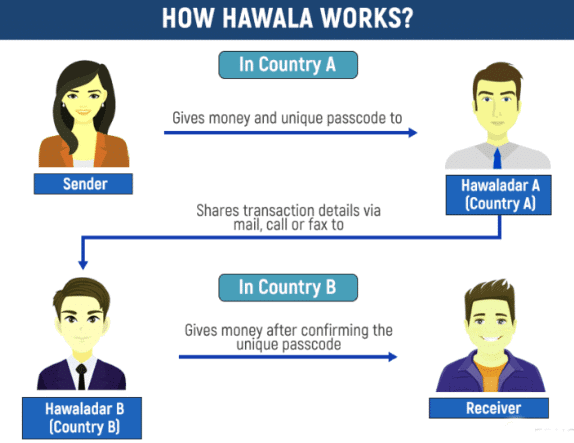
How Does Hawala Work?
- Transaction Process: A sender deposits money with a hawaladar in one location.
- The sender receives a token to share with the recipient.
- The recipient collects the funds from a local hawaladar, allowing money to be transferred without physical movement.
Users of Hawala
- Common Users: Popular among migrant workers for sending remittances home.
- Preference: Individuals in areas with limited banking access often choose hawala for its simplicity.
- Illegal Activities: Also utilized for activities such as drug trafficking and terrorism financing due to its anonymity.
Cryptocurrency Integration
- USDT in Hawala: Recent trends have seen the incorporation of cryptocurrencies like USDT into hawala transactions.
- Benefits of USDT: As a stablecoin, it allows for easy and discreet transfers across borders. Users can purchase USDT with cash and then sell it in another jurisdiction, bypassing traditional banking systems.
- Stability: USDT is preferred for hawala transactions due to its stability, liquidity, and minimal price fluctuations, making it ideal for this type of transaction.
- Regulatory Advantage: Facilitates smooth transfers in crypto-friendly regions without attracting regulatory scrutiny.
Legal Implications
- Legal Status: While hawala itself is not illegal, its association with illicit activities has led to increased scrutiny from authorities.
- Bans and Regulation: Many jurisdictions have prohibited hawala transactions due to their potential for misuse.
- Adaptation: Despite legal challenges, hawala networks continue to operate and adapt to new technologies, including cryptocurrency.
In summary, hawala is an informal money transfer system that operates on trust and is widely used for both legitimate remittances and illegal activities. The emergence of cryptocurrencies like USDT has further transformed hawala transactions, providing both advantages and challenges in terms of legality and regulation.
Disclosure of Form 17C
Why in News?
- On March 24, 2025, the Election Commission of India (ECI) faced calls from petitioners demanding greater transparency regarding voter turnout records. The Supreme Court of India has postponed a hearing on the disclosure of Form 17C, a critical document that captures votes cast at polling stations. This discussion has arisen amidst increasing concerns over inconsistencies in voter turnout data observed during elections. The new Chief Election Commissioner, Gyanesh Kumar, has indicated a readiness to engage in discussions on these pressing issues.
Key Takeaways
- Form 17C is a key electoral document as per the Conduct of Election Rules, 1961.
- Discrepancies in voter turnout data have raised concerns regarding the integrity of election results.
- Opposition parties are demanding immediate access to Form 17C for enhanced transparency.
- The ECI faces challenges related to the management and publication of electoral data.
Additional Details
- Form 17C:This document consists of two parts:
- Part 1: Known as the Account of Votes Recorded, filled by the presiding officer, includes details like the identification number of the Electronic Voting Machine (EVM), total electors, and votes cast.
- Part 2: The Result of Counting, completed by the returning officer on counting day, lists candidates and their corresponding vote counts.
- The importance of voter turnout data lies in its role in ensuring electoral integrity, as discrepancies can undermine public trust in the electoral process.
- Concerns have been raised about indiscriminate disclosure of data, with the ECI cautioning against potential misinformation from online publication.
- Political parties are encouraged to monitor elections through their polling agents, though not all can afford representation at every polling station, leading to disparities in access to information.
The demand for transparency in electoral processes continues to grow, with civil society organizations advocating for the publication of voter turnout data. They emphasize that informed voters are crucial for a healthy democracy, ensuring that every vote is accounted for and accurately represented.
AIKEYME Maritime Exercise
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Indian Navy is preparing to conduct a maritime exercise named AIKEYME, which aims to bolster defense cooperation with various African nations. This initiative aligns with Prime Minister Narendra Modi's vision, termed MAHASAGAR, which promotes security and growth across regions. The exercise is set to take place off the coast of Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania, co-hosted by the Indian Navy and the Tanzania Peoples Defence Force.
Key Takeaways
- AIKEYME stands for Africa-India Key Maritime Engagement.
- The exercise will involve ten African countries: Tanzania, Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, and South Africa.
- The primary goal is to address maritime security threats like piracy and illegal fishing.
Additional Details
- Structure of the Exercise: The AIKEYME exercise will span six days, consisting of two main phases: the harbour phase and the sea phase. The harbour phase will feature table-top exercises on piracy and information sharing, along with training in seamanship and visit board search and seizure (VBSS) operations. The sea phase will include seamanship evolutions, search and rescue operations, small-arms firing, and helicopter operations.
- Indian Ocean Ship (IOS) Sagar Initiative: Concurrently with AIKEYME, the Indian Navy has initiated the IOS Sagar program, deploying the INS Sunayna to the southwest Indian Ocean, with a crew comprising personnel from India and nine African nations to enhance joint operational capabilities.
- Training and Capacity Building: Personnel from the nine African countries will participate in a two-week training capsule at various naval professional schools in Kochi, preparing them for roles aboard INS Sunayna and ensuring effective collaboration during the exercise.
- Strategic Importance: AIKEYME and IOS Sagar signify India’s commitment to being a preferred security partner in the Indian Ocean Region, crucial for countering China’s growing influence in Africa and addressing regional security challenges, including piracy and threats from Houthi rebels.
In summary, the AIKEYME exercise represents a significant step in enhancing maritime security cooperation between India and African nations, reflecting a strategic approach to regional stability and collaborative defense efforts.
India Imposes Anti-Dumping Duties to Curb Cheap Chinese Imports
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 25, 2025, India announced the imposition of anti-dumping duties on five specific products imported from China. This strategic move is aimed at shielding local industries from the negative impacts of low-priced imports that pose unfair competition.
Key Takeaways
- India's trade deficit with China reached USD 85 billion in 2023-24.
- Anti-dumping duties are in accordance with World Trade Organization (WTO) regulations.
- Specific products affected include Soft Ferrite Cores, vacuum insulated flasks, aluminium foil, and Trichloro Isocyanuric Acid.
Additional Details
- Anti-Dumping Duties: These are tariffs imposed on foreign imports suspected of being priced below their fair market value. They aim to level the playing field for domestic industries.
- Investigation Process: The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) investigates claims of dumping, assessing both the volume and price effects on domestic industries. If injury is confirmed, anti-dumping duties are proposed, which are then finalized by the Ministry of Finance.
- Legal Framework: Dumping is defined as selling goods in a foreign market at lower prices than in the domestic market, often leading to international price discrimination.
- Global Perspective: Dumping remains a contentious issue in international trade, with accusations against countries like China. Such practices can threaten jobs and local businesses in importing nations.
The imposition of these anti-dumping duties is a crucial step for India to protect its domestic industries from being undermined by cheaper imports, although it may also lead to increased trade tensions with China.
Kerala Passes Private Universities Bill
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Kerala Assembly recently passed the Kerala State Private Universities (Establishment and Regulation) Bill, officially enabling the operation of private universities in the state. This legislation marks Kerala as the last state in India to allow private universities, indicating a significant shift in the Left's historical opposition to private education. The bill is intended to improve the higher education landscape in Kerala and address the issue of student migration.
Key Takeaways
- The bill includes government representation in the decision-making bodies of private universities.
- Multi-campus universities are permitted, with reserved seats for local residents.
- A students’ council will be established to enhance student representation in governance.
- A regulatory body will be created to oversee private universities and promote educational standards.
Additional Details
- Government Representation: The governing council of each private university will include three government nominees from a total of twelve members. This structure ensures government policies are adhered to within these institutions.
- Multi-Campus Universities: The legislation allows the establishment of universities with multiple campuses, requiring that 40% of seats in each course are reserved for permanent residents of Kerala, alongside additional reservations for SC/ST and OBC communities to promote equitable access.
- Student Representation: A council led by the Pro Vice Chancellor will consist of ten elected members, with specific mandates to include representatives from SC/ST communities and female students, fostering greater student involvement in university governance.
- Regulatory Body: This entity will ensure the effective functioning of private universities, focusing on enhancing teaching, research, and development in the private higher education sector.
The legislation aligns Kerala’s educational framework with those of other Indian states that have established laws governing private universities, such as Gujarat, Haryana, and Karnataka. While Kerala aims to address educational imbalances through this bill, concerns persist regarding the potential adverse effects on public institutions and the overall higher education sector. Protests have emerged from student groups who fear that the introduction of private universities may undermine the quality and accessibility of public education. However, the Kerala government maintains that the bill aims to bolster public institutions while inviting private investment, emphasizing accountability and high standards.
India and Singapore Sign LOI on Green Shipping Corridor
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 25, 2025, during the Singapore Maritime Week, India and Singapore formalized a Letter of Intent (LoI) to collaborate on the Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC). This agreement seeks to foster advancements in maritime digitalization and decarbonization, encouraging the adoption of innovative, low-emission technologies within the maritime industry.
Key Takeaways
- The GDSC initiative is designed to combat environmental issues in shipping by targeting the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- Collaboration aims to promote maritime digitalization and the development of zero or near-zero emission technologies.
- The partnership is expected to set new standards in sustainability and efficiency in maritime operations.
Additional Details
- Objectives of the GDSC:The initiative focuses on several key objectives:
- Promoting maritime digitalization.
- Identifying stakeholders for collaborative projects.
- Accelerating the adoption of green technologies.
- Formalizing the partnership through a memorandum of understanding.
- The agreement leverages India's strengths in information technology and green fuel production, while Singapore contributes its advanced maritime infrastructure and expertise.
- Future prospects include enhancing India's cruise tourism sector by replicating successful models from Singapore, with potential new terminals in Goa, Mumbai, and Chennai.
- During the Singapore Maritime Week, the signing event gathered numerous delegates, promoting dialogue on maritime technology and sustainability.
This collaborative effort between India and Singapore is poised to drive significant innovation in the maritime sector, fostering a resilient ecosystem that benefits both nations and contributes to global maritime sustainability.
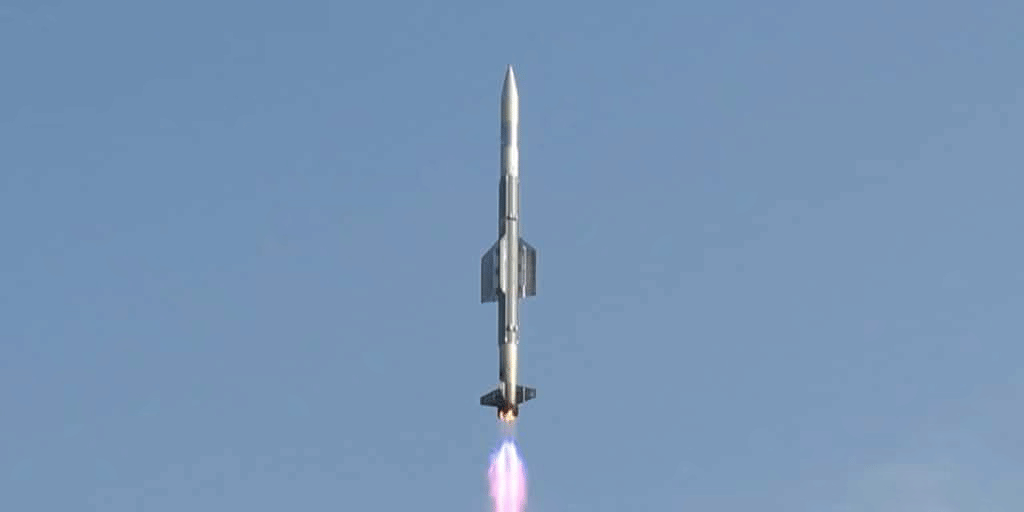
Vertically-Launched Surface-to-Air Missile (VLSRSAM)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 26, 2025, the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with the Indian Navy successfully conducted a flight test of the Vertically-Launched Short-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VLSRSAM) at the Integrated Test Range (ITR) in Chandipur, Odisha. This event marks a significant step forward in enhancing India's defence capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The VLSRSAM is an indigenously developed missile focused on short-range air defence.
- It utilizes advanced technology, including a homegrown Radio Frequency seeker for better target tracking.
- The recent flight test showcased its near-boundary-low altitude engagement capability against high-speed aerial threats.
Additional Details
- Flight Test Execution: The missile was launched from a land-based vertical launcher, successfully hitting a high-speed aerial target. Its agility and precision were evident as it executed a high turn rate to neutralize the target.
- System Components: The test involved multiple systems, including the missile itself, a Multi-Function Radar, and a Weapon Control System, all of which performed optimally under real-time conditions.
- The flight data collection was facilitated by various advanced instruments developed at ITR Chandipur.
The successful flight test of the VLSRSAM is a clear indication of India's growing self-reliance in defence technology. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh highlighted that this missile will act as a force multiplier for the Indian Navy, further solidifying India’s strategic position in regional security.
Judicial Appointments in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The recent incident involving the discovery of cash at the residence of Delhi High Court judge Justice Yashwant Varma has sparked renewed discussions about the judicial appointment process in India. This ongoing debate has evolved throughout the history of the Indian judiciary, particularly since the establishment of the National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC) Act, which aimed to reform judicial appointments before being declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2015.
Key Takeaways
- The process of judicial appointments in India has undergone significant changes since independence in 1947.
- The collegium system was established to safeguard judicial independence from political interference.
- The NJAC was intended to introduce a more balanced approach to judicial appointments but was struck down by the Supreme Court.
- There is ongoing criticism of the collegium system regarding its lack of transparency and representation.
Additional Details
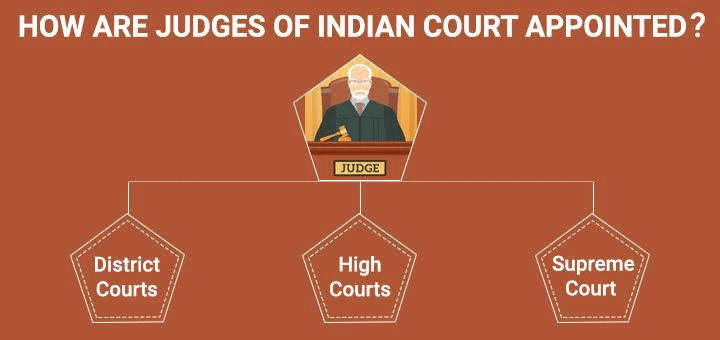
- Historical Context: Since 1947, judicial appointments were initially managed by the executive branch. However, political interference led to the establishment of the collegium system during the 1970s to enhance judicial independence.
- The Collegium System: This system arose from three landmark Supreme Court judgments, which determined that the Chief Justice of India and the four senior-most judges would recommend judicial appointments. While not explicitly stated in the Constitution, it is considered vital for maintaining judicial independence.
- Introduction of the NJAC: Proposed in 2014, the NJAC aimed to replace the collegium system with a commission involving judicial and executive members to enhance appointment processes.
- The NJAC Act was deemed unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 2015, as it could potentially compromise judicial independence through the veto power granted to non-judicial members.
- Critics argue that the collegium system's opacity and lack of accountability necessitate reforms for better representation of societal interests.
The discourse on judicial appointments in India remains dynamic, with ongoing calls for reform to improve transparency and accountability within the appointment process. It is crucial to find a balance that maintains judicial independence while being responsive to societal needs.
New Contracts for NAMIS and Light Vehicles
Why in News?
- On March 28, 2025, the Ministry of Defence of India formalized significant contracts aimed at bolstering the nation's defence capabilities. These agreements, totaling approximately ₹2,500 crore, encompass the acquisition of the Nag Missile System (NAMIS) along with around 5,000 light vehicles. Notably, these contracts fall under the Buy (Indian-Indigenously Designed, Developed and Manufactured) category, underscoring the government's commitment to enhancing indigenous defence production.
Key Takeaways
- The total value of the contracts is around ₹2,500 crore.
- The contracts support indigenously developed defence systems.
- NAMIS is a tracked anti-tank missile system designed for operational effectiveness.
- Approximately 5,000 light vehicles will improve mobility for the Armed Forces.
Additional Details
- Nag Missile System (NAMIS): This system is a tracked anti-tank weapon developed by the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO). With a contract cost of ₹1,801.34 crore, NAMIS enhances the anti-tank capabilities of the Indian Army through its fire-and-forget missile technology, which significantly boosts lethality against enemy armour.
- Operational Advantages: NAMIS is engineered to revolutionize mechanized warfare with an advanced sighting system that ensures greater accuracy and firepower, thus enhancing the operational readiness of the Indian Army in diverse combat scenarios.
- Light Vehicles Specifications: These vehicles are designed with improved engine power and can transport payloads of up to 800 kg, making them suitable for various terrains and operational conditions.
- Impact on Indigenisation and Employment: The contracts are pivotal for promoting indigenisation within India's defence sector, aiming to bolster domestic manufacturing and create both direct and indirect employment opportunities.
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat Initiative: These procurement contracts align with the government's vision of a Self-Reliant India, promoting self-sufficiency in defence manufacturing and empowering local industries.
- Future Prospects: Successful execution of these contracts could lead to further advancements in India’s defence technology and enhance its strategic position in regional and global security frameworks.
In conclusion, the recent contracts for the Nag Missile System and light vehicles represent a significant step towards modernizing India's defence capabilities, fostering indigenisation, and ensuring the nation’s military readiness in the face of evolving security challenges.
Taxation Framework Changes for AIFs
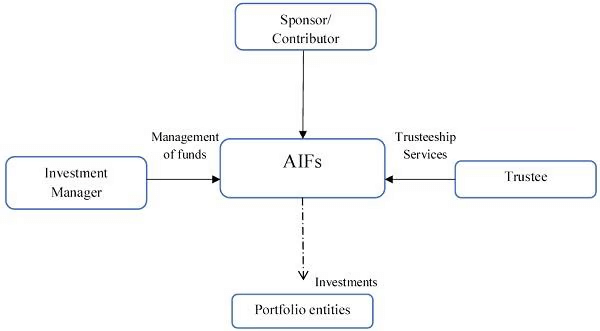 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 28, 2025, significant amendments to the taxation framework for Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) were proposed in the Finance Bill. These changes are intended to clarify the tax treatment applicable to securities held by AIFs and to improve transparency within investment structures. The revisions reflect a broader initiative to align tax regulations with the changing regulatory landscape.
Key Takeaways
- The definition of capital assets has been revised to include securities held by Category I and Category II AIFs.
- New inclusions allow for securities governed by the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) or SEBI.
- Amendments to Section 10(4D) aim to simplify tax exemptions for funds operating in the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC).
- The Union Budget for 2025-26 anticipates significant expenditures and fiscal projections.
Additional Details
- Definition of Capital Asset: The Finance Bill 2025 revises Section 2(14) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, to classify securities from Category I and II AIFs as capital assets. This uniform treatment aims to streamline taxation across various investment vehicles.
- International Financial Services Centres: The expanded definition now includes securities held by AIFs adhering to the IFSCA or SEBI regulations, providing them with greater operational flexibility in both domestic and offshore markets.
- Amendments to Section 10(4D): Proposed changes to Section 10(4D) seek to enhance tax benefits for investment funds within the IFSC, ultimately encouraging more investment in India's financial markets.
- Budgetary Context: The Union Budget for 2025-26 projects total expenditures of Rs 50.65 trillion, with a capital expenditure of Rs 11.22 trillion. Gross tax revenue is estimated at Rs 42.70 trillion.
- Fiscal Deficit and GDP Projections: The fiscal deficit for 2025-26 is projected at 4.4%, a reduction from 4.8% in the previous year, while GDP is estimated at Rs 3,56,97,923 crore, indicating a growth of 10.1% over the previous fiscal year.
- Resource Allocation to States: The budget allocates Rs 25,01,284 crore to states, marking an increase of Rs 4,91,668 crore compared to the previous year's actuals and reflecting the government's commitment to support state initiatives.
These amendments represent a significant shift in the taxation framework for AIFs, aiming to enhance clarity and encourage investment within India's financial landscape.
Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The second Global Conference on Air Pollution and Health, hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Government of Colombia, recently concluded in Cartagena. The main objective of the conference was to mobilize global support aimed at halving air pollution-related deaths by the year 2040. Each year, almost seven million people die prematurely due to air pollution, with developing countries and vulnerable communities facing the most significant impacts.
Key Takeaways
- 2.1 billion people die due to energy poverty.
- 9 out of 10 individuals are exposed to air that violates WHO guidelines.
- 2.7 billion children under 15 are exposed to unsafe air.
- The global health cost of air pollution is approximately $8.1 trillion.
- Pollution affects every organ system and is linked to various health issues.
Additional Details
- Health Impacts of Air Pollution: Air pollution leads to oxidative stress and inflammation, affecting overall health. It has been linked to neurodevelopmental disorders, anxiety, and an increased risk of dementia.
- Benefits of Improved Air Quality: Adhering to WHO guidelines could prevent thousands of asthma cases in young individuals, with substantial economic benefits from reduced health costs.
- Energy Transition: A shift to clean energy is vital for reducing air pollution. Notably, deaths from fossil fuel-derived air pollution declined by 6.9% between 2016 and 2021 due to decreased coal burning.
- Addressing Energy Poverty: Energy poverty remains a challenge for low-income households. Initiatives like India’s Ujjwala programme have improved access to clean energy, but many still face economic barriers.
- Global Investments in Air Quality: Currently, only 1% of international development aid focuses on outdoor air quality. Enhancing this allocation is crucial for effective projects.
- Human Stories and Advocacy: Personal stories, such as that of Rosamund Adoo-Kissi-Debrah advocating for recognition of air pollution’s impact, highlight the urgent need for policy changes.
- Local Actions and Global Change: Local initiatives, like ultra-low emissions zones in London, can lead to significant improvements in air quality through collaborative efforts among cities.
The conference underscored the critical need for global cooperation and investment in air quality initiatives to protect public health and promote a healthier environment for future generations.
Indian Ports Bill 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 29, 2025, the Indian Ports Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha by Union Minister Sarbananda Sonowal. This bill seeks to amend the Indian Ports Act of 1908, aiming to modernize port operations in India. The legislation is responsive to changes in international standards and environmental regulations, promoting planned development in the port sector while addressing emerging challenges.
Key Takeaways
- The Indian Ports Bill aims to modernize the legal framework governing ports.
- It addresses pollution control and compliance with international maritime obligations.
- The bill empowers state maritime boards and establishes a Maritime State Development Council.
- Coastal states have expressed concerns about centralization of power.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: The Indian Ports Act, enacted in 1908, consolidated laws regarding ports and port charges, defining the powers of central and state governments. It included provisions for safety, conservation, and the appointment of port officials. Over time, the original legislation has become outdated as port operations have evolved.
- Objectives: The bill focuses on enhancing ease of doing business, facilitating integrated port development, and ensuring environmental sustainability through pollution control measures.
- Reactions from Coastal States: The bill has faced backlash from coastal states concerned about reduced authority over non-major ports. Notably, Tamil Nadu's Chief Minister has voiced strong opposition, arguing that the bill undermines local governance.
- Parliamentary Deliberations: The bill is currently under scrutiny in Parliament, with MPs raising concerns about potential implications for state powers. The government has stated that it considered state perspectives during drafting.
The Indian Ports Bill 2025 represents a significant step towards modernizing India's port sector, reflecting both local and global considerations while addressing critical environmental and operational challenges.
Cash at Judge’s Door Case
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On March 31, 2025, a special Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) Court in Chandigarh acquitted former Punjab and Haryana High Court Judge Nirmal Yadav after a complex 14-year legal battle involving serious allegations of bribery and corruption. Following the verdict, Justice Yadav expressed her faith in the judiciary, acknowledging the prolonged process but affirming its fairness.
Key Takeaways
- The case, known as the ‘Cash at Judge’s Door’ case, began on August 13, 2008, when Rs 15 lakh was mistakenly delivered to the residence of Justice Nirmaljit Kaur.
- The CBI faced numerous challenges during the investigation, including the death of a key accused and procedural delays.
- On March 29, 2025, the CBI court acquitted Justice Yadav and others due to a lack of evidence and contradictions in witness statements.
Additional Details
- Background of the Case: The incident began when a large sum of money was delivered to the wrong judge, prompting an investigation that spanned over a decade.
- The investigation was complicated by an initial closure report from the CBI, which was later challenged, leading to renewed scrutiny and prosecution efforts.
- The trial witnessed significant delays, including the death of the main accused, which added to the complexities of the case.
The acquittal in this case has sparked discussions about judicial integrity and the handling of corruption allegations against judges, raising concerns about public trust in the judiciary's ability to address such issues effectively.
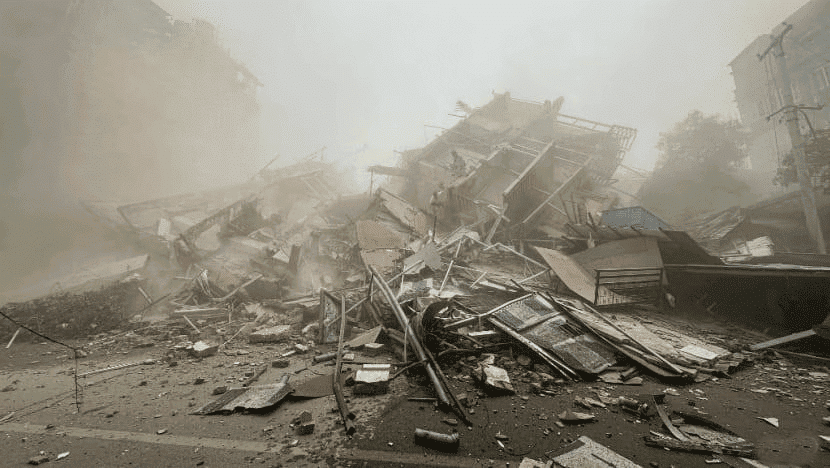
Earthquake Hits Myanmar and Thailand

Why in News?
- The earthquake that struck Myanmar and Thailand on March 28, 2025, has led to significant devastation. The National Centre for Seismology reported considerable damage caused by soil liquefaction and an earthquake frequency that matched the natural vibrations of buildings. The epicenter of this earthquake was located near Mandalay, Myanmar, and it registered a magnitude of 7.5. Following the initial quake, aftershocks exacerbated the situation, complicating rescue efforts and increasing the overall damage.
Key Takeaways
- The earthquake registered a magnitude of 7.5, with an epicenter near Mandalay, Myanmar.
- Soil liquefaction played a critical role in the destruction of infrastructure, particularly in Bangkok.
- Seven aftershocks, with magnitudes reaching up to 7.0, were recorded shortly after the main event.
- Over 1,600 casualties were reported, leading to a state of emergency declared by the military government.
Additional Details
- Earthquake Magnitude: Magnitude measures the energy released during an earthquake, with the moment magnitude scale (Mw) currently being the standard for assessment. This scale accounts for the area of the fault and the size of seismic waves, replacing the older Richter scale due to its limitations.
- Soil Liquefaction: This phenomenon occurs when saturated soil loses its strength during seismic shaking, particularly affecting loose, wet soils. It was a significant factor contributing to the extensive damage observed in urban areas.
- Aftershocks: Aftershocks are smaller earthquakes that follow the main quake, often causing additional damage and hindering rescue efforts. In this instance, seven aftershocks were noted, complicating recovery operations.
- The Sagaing Fault, responsible for the earthquake, has a documented history of seismic activity, including major quakes in 1912 and 1956, highlighting the ongoing seismic risks in the region.
- Modern seismology utilizes seismographs to record ground motion during earthquakes, digitizing these records for enhanced analysis and response.
- Intensity measurement scales, such as the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale, quantify the shaking experienced at different locations, factoring in both human perception and structural damage.
This earthquake serves as a reminder of the seismic risks in the region and the importance of preparedness and response strategies for natural disasters.
|
164 videos|632 docs|1150 tests
|





















