Plants are Living Things Chapter Notes | Year 3 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Alive or Not Alive: Plants |

|
| Plant Parts |

|
| Plants and Light |

|
| Plants Need Water and the Right Temperature |

|
Alive or Not Alive: Plants

Plants grow
- Young plants require water and sunlight to grow and are classified as living organisms. They have the ability to sense light and exhibit a behaviour known as phototropism, where they grow towards the light source.
- During the process of photosynthesis, plants produce oxygen as a byproduct, which is released into the atmosphere. This oxygen is essential for the survival of animals. As plants mature, they produce seeds that have the potential to develop into new plants.
Seven Rules: Alive or Not Alive?
- Living organisms can be identified by seven characteristics:
- They can reproduce (e.g., have offspring or produce seeds).
- They require water and food to survive.
- They can sense and respond to their environment.
- They produce waste products.
- They need air (e.g., oxygen for animals, carbon dioxide for plants).
- They grow and develop.
- They can move independently (even subtly, like plants growing towards light).
Both animals and plants are alive and exhibit all seven characteristics. Materials like wood and straw come from living organisms but do not display these traits. In contrast, materials like sand have never been alive.
When Do Leaves Die?

- Leaves on a living plant are considered alive as they are part of the living organism. However, leaves that fall off a plant are no longer part of it and are regarded as dead.
- Dead leaves on the ground may appear yellow and dry, indicating that they are no longer alive. Even green leaves that have fallen are dead because they are disconnected from the living plant.
Plant Parts
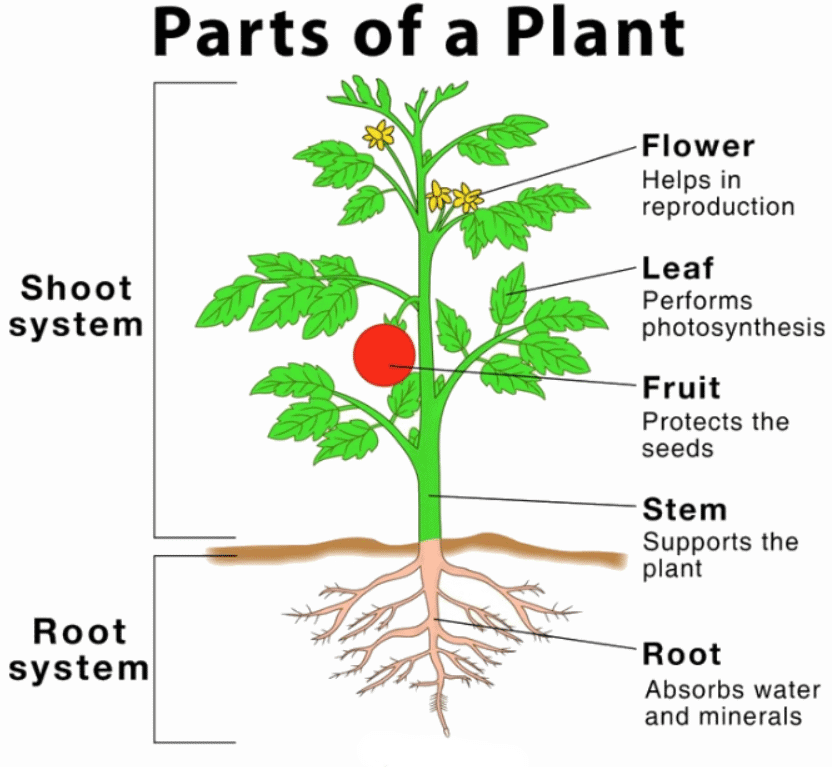
Roots, Stems, Leaves, and Flowers
Plants vary in size, from tiny to enormous, and most begin their existence as seeds that develop into mature plants. They are living organisms with different parts, each serving specific purposes:
- Leaves: Generate food through photosynthesis when exposed to sunlight.
- Stem: Provides support to the plant and transports water from the roots to other parts.
- Flowers: Produce seeds for reproduction.
- Roots: Secure the plant in the soil and absorb water.
All parts of a plant need water, and without it, the plant will perish. Roots absorb water from the soil, which is then distributed through the stem to the leaves, flowers, and other parts.
We Can Eat Parts of Some Plants
- Many parts of plants, including leaves, roots, stems, and fruits, are safe and nutritious for humans to eat.
- However, it is important to only consume parts that are known to be safe and to avoid wild plants unless their safety has been confirmed.
Plants and Light

Plants Need the Right Conditions
Plants require specific conditions to grow and thrive, including the right amounts of:
- Warmth
- Water
- Light
- Air
A healthy plant has robust roots, stems, and leaves. In contrast, an unhealthy plant may exhibit yellowing leaves and wilting, which are indicators of poor health.
What Do Baby Plants Need?
- Flowers on plants produce seeds that contain a tiny root shoot, a stem shoot, and a food store to support early growth. The beginning of a seed’s growth is called germination.
- During germination, the root shoot is the first to grow, helping the seed absorb water, followed by the stem shoot, which grows upwards.
Plants Need Water and the Right Temperature
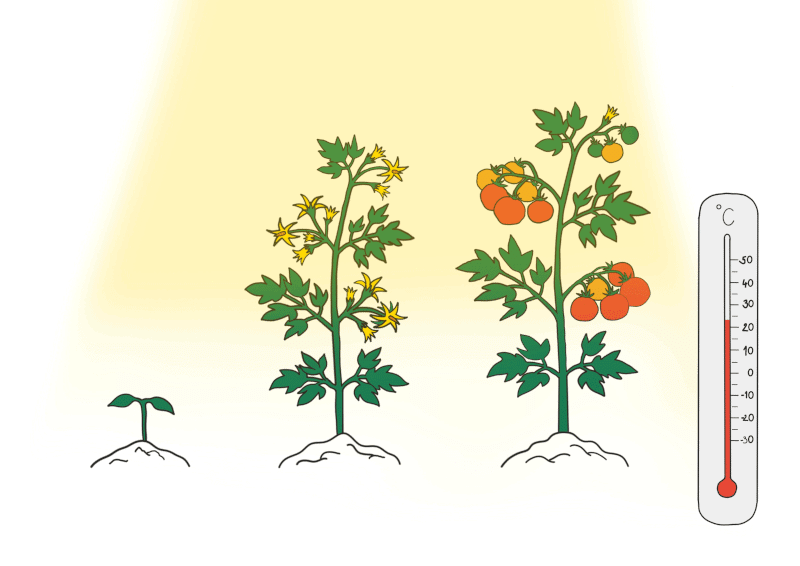
All Plants need water
- Every part of a plant requires water, which is absorbed by the roots from the soil. Water is then transported through the stem to the leaves and flowers.
- Leaves use water during photosynthesis to create food and release some water into the air through a process called transpiration. If plants do not receive enough water, they wilt and may die.
Plants need the right temperature
- In addition to water, plants need a suitable temperature to live and grow. Extreme heat or cold can be harmful or fatal to plants. In cold conditions, water can freeze, making it unavailable to plants, and leaves may not be able to produce food.
- In very hot conditions, plants may lose too much water, causing their roots, stems, and leaves to dry out and become damaged. Some plants are specially adapted to survive in cold environments, while others thrive in hot conditions.
Water Can Move Up Tall Trees
- Some trees can reach heights of over 80 metres, requiring water to be transported to their highest leaves.
- Water moves through narrow tubes within the main stem of the tree, distributing it to every leaf.
|
20 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Plants are Living Things Chapter Notes - Year 3 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What are the main characteristics that define living things, including plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants use light for growth and development? |  |
| 3. Why is water essential for plants? |  |
| 4. What temperature range is ideal for plant growth? |  |
| 5. How do plant parts contribute to their survival? |  |




















