3D Shapes | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
Introduction:
In this chapter, we will learn about 3D shapes, also known as three-dimensional shapes. These shapes have depth in addition to length and width. We will explore the characteristics of different 3D shapes, how to identify them, and how to describe their properties. By the end of this chapter, you'll be able to recognize 3D shapes around you and understand their features!
1. What are 3D Shapes?
- Definition of 3D Shapes:
3D shapes are solid objects that have three dimensions: length, width, and height. Unlike 2D shapes, which are flat, 3D shapes have volume and can be touched and held.
- Examples of 3D Shapes:
Common examples of 3D shapes include cubes, spheres, cones, pyramids, and cylinders. These shapes can be found in everyday objects, such as a box (cube), a ball (sphere), or a can (cylinder).
2. Types of 3D Shapes
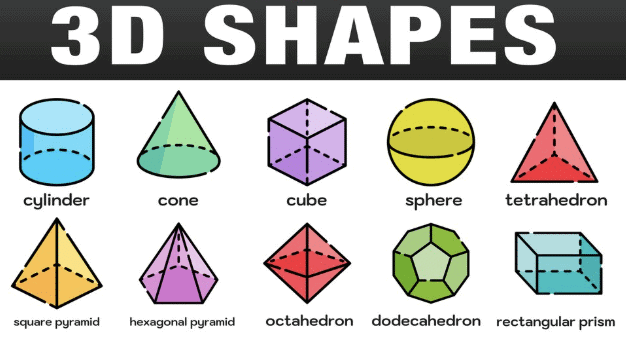
- Cube:
A cube has 6 square faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices. All the faces are the same size, and each angle between the faces is 90 degrees. You can think of a dice as a cube.
- Sphere:
A sphere has no edges or vertices. It is round and looks like a ball. A ball, a globe, or a marble is a sphere.
- Cylinder:
A cylinder has 2 circular faces and 1 curved surface. It looks like a can or a tube. It has 2 edges and 0 vertices.
- Cone:
A cone has a circular base and a single curved surface that comes to a point (called the apex). A party hat or an ice cream cone is shaped like a cone.
- Rectangular Prism:
A rectangular prism has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices, like a cube. However, its faces are rectangles, not squares. A shoebox or a brick is shaped like a rectangular prism.
- Square Pyramid:
A square pyramid has a square base and 4 triangular faces that meet at a point. A pyramid-shaped building or a tent can be examples of square pyramids.
- Triangular Prism:
A triangular prism has 2 triangular faces and 3 rectangular faces. It looks like a box with triangular ends. A roof of a house could be shaped like a triangular prism.
3. Properties of 3D Shapes
- Faces:
The flat surfaces of a 3D shape are called faces. For example, a cube has 6 square faces, while a sphere has 1 curved face.
- Edges:
An edge is a line where two faces meet. For example, a cube has 12 edges, while a sphere has no edges because it is round.
- Vertices:
A vertex (plural: vertices) is a point where edges meet. A cube has 8 vertices, and a sphere has no vertices since it is smooth.
4. Identifying 3D Shapes
- How to Identify a Cube:
A cube has 6 square faces that are all the same size. It has 12 edges and 8 vertices. It looks like a dice or a box.
- How to Identify a Sphere:
A sphere is completely round with no edges or vertices. It looks like a ball, a globe, or a marble.
- How to Identify a Cylinder:
A cylinder has 2 circular faces and 1 curved surface. It looks like a can or a tube.
- How to Identify a Cone:
A cone has 1 circular base and a single curved surface that ends in a point (apex). It looks like an ice cream cone or a party hat.
- How to Identify a Pyramid:
A pyramid has a polygonal base (like a square or triangle) and triangular faces that meet at a point. The base is flat, and the faces are slanted triangles.
5. Nets of 3D Shapes
- What is a Net?
A net is a two-dimensional shape that can be folded to make a 3D shape. It is like a flat version of the shape that can be folded to form the object.
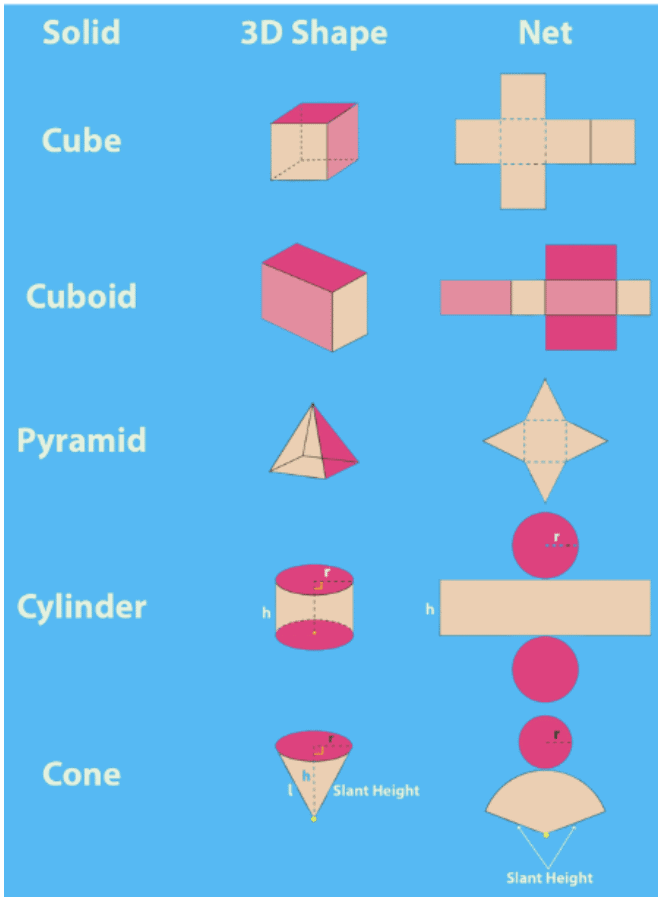
- Example of a Cube Net:
A cube net consists of 6 squares arranged in a certain way. When folded, they form a 3D cube. The squares are joined by edges and fold up to form the cube's faces.
- Example of a Cylinder Net:
A cylinder net consists of 2 circles for the top and bottom faces and a rectangle for the curved surface. When folded, the rectangle becomes the curved part of the cylinder.
- Why Are Nets Useful?
Nets are useful because they show us how to create 3D shapes from flat shapes. You can fold them to create real-life models of the 3D shapes you learn about.
6. Real-Life Examples of 3D Shapes

- Cube:
Examples of cubes in real life include dice, boxes, and certain ice cubes.
- Sphere:
Examples of spheres in real life include balls, marbles, and globes.
- Cylinder:
Examples of cylinders include cans, tubes, and bottles.
- Cone:
Examples of cones include party hats, ice cream cones, and traffic cones.
- Pyramid:
Examples of pyramids include Egyptian pyramids, tents, and certain roof designs.
7. Practice Questions:
- What is the difference between a cube and a rectangular prism?
- How many faces, edges, and vertices does a cone have?
- Can you think of any real-life objects that are shaped like a cylinder?
- Draw a net for a cube.
- What shape is the top of an ice cream cone?
|
65 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on 3D Shapes - Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What are 3D shapes? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of 3D shapes? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of 3D shapes? |  |
| 4. How can you identify 3D shapes? |  |
| 5. What are nets of 3D shapes? |  |
















