Angles and Movement | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
Introduction:
In this chapter, we will learn about angles and how they are formed. We will also explore how objects move in space, such as turning and rotating. By the end of this chapter, you will be able to recognize different types of angles, understand how to measure them, and understand basic movements like turning and rotating.
1. What is an Angle?
Definition of an Angle:
An angle is formed when two lines or rays meet at a point called the vertex. The space between these two lines or rays is called the angle.
Parts of an Angle:
An angle has two main parts:
- Vertex: The point where the two lines meet.
- Arms (or Sides): The two lines or rays that form the angle.
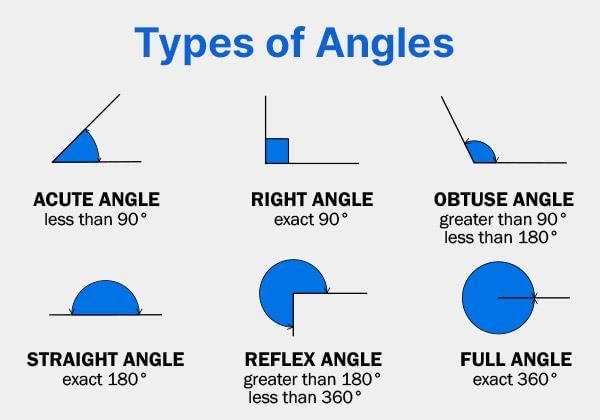
2. Types of Angles
- Acute Angle:
An acute angle is an angle that is less than 90 degrees. It looks sharp and small. For example, a 30-degree angle is acute.
- Right Angle:
A right angle is exactly 90 degrees. It is a perfect L-shape and is commonly seen in corners, like the corner of a square or rectangle.
- Obtuse Angle:
An obtuse angle is larger than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. It looks wide and open. For example, a 120-degree angle is obtuse.
- Reflex Angle:
A reflex angle is larger than 180 degrees but smaller than 360 degrees. It looks like an angle bent backwards. For example, a 270-degree angle is reflex.
 Angle Varieties
Angle Varieties
3. Measuring Angles
Using a Protractor:
A protractor is a tool used to measure angles. It has a scale marked in degrees. To measure an angle, place the protractor with its center at the vertex of the angle and line up one arm of the angle with the zero mark on the protractor. Then, read the number on the protractor where the other arm of the angle points.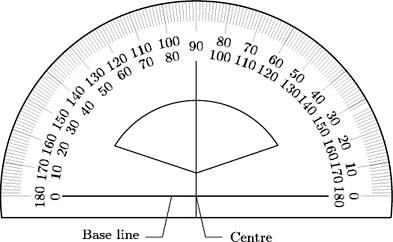 Angle Measurement
Angle Measurement
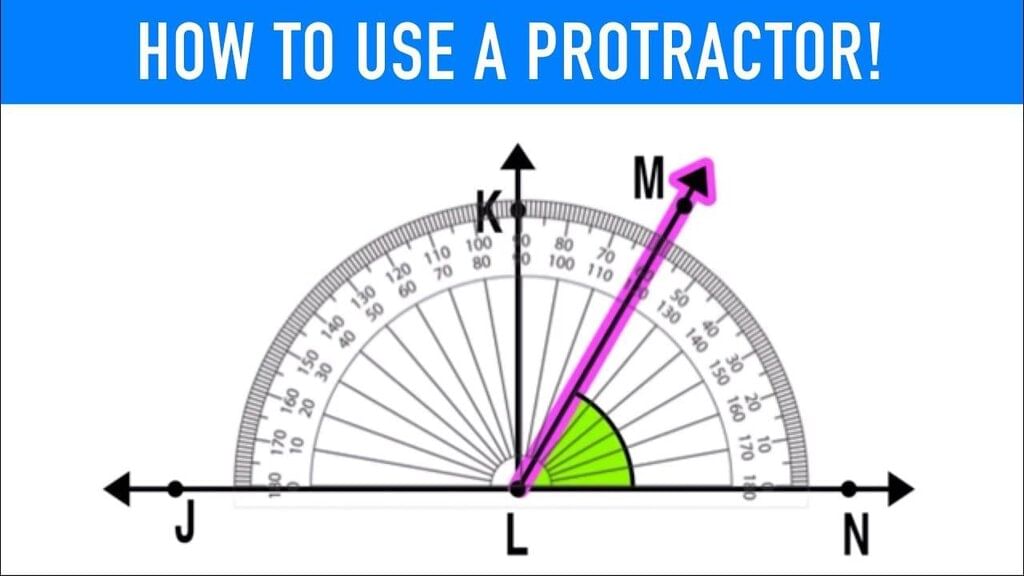
How to Measure an Angle:
To measure an angle, follow these steps:
- Place the protractor on the vertex of the angle.
- Align one side of the angle with the zero line of the protractor.
- Look where the other side of the angle points on the protractor scale to find the angle's measurement.
 Angle Measurement
Angle Measurement
4. Movement and Turning
- What is Movement?
Movement refers to how objects change their position. In this chapter, we focus on turning or rotating an object. Movement can be measured in angles.
- Turning and Rotation:
When something turns, it rotates around a point. The amount of turning is measured in degrees. For example, a complete turn around a point is 360 degrees.
- Quarter Turn:
A quarter turn is a 90-degree rotation. For example, if you turn your body to face a different direction, that’s a 90-degree turn.
- Half Turn:
A half turn is a 180-degree rotation. For example, if you turn around to face the opposite direction, that’s a 180-degree turn.
- Full Turn:
A full turn is a 360-degree rotation. If you complete a full circle and return to your starting point, you have made a 360-degree turn.
5. Rotating Shapes
How to Rotate a Shape:
When we rotate a shape, we turn it around a fixed point. The shape stays the same, but its position changes. For example, if you rotate a square 90 degrees, it will turn to face a different direction but still remain a square.
Clockwise and Anticlockwise Rotation:
Rotation can happen in two directions:
- Clockwise: This is the direction of a clock's hands. It is a turn to the right.
- Anticlockwise: This is the opposite direction of the clock’s hands. It is a turn to the left.
Rotating Shapes by 90, 180, and 270 Degrees:
When rotating shapes, we can turn them by different amounts. For example:
- A 90-degree clockwise rotation moves the shape one-quarter of a full turn.
- A 180-degree clockwise rotation turns the shape halfway around.
- A 270-degree clockwise rotation turns the shape three-quarters of a full turn.
6. Real-Life Applications of Angles and Movement
Angles in Everyday Life:
Angles are everywhere around us. For example:
- The corners of a book are right angles (90 degrees).
- The hands of a clock form angles as they move around the clock.
- The roof of a house often forms an acute or obtuse angle.
Movement in Sports:
Angles and movement are important in sports. For example, a basketball player makes turns when moving around the court, and the angle at which they shoot the ball can affect whether they score a basket.
Navigation and Direction:
In navigation, we use angles to determine direction. For example, a compass shows directions based on angles, like North, South, East, and West, which are all based on turning 90 degrees or 180 degrees.
7. Practice Questions:
- What is the angle between the hour hand and minute hand at 3:00?
- Draw and label an acute angle, right angle, obtuse angle, and reflex angle.
- Rotate the following shape 90 degrees clockwise. What is the new position of the shape?
- If a car turns 180 degrees, what type of turn has it made?
- What angle do you turn to face the opposite direction (a half-turn)?
|
65 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Angles and Movement - Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What is an angle and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of angles? |  |
| 3. How do we measure angles? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between movement and turning? |  |
| 5. Can you give examples of real-life applications of angles and movement? |  |




















