Time (2) | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| 1. Understanding Time |

|
| 2. Reading the Clock |

|
| 3. Digital Clocks |

|
| 4. Calculating Time |

|
| 5. Duration of Time |

|
| 6. Real-Life Uses of Time |

|
Introduction
In this chapter, we will learn how to tell time, use a clock, and understand different units of time such as hours, minutes, and seconds. Time is an important part of our daily lives, helping us stay organized and manage activities. By the end of this chapter, you will be able to read both digital and analog clocks, and solve problems involving time.
1. Understanding Time
What is Time?
Time helps us understand the order of events and how long things take. We use time to know when to do something and how long something lasts. Time is measured in units such as seconds, minutes, and hours.
Units of Time:
There are different units we use to measure time:
- Second (s): The smallest unit of time. There are 60 seconds in one minute.
- Minute (min): A minute has 60 seconds. There are 60 minutes in one hour.
- Hour (h): An hour has 60 minutes. There are 24 hours in a day.
2. Reading the Clock
- Analog Clock:
An analog clock has two hands: the hour hand (short hand) and the minute hand (long hand). The hour hand shows the current hour, and the minute hand shows the current minute.
Example: If the hour hand is pointing at 3 and the minute hand is pointing at 12, it is 3 o’clock.
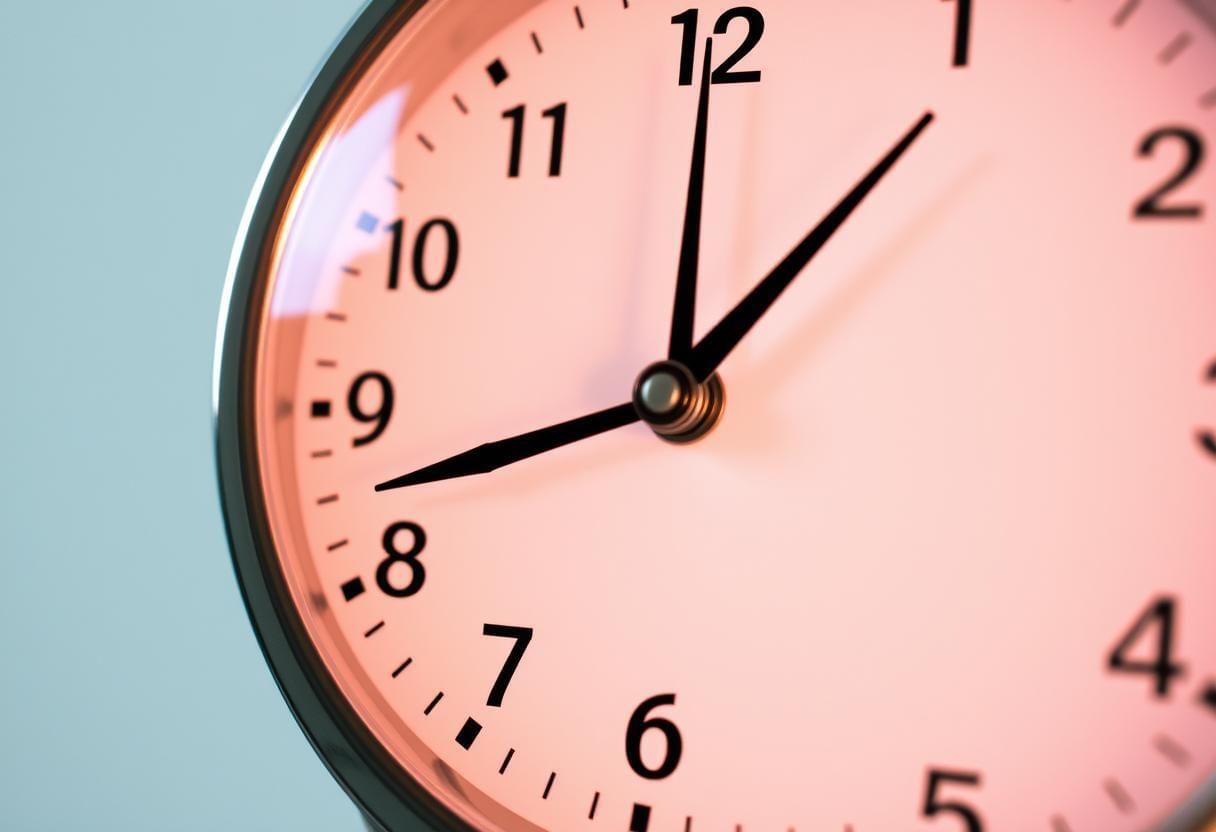

- Reading the Hour Hand:
The hour hand moves from one number to the next as the time passes. For example, if the time is 3:00, the hour hand will point to 3. As time goes on, the hour hand will move towards 4, but it will never reach 4 until it’s 4 o’clock.
- Reading the Minute Hand:
The minute hand shows the minutes. Each number on the clock represents 5 minutes. For example, if the minute hand is on 1, it means 5 minutes have passed. If it’s on 2, 10 minutes have passed, and so on.
- Half Past:
When the minute hand is on 6, it means half an hour (or 30 minutes) has passed. For example, if the time is 6:30, the hour hand will be halfway between 6 and 7.
3. Digital Clocks

Reading a Digital Clock:
A digital clock shows the time using numbers. For example, 3:15 means it is 3 hours and 15 minutes. The hours are shown first, followed by the minutes. A digital clock does not have hands like an analog clock.
12-Hour and 24-Hour Clocks:
Digital clocks can show time in two ways:
- 12-Hour Clock: This is the most common way to show time. It shows the time from 1 to 12, and then starts again at 1. For example, 3:00 PM means 3 o’clock in the afternoon.
- 24-Hour Clock: This clock shows time from 0 to 23. It’s commonly used in timetables. For example, 15:00 in a 24-hour clock is the same as 3:00 PM in a 12-hour clock.
4. Calculating Time
- Adding Time:
When we add time, we add the hours and minutes separately. For example, if the time is 2:30 and we add 1 hour and 20 minutes, we get:
2:30 + 1:20 = 3:50We added 1 hour to 2:30, making it 3:30, then we added 20 minutes to 3:30, making it 3:50.
- Subtracting Time:
When we subtract time, we subtract the hours and minutes separately. For example, if the time is 5:15 and we subtract 2 hours and 45 minutes, we get:
5:15 - 2:45 = 2:30We subtract 2 hours from 5:15, making it 3:15, then we subtract 45 minutes, making it 2:30.
5. Duration of Time
- What is Duration?
Duration refers to how long something lasts. We can find the duration by subtracting the start time from the end time. For example, if a movie starts at 1:00 and ends at 3:00, the duration is 2 hours.
- Finding the Duration:
Example: If a bus leaves at 9:30 and arrives at 11:15, we can calculate the duration by subtracting 9:30 from 11:15:
11:15 - 9:30 = 1 hour and 45 minutesThe bus journey lasts for 1 hour and 45 minutes.
6. Real-Life Uses of Time
- Using Time in Daily Life:
We use time every day to plan our activities, such as waking
 Time Management
Time Management
|
65 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Time (2) - Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What are the different ways to read a traditional analog clock? |  |
| 2. How do digital clocks display time differently from analog clocks? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of calculating time in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How can I measure the duration of time for an event? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life situations where understanding time is essential? |  |














