Patterns and symmetry | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
Introduction
Symmetry is an important idea in geometry. It is found in nature and used in many fields like art, fashion, car design, and architecture. You can see symmetry in beehives, flowers, leaves, rugs, and even religious symbols.
A shape has line symmetry if it can be folded along a line so that both sides match perfectly. This is like a mirror reflection. 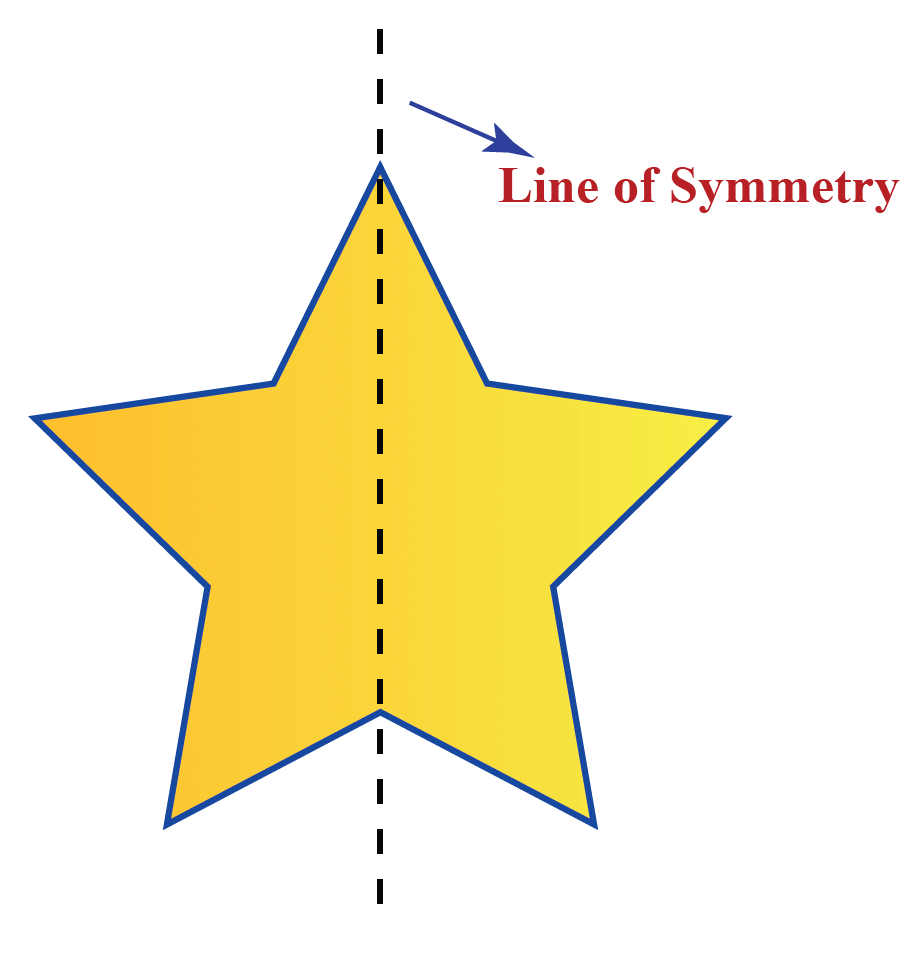
Symmetry is important because it is common in daily life and helps create beautiful designs.
Line of Symmetry
If you fold a shape and the two halves do not match, is it a line of symmetry?
No, it is not a line of symmetry.
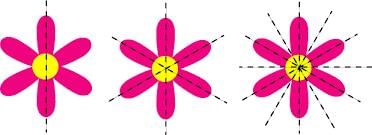
When we fold a shape along a certain line and both halves match exactly, that line is called a line of symmetry.
For example, in a blue triangle, if we draw a dotted line down the middle and fold it, the two sides cover each other perfectly. This shows that the dotted line is a line of symmetry for the triangle.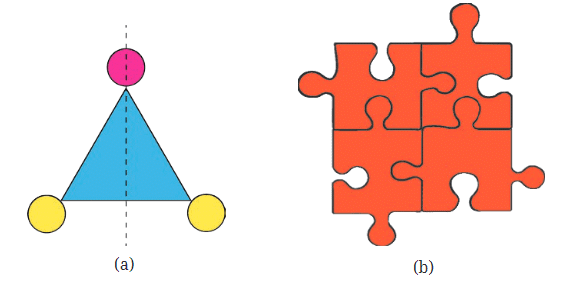
However, if we look at a shape like four puzzle pieces with a dotted line through the middle, folding it would not make the two sides match perfectly. This means that the line is not a line of symmetry for that shape.
Figures with more than one line of symmetry
Some shapes have multiple lines of symmetry:
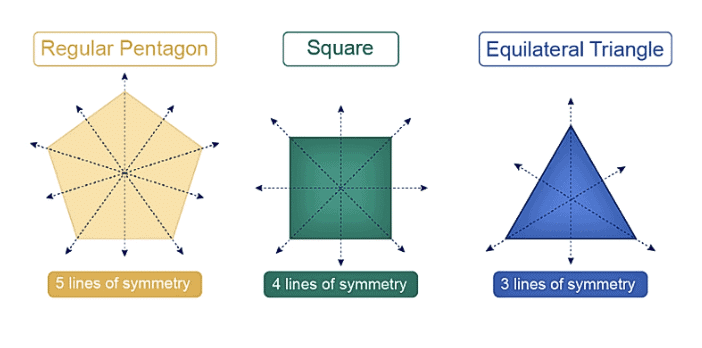
- A square has four lines of symmetry.
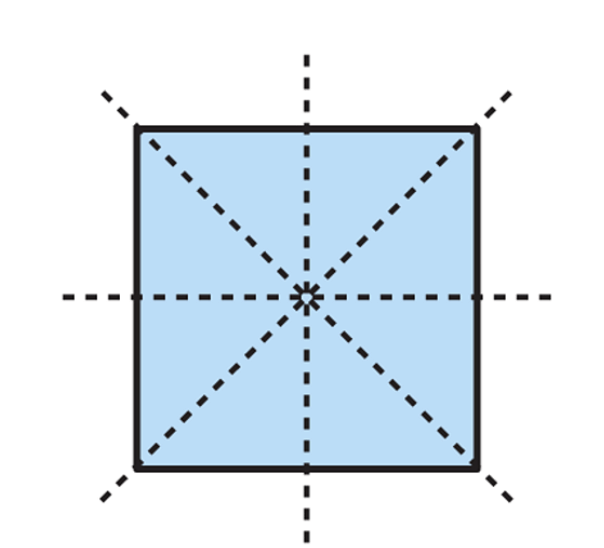
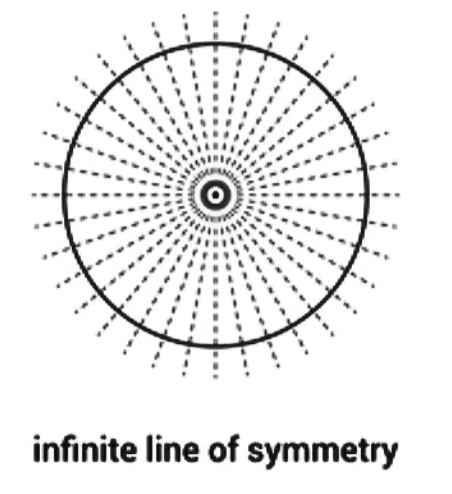
- A circle has infinite lines of symmetry.
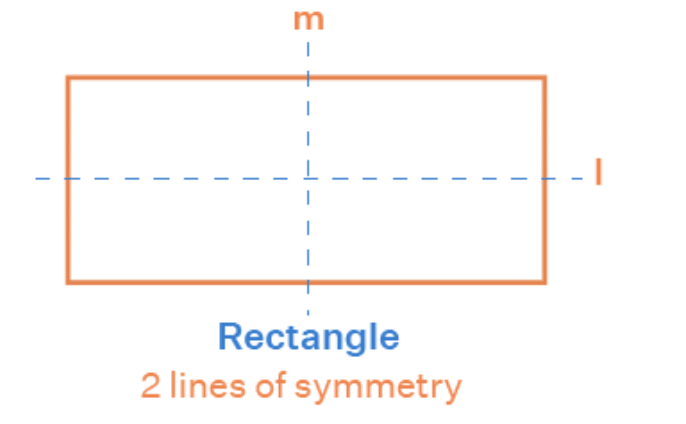
- A rectangle has two lines of symmetry (one vertical and one horizontal).
- A regular polygon has as many lines of symmetry as it has sides.A shape has line symmetry when one half is a mirror image of the other.
Reflection
When a shape has a line of symmetry, one part of the shape is a mirror image of the other. This is called reflection symmetry. It’s like looking at yourself in a mirror—what you see is a reflection of your real self.
Example: Butterfly: Its left wing is a mirror image of its right wing.
Creating Shapes with Line Symmetry
Creating symmetrical shapes is a fun and creative way to explore the concept of symmetry. There are several methods to generate such shapes, and two popular techniques are using ink blots and paper folding and cutting. Let's explore how these methods work.
1. Ink Blot Devils: This is a simple and exciting method to create symmetrical shapes using ink or paint.
Steps:
- Fold a Paper: Take a clean sheet of paper and fold it in half.

- Apply Ink or Paint: Open the paper and put a few drops of ink or paint on one half of the paper.
- Press and Open: Fold the paper back and press it so that the ink spreads. Then, carefully open the paper to reveal the design.
2. Paper Folding and Cutting: Another way to create symmetrical designs is by folding and cutting paper. This technique can produce intricate and beautiful patterns.
Steps:
- Fold the Paper: Take a sheet of paper and fold it along the dotted line (this line can be any straight line across the paper).
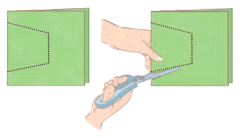
- Cut Along the Fold: While the paper is folded, cut along the dotted line as shown in the figure.
- Unfold to Reveal: After cutting, carefully unfold the paper to reveal the pattern.
[Question: 1767684]
Symmetries of a Circle
A circle is a special shape because it has infinite lines of symmetry. Specifically, every line that goes through the centre (every diameter) creates a line of reflectional symmetry. The circle is the most perfect symmetrical shape because it can be rotated around its centre by any angle, and it also has an unlimited number of lines of symmetry. If you look at any circular pattern, you'll see that every line through the centre acts as a line of reflectional symmetry, and it maintains its shape when rotated around the centre at any angle.
Example: Wheel: No matter how you turn it, it always looks the same.
|
65 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Patterns and symmetry - Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What is a line of symmetry? |  |
| 2. How can I identify if a shape has line symmetry? |  |
| 3. Can you give examples of shapes that have line symmetry? |  |
| 4. How do I create a shape with line symmetry? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding line symmetry important in patterns? |  |
















