UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) > Mind Map: Rural and Agrarian Social Structure
Mind Map: Rural and Agrarian Social Structure | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
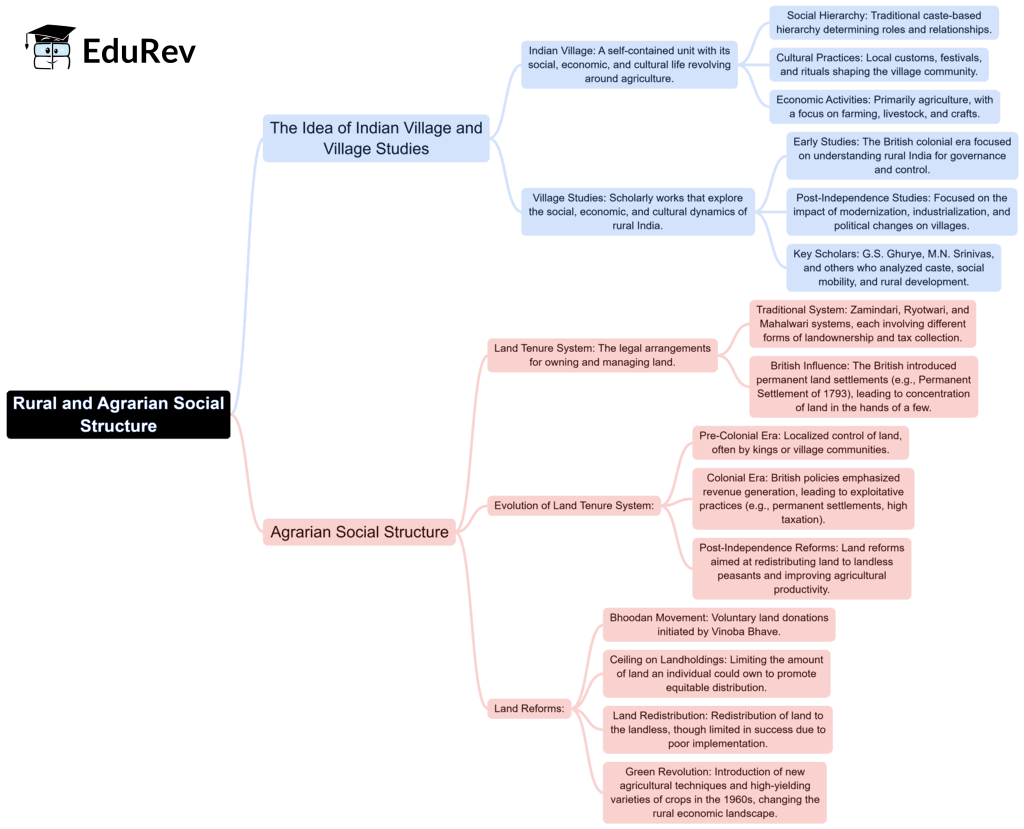
The document Mind Map: Rural and Agrarian Social Structure | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
112 videos|389 docs
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Rural and Agrarian Social Structure - Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What is the significance of rural and agrarian social structures in India? |  |
Ans. Rural and agrarian social structures are crucial in India as they form the backbone of the economy and social fabric. They dictate land ownership patterns, agricultural practices, and community interactions. Understanding these structures helps in addressing issues like poverty, unemployment, and social inequality, which are prevalent in rural areas.
| 2. How do caste and class influence rural social structures? |  |
Ans. Caste and class significantly influence rural social structures by determining social hierarchies, access to resources, and occupational roles. The caste system can limit social mobility and access to education or employment opportunities, while class distinctions often affect wealth distribution and power dynamics within the community.
| 3. What are the main challenges faced by the rural agrarian community? |  |
Ans. The rural agrarian community faces several challenges, including lack of access to modern technology, inadequate irrigation facilities, fluctuating market prices, and climate change impacts. Additionally, social issues like caste discrimination and limited access to education and healthcare further exacerbate their struggles.
| 4. How does land tenure affect agrarian social structure? |  |
Ans. Land tenure significantly impacts agrarian social structure by influencing land ownership patterns and agricultural productivity. Secure land tenure encourages investment in land improvements and sustainable practices, while insecure tenure can lead to land disputes and reduced agricultural output, affecting the livelihoods of rural communities.
| 5. What role does migration play in rural and agrarian social structures? |  |
Ans. Migration, both seasonal and permanent, plays a vital role in shaping rural and agrarian social structures. It often serves as a coping mechanism for economic distress, leading to changes in family dynamics and social relationships. Migration can also result in remittances that support local economies but may contribute to labor shortages in agriculture.
Related Searches




















