UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 2nd May 2025
The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 2nd May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

Reviving a Far-Sighted but Forgotten Bill Mechanism
Why in News?
- Private Member’s Bills (PMBs) in Parliament are facing challenges, leading to a decline in their relevance and impact.
- Historically significant, PMBs now struggle due to disruptions, institutional neglect, and the dominance of government business.
What Are Private Member’s Bills (PMBs)?
- PMBs are proposed by Members of Parliament (MPs) who are not part of the government.
- Traditionally, Fridays in Parliament are set aside for discussing PMBs.
- These bills aim to allow individual MPs to suggest new laws, showcasing their independent ideas and addressing concerns from their constituents.
Sharp Decline in PMB Relevance
- Since India’s Independence, a mere 14 PMBs have successfully become law.
- Notably, none have been approved by both Houses of Parliament since 1970.
- Recent Trends: In the 17th Lok Sabha (2019–24), there were 729 PMBs in Lok Sabha and 705 in Rajya Sabha. However, only 2 PMBs were discussed in Lok Sabha, and 14 in Rajya Sabha. In the 18th Lok Sabha, only 20 MPs have introduced PMBs, and none of the 64 PMBs introduced during the Budget Session 2024 were debated.
Causes of Decline:
- Frequent disruptions during sessions and early adjournments.
- Fridays are often used for general discussions or government business instead of PMBs.
- There is no dedicated mechanism to prioritize or support PMBs.
PMBs: An Avenue for Innovation and Reform
- Despite low passage rates, certain PMBs have had a significant impact.
- For instance, the Right to Disconnect Bill (2019) by Supriya Sule sparked national discussions on mental health and digital labor rights.
- Similarly, the Transgender Persons Bill (2014) by Tiruchi Siva was passed in the Rajya Sabha and later became the foundation for the 2019 legislation.
- PMBs introduced by MPs from the ruling party also reflect responsiveness to local constituency issues.
Shrinking Space for Legislative Autonomy
- The Anti-Defection Law, enacted through the 52nd Constitutional Amendment, restricts MPs’ ability to stray from party lines.
- Within this constrained framework, PMBs provide a democratic avenue for independent representation.
- MPs are not merely representatives of their parties; they are elected voices of the people, and PMBs allow them to express this autonomy.
Key Reforms to Reinvigorate PMBs
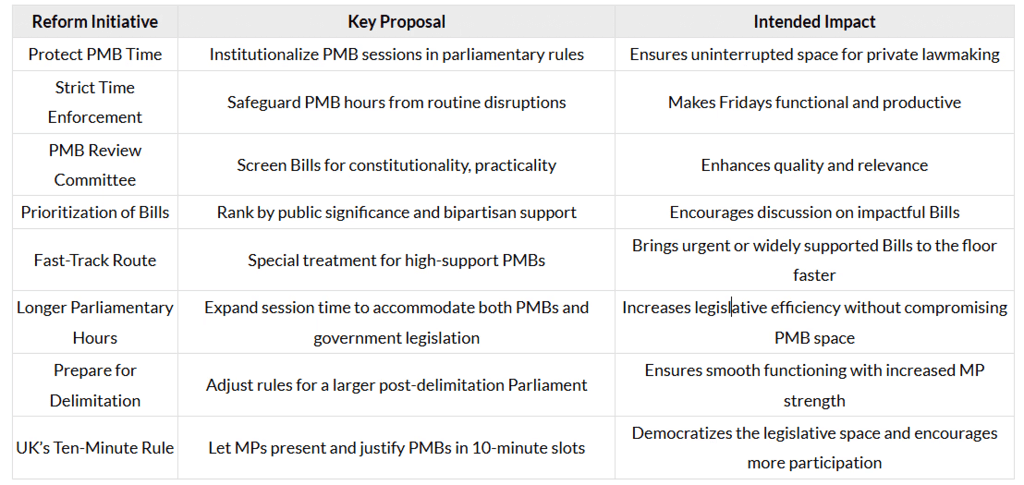
Conclusion
Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar recently described PMBs as “forward-looking” and a “gold mine” for lawmaking. To strengthen this mechanism, it is crucial to implement procedural reforms and recommit to participatory democracy.
China’s Strategic Push — Asia Ties Amid Tariff Tensions

Why in News?
- President Xi Jinping’s recent tour of Vietnam, Malaysia, and Cambodia is a strategic move by China to strengthen its economic ties and counter rising U.S. tariffs in Southeast Asia.
- During his visit from April 14 to 18, 2025, Xi aimed to reposition China as a reliable economic partner in the region amidst growing tensions with the U.S.
Southeast Asia as a Geopolitical Buffer
- China is responding to significant tariff impacts imposed by the U.S. on Southeast Asian nations, with tariffs reaching up to 59% for Cambodia, 46% for Vietnam, and 24% for Malaysia.
- In Cambodia, China is asserting its role as the top investor and trade partner, while in Vietnam, China signed 45 cooperation agreements.
- In Malaysia, over 30 deals were made in areas such as AI, digital economy, and agriculture.
Signature Projects and Agreements
- During Xi’s visit, notable projects and agreements were highlighted, such as the Funan Techo Canal in Cambodia, which exemplifies China’s infrastructure diplomacy in the region.
- The agreements signed during this tour span various sectors, including the digital economy, artificial intelligence, infrastructure development, and agriculture.
- Trade between China and Cambodia has seen significant growth, surpassing $15 billion in 2024, reflecting the deepening economic ties between the two nations.
Strategic Messaging Against the U.S.
- Xi’s diplomacy aims to contrast China’s cooperative approach with the U.S. strategy, which is perceived as more interventionist.
- China emphasizes non-interference and tangible economic cooperation through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and trade deals.
- In contrast, the U.S. focuses on security arrangements, such as AUKUS and the Quad.
- China’s soft power strategy includes promoting a Code of Conduct in the South China Sea and cultural diplomacy, while the U.S. engages episodically and reactively.
- China offers clear incentives for market access and bilateral trade boosts, whereas the U.S. Indo-Pacific Economic Framework lacks similar market access guarantees.
Intra-ASEAN Diplomacy and Regional Balancing
- Xi’s tour also aimed to reassure ASEAN nations, particularly Vietnam, regarding South China Sea disputes and promote peaceful resolutions and BRI collaboration in Malaysia.
- In Cambodia, Xi reinforced China’s status as a core ally.
- This tour not only boosts China’s standing within ASEAN but also has the potential to create divisions in regional consensus regarding alignment with the U.S.
Wider Strategic Implications
- China’s efforts undermine U.S. coalition-building in the Indo-Pacific, enhancing its role in regional rule-making and economic integration.
- By positioning itself as an indispensable partner amid global economic uncertainties, China raises questions about ASEAN’s capacity to balance relations between the two superpowers.
Domestic and Global Message
- Domestically, the tour bolsters Xi Jinping’s political credibility, countering narratives of China’s diplomatic isolation or slowdown.
- Globally, it signals to the Global South that China remains open for business and partnership, even as Western criticisms grow.
The document The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 2nd May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 2nd May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of China's strategic push for ties in Asia amid tariff tensions? |  |
Ans. China's strategic push for ties in Asia is significant as it aims to strengthen economic and political relationships in the region, particularly in the context of increasing tariff tensions with other major economies. This initiative may help China to bolster trade partnerships, enhance regional stability, and counteract any economic isolation resulting from tariffs imposed by countries like the United States.
| 2. How do tariff tensions affect international trade relationships in Asia? |  |
Ans. Tariff tensions can create friction in international trade relationships, leading to increased costs for businesses and consumers. In Asia, these tensions may prompt countries to seek alternative trade partnerships, diversify their supply chains, and enhance regional cooperation to mitigate the impact of tariffs, ultimately reshaping trade dynamics in the region.
| 3. What mechanisms can be revived or implemented to improve trade relations in Asia? |  |
Ans. To improve trade relations in Asia, mechanisms such as free trade agreements, regional trade blocs, and collaborative economic initiatives can be revived or implemented. These mechanisms aim to reduce trade barriers, promote investment, and facilitate smoother trade flows among Asian countries, fostering economic growth and cooperation.
| 4. What role do countries in Asia play in counterbalancing global economic powers? |  |
Ans. Countries in Asia play a crucial role in counterbalancing global economic powers by forming strategic alliances and trade networks. By working together, Asian nations can enhance their collective bargaining power, promote regional integration, and establish themselves as significant players in the global economy, thus influencing international trade policies and dynamics.
| 5. How can Asian countries benefit from strengthening ties amidst global economic challenges? |  |
Ans. Asian countries can benefit from strengthening ties amidst global economic challenges by enhancing trade, attracting foreign investment, and sharing resources and technology. Collaborative efforts can lead to increased resilience against economic shocks, improved competitiveness, and a unified approach to addressing common challenges, ultimately contributing to sustainable regional growth and stability.
Related Searches
















