Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 30th April 2025) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
HKH Snow Update Report 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Kathmandu-based International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) has released the HKH Snow Update Report 2025, highlighting alarming declines in snow persistence across the three major river basins of the Indian Subcontinent. This trend poses significant risks to water security for millions, underscoring the urgent need for effective water management strategies.
Key Takeaways
- All three major river basins (Ganga, Indus, Brahmaputra) are experiencing severe reductions in snow persistence.
- Recent data shows the Ganga basin at its lowest snow persistence in 23 years, indicating a worrying trend.
- Almost 300 million people face risks to water supply due to reduced snowmelt.
Additional Details
- Snow Persistence: This term refers to how long snow remains on the ground after a snowfall, which is crucial for seasonal water supply, especially during early summer months. The HKH region's water resources heavily depend on snowmelt.
- In the Ganga basin, snow persistence has fallen to -24.1%, while the Indus and Brahmaputra basins both show declines of -27.9%. This pattern signifies a critical loss of snow cover.
- The Tibetan Plateau has seen a drastic decrease in snow persistence from +92.4% in 2022 to -29.1% in 2025, highlighting the region's climate sensitivity.
- The ongoing trend of below-normal snow conditions for three consecutive years could lead to long-term water stress, especially for communities already dealing with heatwaves.
The report emphasizes the necessity for improved water management practices, enhanced drought preparedness, and better early warning systems. It calls for scientific, forward-looking policies and regional cooperation to effectively manage transboundary water issues. Historical data shows fluctuations in snow persistence over the past two decades, with the highest recorded level in the Ganga basin at +30.2% in 2015, illustrating the urgent need for adaptive strategies in response to climate change.
Davis Strait Proto-Microcontinent
Why in News?
- Recently, a significant geological discovery was made beneath the icy waters of the Davis Strait, which separates Canada’s Baffin Island from Greenland. Scientists from the UK and Sweden have identified a previously hidden landmass dubbed the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent. This ancient crustal fragment is thought to be a remnant of the tectonic activities that transpired millions of years ago when Greenland and North America began drifting apart.
Key Takeaways
- The Davis Strait proto-microcontinent is submerged under Greenland’s western offshore waters.
- This landmass features unusually thick continental crust, measuring between 12 and 15 miles (approximately 19 to 24 kilometers).
- Researchers employed satellite gravity data and seismic readings to uncover this hidden geological structure.
Additional Details
- Tectonic History: The tectonic evolution in the Davis Strait commenced about 120 million years ago with the separation of Greenland and North America. This drift accelerated approximately 61 million years ago, leading to the formation of the seafloor in the Davis Strait.
- Formation of the Microcontinent: Changes in tectonic activity around 56 million years ago resulted in the emergence of the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent. Notably, a geological event around 48 million years ago nearly led to the rifting of the North American plate but was halted by the emergence of a new fault.
- The Davis Strait spans approximately 400 miles (650 km) from north to south, with widths varying between 200 to 400 miles, serving as a crucial link between Baffin Bay and the Labrador Sea.
The discovery of the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent significantly enriches our understanding of the geological history of the region. It offers essential insights into the tectonic processes that have shaped the North Atlantic and the dynamics of continental drift. This finding may also have profound implications for future geological studies and environmental assessments in the Arctic region.
Standing Deposit Facility (SDF)

Why in News?
The Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) has gained importance as a key tool for the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in managing liquidity within the banking system. Introduced on April 8, 2022, the SDF allows banks to deposit surplus funds with the RBI without the need for collateral. This mechanism has evolved to meet the challenges faced during periods of high liquidity and has seen increased usage in recent months.
Key Takeaways
- The SDF serves as a liquidity absorption tool.
- It replaces the reverse repo rate as the lower bound of the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) corridor.
- Recent trends indicate a rise in banks utilizing the SDF for surplus funds.
Additional Details
- Purpose of the SDF: The SDF is designed to allow banks to park excess funds while earning interest, particularly during times of surplus liquidity when traditional methods may require collateral in the form of government securities.
- Recent Utilisation Trends: Banks have recently deposited an average of ₹2.13 trillion under the SDF, an increase from ₹1.12 trillion in February, indicating a growing demand for precautionary funds.
- Impact on Banking Operations: The introduction of the SDF has changed how banks manage liquidity, as they prefer holding larger balances under the SDF instead of utilizing the variable rate reverse repo (VRRR) to meet immediate liquidity needs.
- SDF Rate and LAF Corridor: The SDF rate is set at 25 basis points below the policy repo rate, with the marginal standing facility (MSF) rate set 25 basis points above, restoring the LAF corridor to its pre-pandemic width of 50 basis points.
- Flexibility in Accessing SDF: Access to the SDF and MSF is discretionary for banks, providing them with the flexibility to respond dynamically to liquidity needs, unlike more regulated tools such as the cash reserve ratio.
In conclusion, the Standing Deposit Facility has emerged as a critical component in the RBI's toolkit for liquidity management. Its introduction and the recent trends in its usage reflect the evolving landscape of banking liquidity and the necessity for flexible instruments in the financial system.
Shenzhou-20 Mission
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On April 24, 2025, China is set to launch the Shenzhou-20 mission, which will transport three astronauts to the Tiangong space station. This launch coincides with China's 10th Space Day, celebrating its advancements in space exploration. The crew will take over from the Shenzhou-19 astronauts, who will return to Earth shortly after the launch.
Key Takeaways
- The Shenzhou-20 mission is aimed at rotating the crew in orbit.
- Astronauts will conduct scientific experiments and install a space debris protection device.
- Life science research will include studies on zebrafish, planarians, and streptomyces.
Additional Details
- Significance of Space Day: April 24 marks China's Space Day, commemorating the launch of its first satellite, Dongfanghong-1, in 1970. This day symbolizes China's dedication to enhancing its space program and fostering public interest in space exploration.
- Future of China’s Space Programme: Shenzhou-20 is the 35th mission in China’s manned space program. The Tiangong space station is anticipated to be the only operational space station once the International Space Station (ISS) is retired, as China continues to develop its space capabilities.
- International Relations and Collaborations: China's space endeavors have raised global concerns about military applications. Collaborations with Pakistan and future participation from astronauts from Hong Kong and Macau aim to enhance scientific research and promote international cooperation in space.
Tiangong Space Station
- Meaning: "Tiangong" translates to "Heavenly Palace" in Chinese.
- Overview: It is China's first modular space station, developed by the China National Space Administration (CNSA), operational since 2021 and expected to run until 2028.
- Structure:The station consists of three modules:
- Tianhe: Core module launched in April 2021.
- Wentian and Mengtian: Lab modules launched in 2022.
- Tiangong is smaller than the ISS, which has 16 modules, but is equipped with independent power, propulsion, life support, and living facilities.
- It will share orbit with the upcoming Xuntian space telescope, allowing astronauts to maintain and upgrade the telescope easily.
- China is the third country, after the USA and Russia, to send humans to space and to build its own space station.
The Shenzhou-20 mission represents a significant milestone in China's ongoing efforts in space exploration, emphasizing international collaborations and advancements in scientific research.
Climate Tipping Points
 Why in News?
Why in News?
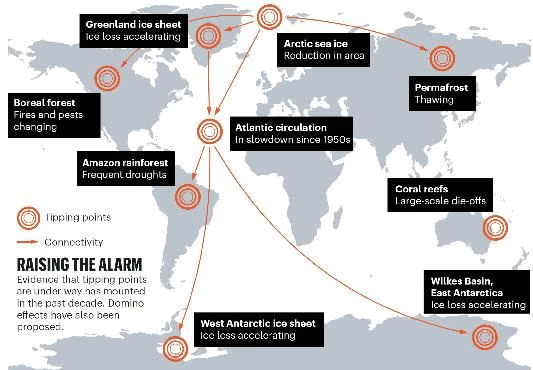
- Recent studies have revealed a concerning 62% risk of triggering critical climate tipping points if the current global emission policies remain unchanged. These tipping points encompass significant events such as the collapse of ice sheets and the decline of coral reefs. Research conducted by the universities of Exeter and Hamburg analyzed 16 essential areas within the Earth's system, underscoring the urgency to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to prevent irreversible harm to both ecosystems and human societies. The findings also indicate that adopting more sustainable practices could decrease this risk to 37%.
Key Takeaways
- 62% risk of triggering climate tipping points due to ongoing emissions.
- Immediate action can reduce this risk to 37%.
- Critical areas affected include the Amazon rainforest and coral reefs.
Additional Details
- Climate Tipping Point: This term describes a crucial threshold where small changes can lead to significant and often irreversible shifts in the climate system. Examples include the melting of polar ice caps and the degradation of coral reefs.
- The recent study evaluated various emission scenarios—low, medium, and high—revealing a 62% average risk of triggering tipping points, with the Amazon rainforest facing a 53% chance of reaching its tipping point.
- Greenhouse gas emissions are responsible for trapping heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming, which accelerates ice sheet melting and ecosystem degradation.
- The urgency for global climate action is paramount, with the study highlighting that the risks associated with crossing tipping points are imminent and will be determined in the next few decades.
This research emphasizes the necessity for immediate global climate action and advocates for rapid policy changes aimed at significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The potential for mitigation through swift actions presents a hopeful path toward preserving the planet's future.
Surrogacy Law for Unmarried Women
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Bombay High Court has recently directed a 38-year-old divorced woman to seek a ruling from the Supreme Court regarding the legality of surrogacy for single women. The court deemed her application invalid under Section 4 of the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, which prohibits surrogacy for individuals who have surviving children. The court expressed concerns that granting temporary permission could have broader implications and may commercialize surrogacy.
Key Takeaways
- The High Court's ruling affects the rights of unmarried women seeking surrogacy.
- The Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, restricts surrogacy based on certain criteria.
- Concerns about the commercialisation of surrogacy were raised during the court proceedings.
Additional Details
- What is Surrogacy? Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman, known as a surrogate, carries a child for another individual or couple. The surrogate may or may not be genetically related to the child, depending on the type of surrogacy. The primary aim is to assist those who are unable to conceive.
- Types of Surrogacy:There are two main types of surrogacy:
- Altruistic Surrogacy: Involves no financial compensation beyond necessary medical expenses.
- Commercial Surrogacy: Involves payment beyond medical costs and is prohibited under the 2021 Act to prevent exploitation.
- Eligibility Criteria: According to the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, intended parents must be a legally married couple with a medical need for surrogacy. The woman must be aged between 25 and 50, and the man between 26 and 55. Importantly, they cannot have any living children.
- The High Court has voiced apprehensions regarding the implications of allowing unmarried individuals to pursue surrogacy, highlighting potential legal and ethical complexities in parental rights and child welfare.
This ruling underscores the ongoing debates surrounding surrogacy laws, particularly the rights of unmarried women. The outcome at the Supreme Court may significantly influence future policies and the legal landscape of surrogacy in India.
India’s 5-Point Action Plan Post Pahalgam Terror Attack
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The recent terrorist attack in Pahalgam has resulted in the tragic loss of 26 lives, including that of a foreign national. This incident has been linked to militant groups operating from Pakistan, prompting India to take significant retaliatory measures. In light of the situation, the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) convened to formulate a robust five-point action plan aimed at addressing Pakistan's diplomatic and military presence.
Key Takeaways
- The CCS is India’s top decision-making body focused on national security matters.
- Significant actions include the suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty and the closure of the Attari-Wagah border.
- All Pakistani military advisors in India have been declared persona non grata.
- The Indian High Commission in Pakistan will reduce its staff significantly.
Additional Details
- Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS): This committee, chaired by the Prime Minister, includes key ministers such as those from Defence, Home Affairs, Finance, and External Affairs. It plays a crucial role in discussing national security issues and making decisions on defence expenditures and security appointments.
- Historical Context: CCS meetings have been pivotal during critical events in India’s history, such as during the Kargil conflict and the IC 814 hijacking.
- Current Security Operations: In the aftermath of the attack, Indian security forces have initiated operations to apprehend the attackers, believed to consist of a group of seven terrorists, including individuals from Pakistan.
In summary, the Indian government has taken decisive steps in response to the Pahalgam terror attack, signaling a strong stance against terrorism and its cross-border implications. The actions outlined in the five-point plan reflect a commitment to national security and the safety of its citizens.
M4 Carbine Assault Rifles

Why in News?
- Recent incidents in Kashmir have highlighted the alarming trend of terrorists utilizing M4 carbine assault rifles, raising significant security concerns in the region. A recent attack in Pahalgam, where assailants armed with M4 carbines and AK-47s targeted tourists, has drawn attention to the origins and implications of these American-made weapons.
Key Takeaways
- The M4 carbine is a lightweight, gas-operated firearm, serving as a shorter and lighter variant of the M16A2 rifle.
- Since its introduction into military service in 1994, the M4 has become a preferred choice for modern military operations due to its versatility.
- Over 60 countries have adopted the M4 carbine, contributing to its widespread use.
Additional Details
- M4 Carbine Specifications: The M4 can fire between 700 and 950 rounds per minute, with an effective range of 500 to 600 meters and a maximum range of 3,600 meters, making it suitable for various military engagements.
- The global proliferation of the M4 raises concerns, especially regarding its acquisition by terrorist groups through black markets, particularly following the Taliban's takeover of Afghanistan in 2021.
- Indian intelligence agencies have reported that groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba have been procuring M4 carbines, with potential support from Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), which poses strategic implications for India's security.
The emergence of advanced weaponry, such as the M4 carbine, in the hands of terrorist groups indicates a troubling shift towards more sophisticated and lethal attacks in Jammu and Kashmir. This underscores the urgent need for enhanced security measures and international cooperation to address the challenges posed by the proliferation of such weapons.
Krishna River Faces Severe Drought Issues
 Why in News?
Why in News?
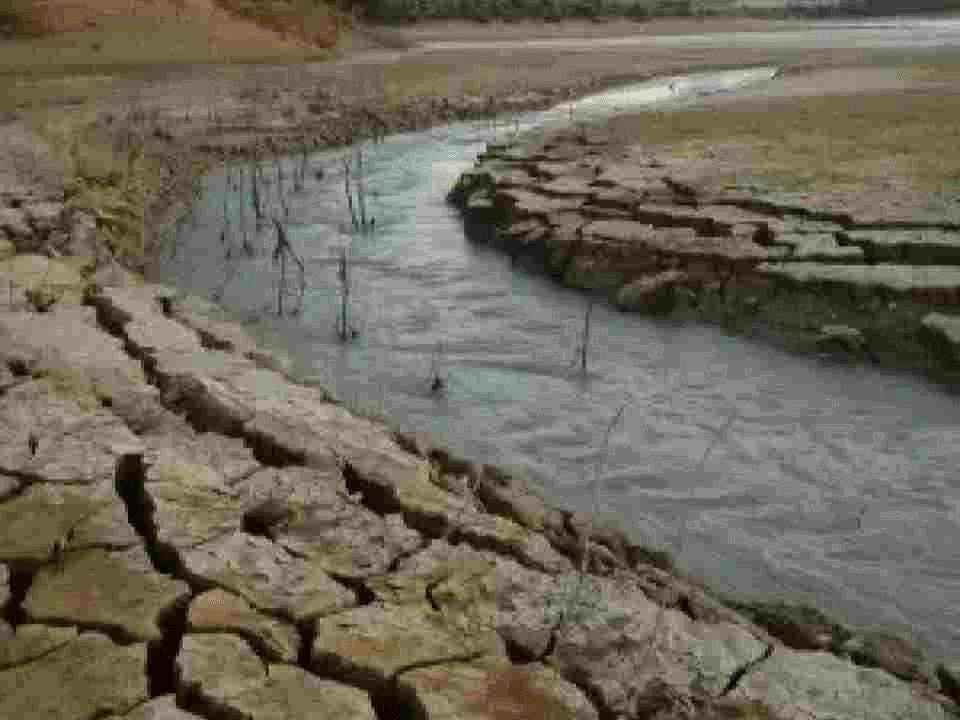
- Recent reports highlight alarming drought conditions affecting the Krishna River, a crucial water source for northern Karnataka. The river is drying up earlier than expected, which is severely impacting both agriculture and the drinking water supply in the region. These conditions have led to urgent requests for water releases from neighboring Maharashtra.
Key Takeaways
- The Krishna River spans approximately 1,400 kilometers and supports agriculture and ecosystems in western and southern India.
- Drought conditions are particularly severe in Kalyan Karnataka, leading to significant agricultural losses.
- Karnataka's Chief Minister has sought assistance from Maharashtra for water to alleviate the crisis.
Additional Details
- Importance of the Krishna River: This river is vital for agriculture, with 75.86% of its basin area cultivated, highlighting its role in food production.
- Drought Conditions: The river's drying up in April has devastated crop yields, while government-provided drinking water is insufficient to address the agricultural crisis.
- Government Responses: Chief Minister Siddaramaiah has requested the release of 2 tmcft from the Koyana and 1 tmcft from the Varana reservoirs, but Maharashtra has not yet responded.
- Historical Water Agreements: A water-sharing agreement established in 2004 has faced implementation challenges, including delays and rising costs.
- Ecological Challenges: The river contributes to soil erosion during monsoon seasons, placing its delicate ecosystem at risk and affecting biodiversity.
- Future Prospects: Climate change is expected to worsen water scarcity issues, making sustainable management and inter-state cooperation crucial for the river's health.
The situation regarding the Krishna River underscores the critical need for effective water resource management and collaboration between states to ensure the sustainability of this vital waterway and the communities that depend on it.
Tropical Forest Forever Facility (TFFF)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- In 2023, the Brazilian government launched the Tropical Forest Forever Facility (TFFF) at the COP28 climate summit in Dubai. This initiative aims to provide financial incentives for tropical nations to conserve their forests, employing satellite monitoring to evaluate forest preservation and reward countries based on their performance.
Key Takeaways
- The TFFF is designed to incentivize forest conservation and restoration on a large scale.
- Brazil, Indonesia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo are key participants, collectively hosting about 52% of the world's rainforests.
- The initiative's dual versions are expected to be launched around COP30 in Belem, Brazil.
Additional Details
- Financial Model: The TFFF offers a fixed payment per hectare of forest annually, aiming to generate $4 billion each year through approximately $125 billion in investments.
- Concerns Raised: The Global Forest Coalition (GFC) has voiced significant concerns regarding the TFFF, suggesting it may commodify forests and inadequately involve forest communities.
- Only 20% of the financial payments are projected to reach local communities, raising worries about their support.
- Commodification Issues: The GFC criticizes the TFFF for assigning a monetary value to ecosystem services, potentially diminishing the intrinsic value of forests.
- The coalition advocates for alternative funding mechanisms, such as reallocating national defense budgets or implementing an oil tax to generate more substantial funding for forest conservation.
The TFFF represents a significant step in forest conservation efforts, but its implementation faces scrutiny and calls for a more inclusive and sustainable approach that prioritizes both ecological integrity and the rights of indigenous peoples.
NIA Investigates Pahalgam Terror Attack
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Pahalgam terror attack, which took place on April 22, 2025, has gained significant attention due to the tragic loss of 26 tourists' lives in Jammu and Kashmir. The investigation has been taken over by the National Investigation Agency (NIA), highlighting the severity of the situation, especially after the Resistance Front, linked to the Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba, claimed responsibility for the attack.
Key Takeaways
- The NIA's involvement signifies a critical approach towards combating terrorism in the region.
- The attack marks a concerning event for tourism and security in Jammu and Kashmir.
Additional Details
- Background of the NIA: The NIA was established in 2008 in response to the 26/11 Mumbai attacks to address terrorism-related cases that often have complex inter-State and international implications. Its primary goal is to investigate and prosecute offenses that threaten India's sovereignty and security.
- Jurisdiction and Powers: The NIA operates under the NIA Act, amended in 2019, which allows it to investigate various offenses, including those under the Indian Penal Code, the Information Technology Act, and the Arms Act. The Supreme Court has broadened the NIA’s scope to include related offenses committed by individuals not directly accused in the main case.
- Legal Framework for Trials: Cases investigated by the NIA are tried in special NIA courts designated by the Central government in consultation with the Chief Justice of the High Court. This framework ensures that terrorism cases are handled efficiently and with the necessary expertise, leading to a significant number of convictions since the agency's inception.
The investigation into the Pahalgam terror attack by the NIA underscores the ongoing challenges of terrorism in India and the importance of a specialized agency in addressing such complex issues effectively.
Rafale-Marine Fighter Jet
 Why in News?
Why in News?
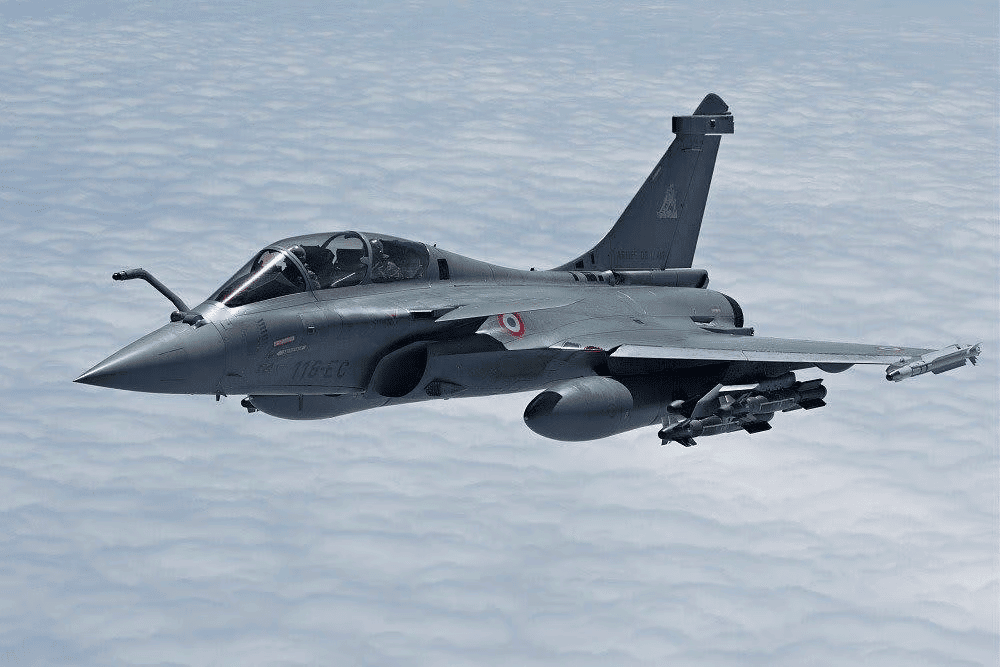
- On April 29, 2025, India finalized a significant defense agreement with France, valued at ₹63,000 crore, to acquire 26 Rafale-Marine fighter jets for its Navy. This deal encompasses 22 single-seater jets designed for carrier operations and four twin-seater trainer jets, with deliveries anticipated to commence in 2028 and conclude by 2030.
Key Takeaways
- India's acquisition of 26 Rafale-Marine jets enhances its naval capabilities.
- The deal includes provisions for technology transfer to support indigenous production.
- The Rafale-Marine is classified as a 4.5-generation fighter, renowned for its operational versatility.
Additional Details
- About Rafale-Marine: The Rafale-Marine is a sophisticated twin-engine fighter jet developed by Dassault Aviation, known for its versatility in performing various missions such as air defense, reconnaissance, and precision strikes. While it does not qualify as a fifth-generation stealth aircraft, its design incorporates features that minimize radar visibility.
- Carrier-Based Design Features: The Rafale-Marine is engineered specifically for aircraft carrier operations. It features a lighter design, reinforced airframe, and a tailhook for landing on the confined spaces of a carrier deck. The aircraft can utilize ski-jumps for takeoff, optimizing the angle of attack for safer ascension.
- Enhanced Operational Capabilities: The aircraft is capable of executing a range of missions, including anti-ship strikes and anti-submarine warfare. Its corrosion-resistant materials ensure durability in maritime environments, and compatibility with the existing MiG-29K fleet will significantly bolster India's naval air power.
- Indigenous Production and Technology Transfer: In alignment with the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the deal includes a technology transfer clause, enabling India to incorporate indigenous weaponry into the Rafale-Marine jets. A production facility for the aircraft’s fuselage and maintenance operations will also be established in India, creating job opportunities in the defense sector.
- Strategic Implications: The acquisition of the Rafale-Marine is poised to enhance India's naval capabilities, acting as a force multiplier that improves operational synergy between the Navy and the Indian Air Force (IAF). The shared design with existing IAF Rafale jets will streamline training and logistics, leading to enhanced joint operational effectiveness.
In summary, the procurement of the Rafale-Marine fighter jets marks a significant advancement in India's defense capabilities, focusing on indigenous production and enhancing operational readiness within its naval forces.
Kartarpur Corridor
 Why in News?
Why in News?
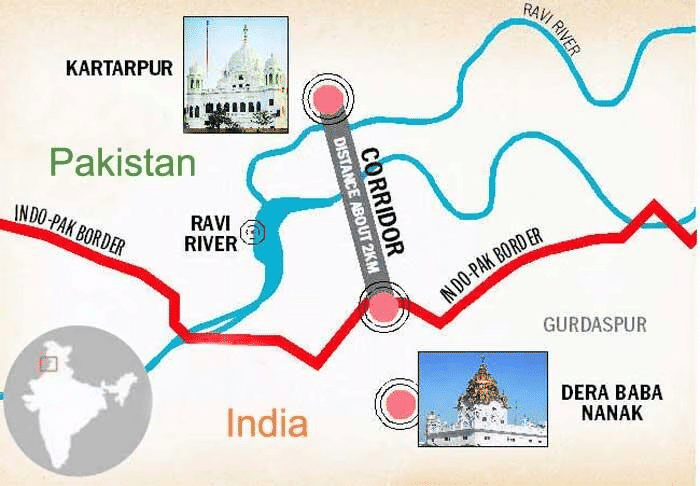
- The Kartarpur Corridor serves as a significant religious and cultural link between India and Pakistan. It connects the historic Darbar Sahib Gurdwara in Narowal, Pakistan, to the Dera Baba Nanak shrine located in Gurdaspur, India. This corridor was inaugurated on November 9, 2019, coinciding with the 550th birth anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev, the founder of Sikhism. Despite ongoing tensions between the two nations, the corridor remains operational, providing pilgrims with access to this revered site.
Key Takeaways
- The corridor allows visa-free access for up to 5,000 Indian pilgrims daily.
- It is operational year-round, facilitating visits to the Gurdwara.
- The corridor symbolizes religious freedom and cultural exchange despite political tensions.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: Guru Nanak Dev was born in 1469 in Nankana Sahib, now part of Pakistan. He is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus, and his teachings emphasized a direct relationship with the divine, rejecting ritualism. The Gurdwara Darbar Sahib is his final resting place, making it a vital pilgrimage site for Sikhs worldwide.
- Current Developments: Following a recent terror attack in Pahalgam, tensions between India and Pakistan have escalated. Nonetheless, many devotees advocate for the continued operation of the Kartarpur Corridor, viewing it as a beacon of peace and unity.
- Security Measures: In response to the Pahalgam attack, the Government of India has implemented several security measures, including expelling Pakistani military attaches and suspending the 1960 Indus Waters Treaty. The integrated check-post at Attari was closed, and Pakistani nationals under the SAARC Visa Exemption Scheme were asked to leave India within 48 hours.
The Kartarpur Corridor not only facilitates religious pilgrimage but also represents a crucial avenue for fostering cross-border relationships, emphasizing the importance of peace and understanding amidst geopolitical challenges.
Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha

Why in News?
- The role of the Deputy Speaker of the Lok Sabha is critical within the Indian parliamentary framework. Established under Article 93 of the Constitution, this position is vital for ensuring the continuity and stability of legislative activities. Recently, however, there has been significant neglect of this office, which raises constitutional concerns.
Key Takeaways
- The Deputy Speaker is essential for maintaining legislative order and balance.
- Current vacancy issues in this role have implications for parliamentary operations.
- There is a need for legislative reforms to ensure timely elections for this position.
Additional Details
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 93 mandates the election of both a Speaker and a Deputy Speaker at the earliest opportunity.
- According to Article 95(1), if the Speaker's position becomes vacant, the Deputy Speaker assumes their responsibilities.
- Article 178 extends similar provisions to State Legislative Assemblies.
- The Lok Sabha rules include references to the "Speaker" as also covering the "Deputy Speaker" where applicable.
- The Constitution does not specify a timeline for the election of a Deputy Speaker, which allows for delays.
Election Process:
- Rule 8 of Lok Sabha Rules governs the election process.
- The Deputy Speaker is elected by a simple majority of members present and voting.
- This election typically occurs during the second session but can also happen in the first.
- The Deputy Speaker serves until the Lok Sabha is dissolved.
Historical Context:
- The position of Deputy Speaker dates back to the colonial era, with Sachidanand Sinha being the first Deputy Speaker in 1921.
- The role was institutionalized by India's independence in 1947, with M.A. Ayyangar as the first elected Deputy Speaker post-independence.
The ongoing vacancy in the Deputy Speaker's position during the 17th Lok Sabha (2019-2024) and its continuation into the 18th Lok Sabha raises significant questions about adherence to constitutional requirements. This absence centralizes power within the Speaker and the ruling party, undermining necessary checks and balances.
The lack of a Deputy Speaker poses risks to parliamentary stability, especially in emergencies. Additionally, this vacancy indicates a disregard for parliamentary traditions, particularly the norm of offering the position to the Opposition, promoting inclusivity.
There is a pressing need for legislative reform to possibly revise constitutional language to mandate a timeline for electing a Deputy Speaker. Establishing a specific deadline could ensure compliance and prevent future delays. Alternatively, a statutory mechanism could empower the President to initiate the election process within a defined timeframe.
Ultimately, the role of the Deputy Speaker is foundational to upholding the integrity of legislative processes. Neglecting this position undermines the core principles of democratic balance and adherence to constitutional norms. It is crucial for Parliament to reaffirm its commitment to rule-based governance and promptly restore the Deputy Speaker's position.
Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- On April 30, 2025, India made a significant advancement in its clean energy efforts with the introduction of the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India (GHCI). This scheme aims to establish a transparent and reliable system for certifying the production of green hydrogen, enhancing market trust and traceability.
Key Takeaways
- The GHCI provides a framework for certifying green hydrogen production in India.
- It enhances transparency, accountability, and trust among stakeholders in the green hydrogen sector.
- MSMEs play a crucial role in supporting India's green hydrogen goals.
- India’s National Green Hydrogen Mission aims for a production capacity of 5 million metric tonnes by 2030.
Additional Details
- Importance of Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen is generated using renewable energy sources and serves as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. This transition can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy security.
- Purpose of GHCI:The scheme is designed to:
- Create a structured system for green hydrogen certification in India.
- Ensure that hydrogen production is traceable and credible in the market.
- Standardize production methods and ensure quality assurance.
- Facilitate investments by building trust among stakeholders.
- Certification Process: All domestic green hydrogen producers (excluding those focused solely on exports) will be required to undergo a mandatory certification process conducted by Accredited Carbon Verification (ACV) Agencies recognized by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- From 2026, certified green hydrogen will be tradable within India’s carbon market, allowing for enhanced market dynamics.
- Role of MSMEs: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are essential for achieving India's green hydrogen ambitions. They can innovate and provide localized solutions, contributing to manufacturing, service provision, and hydrogen generation from biomass.
- The National Green Hydrogen Mission anticipates attracting investments of over ₹8 lakh crore and creating more than six lakh jobs while significantly reducing fossil fuel imports.
In summary, the Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme of India represents a pivotal step in the country’s clean energy transition, aiming to create a trustworthy framework for green hydrogen production and enhancing the role of MSMEs in the energy supply chain.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
















