The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 3rd May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

A Profound Shift in the Global Order
Why is it Newsworthy?
The global framework established after World War II, supported by organizations like the WTO and the UN, is currently experiencing a significant shift.
As Western influence wanes and Asia, particularly India and China, rises in prominence, there is a pressing need to reevaluate multilateralism, trade practices, and global governance structures.
Importance
- Shift in Global Power: Asia is reclaiming its historical role and is expected to account for two-thirds of global GDP and power.
- Opportunity for India: The decline of outdated multilateral institutions and trade models presents India with an opportunity to propose new frameworks and establish itself as a strategic leader.
- Technology as a Driving Force: Emerging technologies like AI, semiconductors, and digital platforms are becoming the new focal points of trade, replacing traditional goods-based commerce.
Key Issues and Insights
1. Decline of the Post-Colonial Global Framework: The WTO, UN, and similar organizations are losing their credibility and relevance in the current global scenario. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the G7’s insular approach, diminishing the global North’s moral authority.
2. Rise of Regional and Bilateral Agreements: Bilateral trade agreements are gaining prominence over multilateralism, often at the cost of domestic autonomy. New regional groupings like BRICS+ are emerging to fill the void left by traditional institutions.
3. India’s Strategic Position in Asia: India has a crucial role in collaborating with ASEAN and the African Union to establish a new trade-consumption network. Proposing an Asian Common Market could counterbalance Western trade blocs.
4. Technological and Innovative Opportunities: India has the potential to lead in AI and software innovation, particularly in open-source systems. Companies like Huawei and DeepSeek highlight India’s capabilities in AI and chip design, such as 7nm technology.
5. Learning from the Chinese Model: India should adopt an internally-driven growth model similar to China’s, focusing on reducing electricity costs, enhancing patent output, and fostering home-grown innovation.
Path Ahead
1. Formulating Alternative Multilateral Approaches: India should spearhead the development of new global governance frameworks that are inclusive of Asian and African perspectives.
2. Enhancing Research and Development: Significant investment in AI, semiconductor technology, and language models is essential to boost India’s position in these critical areas.
3. Revamping Trade Architecture: India needs to move beyond traditional tariff-based approaches to comprehensive agreements that encompass services, investment, and infrastructure.
4. Promoting Open-Source Technologies: Open-source technology can serve as a tool of soft power for India in the evolving digital landscape, enhancing its global influence.
5. Building Strategic Trade Partnerships: India should focus on forming bilateral trade alliances with regions like ASEAN and Africa, where there is a growing consumer base and rising demand.
Strengthening Parliamentary Oversight in India
Why is it News?
The editorial emphasizes the urgent need to balance 'maximum governance' with 'maximum accountability.'
- It argues that a strong Parliament is essential for democracy and executive scrutiny in India.
Significance
- Democratic Accountability: An active legislature is crucial for holding the executive accountable regularly.
- Governance Quality: Oversight mechanisms enhance transparency and implementation.
- Parliamentary Integrity: Strong checks and balances boost public confidence in democratic institutions.
Key Issues and Analysis
1. Diminishing Role of Legislative Oversight.
- Although the Constitution empowers Parliament to scrutinize the executive, this role has diminished recently.
- There is a tendency to prioritize governance efficiency over transparency, weakening democratic checks.
2. Underutilization of Parliamentary Mechanisms.
- Important tools like Question Hour and Zero Hour, meant for real-time accountability, are often disrupted by protests and political conflicts.
- In the current Lok Sabha, Question Hour was used only 60% of the time in the Lok Sabha and 52% in the Rajya Sabha.
- Questions raised are often narrow, missing broader cross-sectoral issues.
3. Limitations of Parliamentary Committees.
- Departmentally Related Standing Committees (DRSCs) produce thorough reports, but these are seldom debated or acted upon.
- The temporary nature of committee membership hinders the development of expertise.
- Consultations with stakeholders are often limited to a narrow circle of voices.
Notable Successes of Oversight Mechanisms
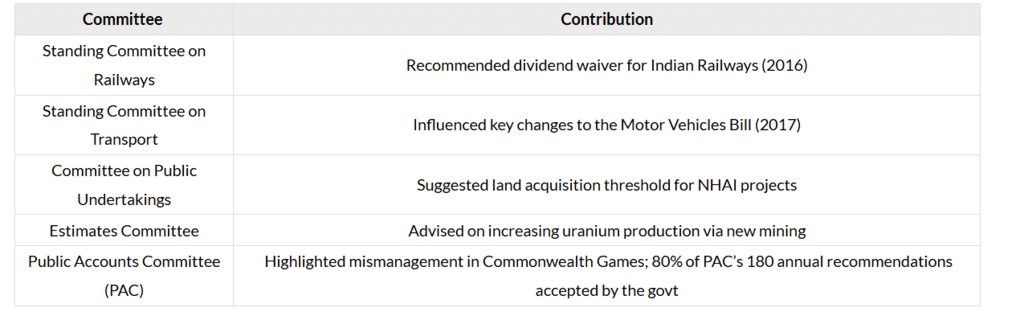
Suggested Reforms and Best Practices
1. Institutionalize Post-Legislative Scrutiny:
- Currently, India lacks a system to assess the implementation of laws after they are enacted.
- Establishing subcommittees under DRSCs or a dedicated review body could address this gap.
- For example, in the UK, major laws are reviewed 3 to 5 years after enactment by relevant departments and parliamentary committees.
2. Increase Public Access and Discourse:
- To enhance citizen engagement, committee findings should be translated into local languages.
- Utilizing visual explainers, short videos, and infographics can make information more accessible.
- Additionally, mandating ministerial responses to key DRSC reports tabled in Parliament will ensure accountability.
3. Leverage Technology for Effective Oversight:
- MPs currently lack access to expert staff and analytical tools, which hampers effective oversight.
- Implementing Artificial Intelligence and data analytics can assist in analyzing budgets, identifying policy gaps, and formulating evidence-based questions for the executive.
Conclusion
Strengthening legislative oversight should be seen as a means to enhance governance, not as a challenge to the executive.
As K.R. Narayanan, the Vice President, mentioned during the 1993 launch of DRSCs, these committees are intended to bolster administration, not undermine it.
A well-scrutinized Parliament ensures that governance remains accountable, transparent, and truly representative of the people's interests.
|
63 videos|5408 docs|1146 tests
|
FAQs on The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 3rd May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What are the key factors contributing to the shift in the global order as discussed in the editorial? |  |
| 2. How does strengthening parliamentary oversight in India relate to the global order? |  |
| 3. What role does public participation play in strengthening parliamentary oversight in India? |  |
| 4. What are the challenges faced by the Indian Parliament in enhancing its oversight functions? |  |
| 5. How can technology improve parliamentary oversight in India? |  |





















