Topic wise Previous Year Questions (Solved) : Oceanography | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Q1: With suitable examples explain the factors causing sea level changes. (2024)
Ans: Sea level changes, driven by natural and anthropogenic factors, significantly impact coastal ecosystems and human settlements. These changes, observed globally in 2024, result from a combination of thermal expansion, ice melt, and other processes.
- Thermal Expansion: Warmer oceans expand, raising sea levels. In 2024, the Pacific Ocean’s warming contributed to a 3 mm annual rise, affecting low-lying islands like Kiribati.
- Melting Ice Caps and Glaciers: Polar ice melt adds water to oceans. In 2024, Greenland’s ice loss accelerated sea level rise, threatening coastal cities like Miami.
- Groundwater Extraction: Excessive pumping causes land subsidence, exacerbating local sea level rise. In 2024, Jakarta’s subsidence worsened flooding risks.
- Isostatic Rebound: Post-glacial land uplift or subsidence alters relative sea levels. In 2024, parts of Scandinavia experienced uplift, reducing local sea level rise.
- Climate Variability: Phenomena like El Niño temporarily raise sea levels. In 2024, El Niño-induced surges impacted Peru’s coast.
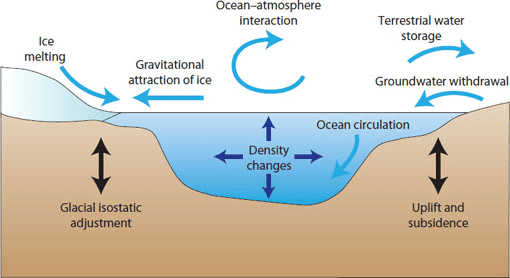 Sea level changes pose risks to coastal infrastructure and ecosystems, necessitating adaptive measures like seawalls and relocation, as seen in 2024’s global efforts.
Sea level changes pose risks to coastal infrastructure and ecosystems, necessitating adaptive measures like seawalls and relocation, as seen in 2024’s global efforts.
Q2: With suitable sketches elaborate the bottom topography of the Indian Ocean. (2024)
Ans: The Indian Ocean’s bottom topography, shaped by tectonic processes and sedimentation, features diverse landforms like ridges, basins, and trenches, influencing ocean currents and marine ecosystems, as studied in 2024.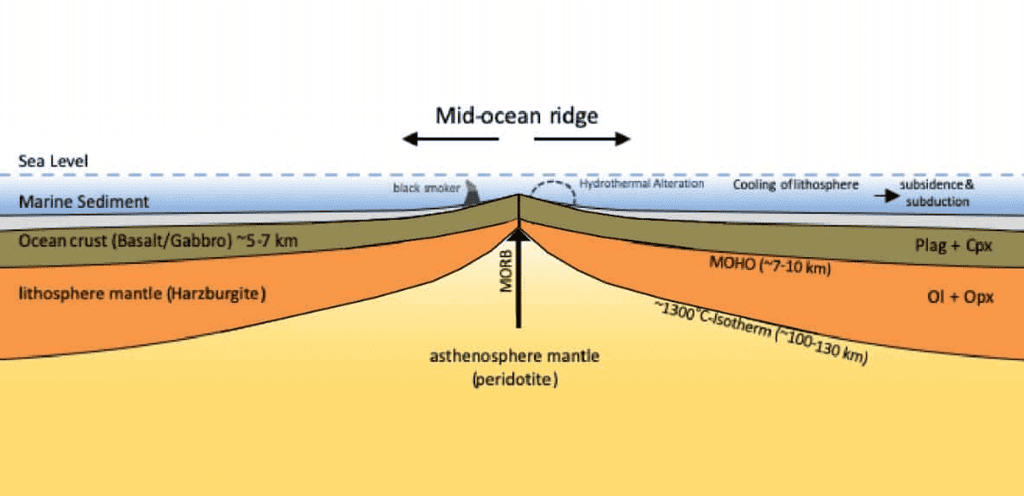
- Mid-Oceanic Ridges: The Central Indian Ridge and Carlsberg Ridge form elevated, volcanic chains, splitting the ocean floor. In 2024, these ridges influenced monsoon currents.
- Ocean Basins: Deep basins like the Arabian Basin (4,000–5,000 m) and Wharton Basin host sediment deposits, supporting marine biodiversity, as mapped in 2024.
- Trenches: The Java Trench, reaching 7,450 m, is a subduction zone causing seismic activity. In 2024, it was monitored for tsunami risks.
- Seamounts and Plateaus: The Chagos-Laccadive Plateau and Ninetyeast Ridge rise from the ocean floor, affecting currents. In 2024, these features supported coral ecosystems.
- Continental Shelves: Narrow shelves along India’s coast widen near Sri Lanka, hosting fisheries, vital in 2024 for livelihoods.
The Indian Ocean’s topography shapes its ecological and economic significance, requiring sustainable management, as emphasized in 2024.
Q3: What is ocean ranching? How are aqua-cowboys related to such activities? (2023)
Ans: Ocean ranching is a form of aquaculture where juvenile marine species, such as fish or shellfish, are raised in controlled environments and released into the open ocean to grow, later harvested when mature. Aqua-cowboys play a key role in this process, as seen in 2023.
- Ocean Ranching Process: Hatcheries rear species like salmon or tuna, releasing them into designated ocean areas. In 2023, Norway’s salmon ranching boosted fish stocks in the North Atlantic.
- Role of Aqua-Cowboys: Aqua-cowboys are skilled workers who manage the release, monitoring, and harvesting of ranched species. In 2023, they used GPS and drones in Japan to track tuna migrations.
- Economic Benefits: Ranching supports fisheries and reduces wild stock depletion. In 2023, Chile’s ranching programs enhanced coastal economies.
- Challenges: Overcrowding and disease spread, as seen in 2023’s Pacific salmon declines, threaten sustainability.
- Environmental Impact: Ranching can disrupt ecosystems if not managed, but aqua-cowboys’ expertise minimizes harm, as in Australia’s 2023 oyster ranching.
Ocean ranching, driven by aqua-cowboys, promotes sustainable fisheries but requires careful management, as evident in 2023.
Q4: How are ocean currents generated? Discuss their effects on coastal climates with special reference to the Pacific Ocean. (2023)
Ans: Ocean currents, large-scale water movements, are generated by various forces and significantly influence coastal climates, particularly in the Pacific Ocean, as observed in 2023.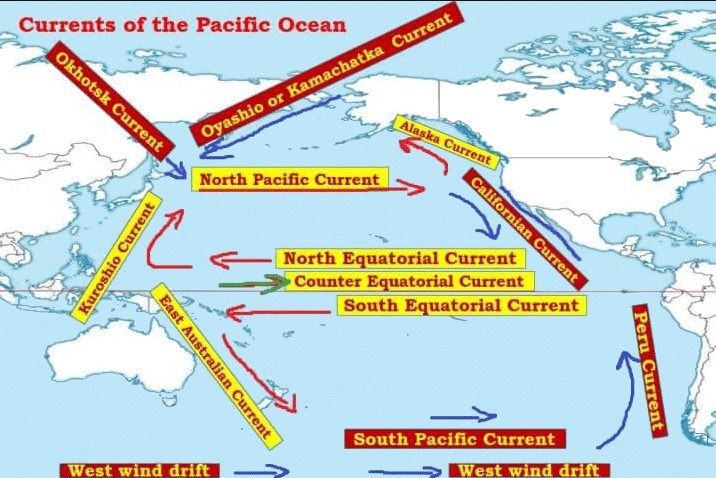
- Generation of Currents:
- Wind Stress: Prevailing winds, like trade winds, drive surface currents. In 2023, the Pacific’s North Equatorial Current was powered by trade winds.
- Coriolis Effect: Earth’s rotation deflects currents, creating gyres. The North Pacific Gyre moved clockwise in 2023.
- Thermohaline Circulation: Density differences from temperature and salinity drive deep currents, influencing the Pacific’s conveyor belt in 2023.
- Effects on Coastal Climates:
- Warm Currents: The Kuroshio Current warmed Japan’s coast in 2023, extending growing seasons.
- Cold Currents: The California Current cooled San Francisco’s climate, causing foggy summers in 2023.
- Precipitation Patterns: The Peru Current’s cold waters reduced rainfall in Chile’s Atacama Desert in 2023.
- Challenges: Climate change alters currents, affecting climates, as seen in 2023’s El Niño disruptions.
Pacific Ocean currents shape coastal climates, requiring monitoring for sustainable planning, as in 2023.
Q5: Give an account of marine resources and their economic significance. How has marine pollution affected such resources? (2023)
Ans: Marine resources, including fisheries, minerals, and energy, are vital for global economies, but pollution significantly threatens their sustainability, as observed in 2023.
- Marine Resources and Economic Significance:
- Fisheries: Fish and shellfish support livelihoods. In 2023, India’s fisheries contributed $15 billion to its economy.
- Minerals: Seabed minerals like manganese nodules hold future potential, explored in the Pacific in 2023.
- Energy: Offshore oil, gas, and wind energy drive economies. Norway’s 2023 offshore wind farms powered millions.
- Impact of Marine Pollution:
- Plastic Pollution: Microplastics harmed fish stocks, reducing India’s coastal catches in 2023.
- Oil Spills: Spills degraded habitats, as seen in Nigeria’s 2023 coastal oil contamination.
- Chemical Runoff: Agricultural runoff caused algal blooms, affecting Australia’s coral fisheries in 2023.
- Mitigation Efforts: Global initiatives, like the 2023 UN Ocean Treaty, aimed to curb pollution.
Marine resources are economically crucial but vulnerable to pollution, necessitating sustainable practices, as seen in 2023.
Q6: When corals are affected by stress it causes them to turn completely white. Explain the reasons for such an occurrence. (2022)
Ans: Coral bleaching, where corals turn white due to stress, results from the expulsion of symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae), critical for their survival. This phenomenon, widespread in 2022, threatens marine ecosystems.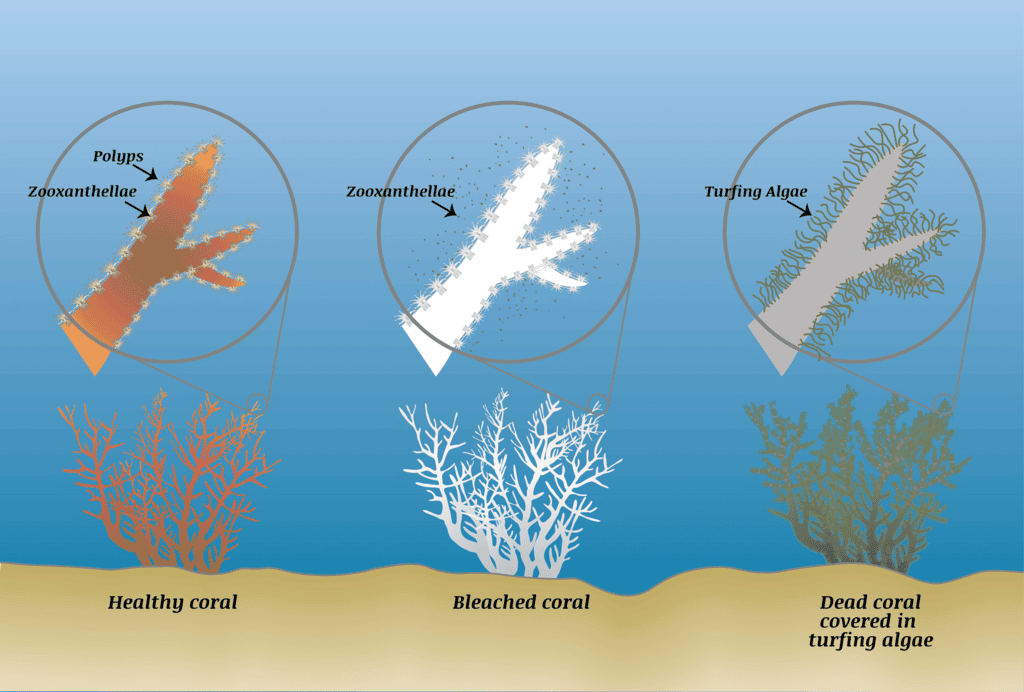
- Rising Sea Temperatures: Warmer waters disrupt zooxanthellae, causing bleaching. In 2022, Australia’s Great Barrier Reef saw mass bleaching due to record ocean heat.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO2 lowers pH, weakening coral skeletons. In 2022, Caribbean corals bleached due to acidification.
- Pollution: Chemical runoff and plastics stress corals. In 2022, India’s Andaman corals suffered from coastal pollution.
- Overfishing and Physical Damage: Loss of fish and human activities harm corals. In 2022, Southeast Asian reefs bleached due to destructive fishing.
- Mitigation: Conservation efforts, like coral restoration in the Maldives in 2022, aimed to reduce stress.
Coral bleaching reflects environmental stress, requiring global action to protect reefs, as emphasized in 2022.
Q7: What is the relationship between ocean currents and global surface wind systems? Explain with examples how does the gyre in the Northern Hemisphere differ from the one in the Southern Hemisphere. (2022)
Ans: Ocean currents and global surface wind systems are closely linked, with winds driving surface currents and currents influencing climate, as observed in 2022.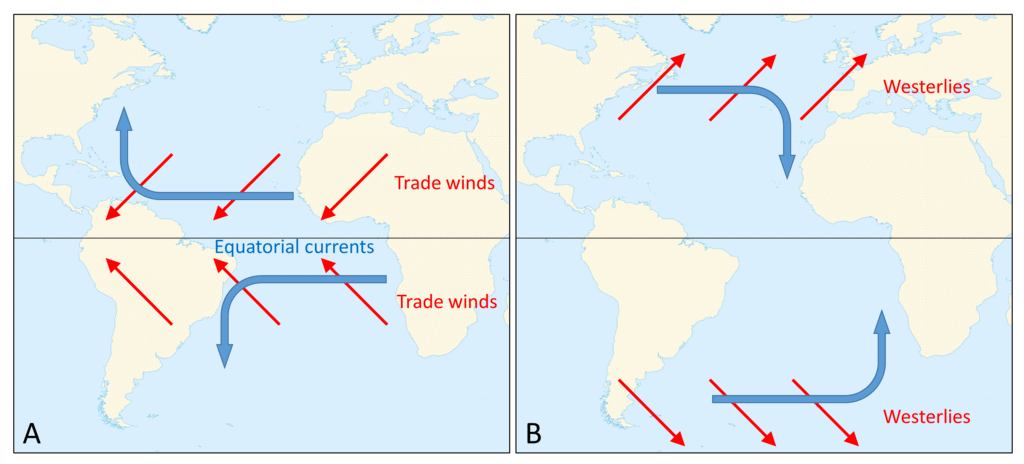
- Relationship with Winds: Trade winds and westerlies push surface waters, forming currents. In 2022, the Atlantic’s trade winds drove the North Equatorial Current, while westerlies powered the Antarctic Circumpolar Current.
- Northern Hemisphere Gyres: Clockwise due to the Coriolis effect, the North Atlantic Gyre (e.g., Gulf Stream) warmed Europe’s climate in 2022, supporting agriculture.
- Southern Hemisphere Gyres: Counterclockwise, the South Pacific Gyre (e.g., Peru Current) cooled Chile’s coast in 2022, reducing rainfall.
- Differences: Northern gyres are constrained by continents, intensifying currents like the Kuroshio, while Southern gyres, like the South Indian Gyre, are broader due to fewer land barriers, as seen in 2022.
- Impacts: Gyres influence weather, with Northern gyres moderating winters and Southern gyres cooling coasts.
The wind-current relationship shapes gyres, impacting global climates, as evident in 2022.
Q8: Discuss the hazards associated with the rising of sea surface temperature. (2021)
Ans: Rising sea surface temperatures (SSTs), driven by climate change, pose significant hazards to ecosystems, economies, and human populations, as observed in 2021.
- Extreme Weather Events: Higher SSTs fuel intense hurricanes and typhoons. In 2021, Typhoon Rai devastated the Philippines, driven by warm Pacific waters.
- Coral Bleaching: Elevated temperatures cause coral death, harming marine biodiversity. In 2021, the Great Barrier Reef faced widespread bleaching.
- Sea Level Rise: Thermal expansion contributes to rising seas, flooding coastal areas. In 2021, Bangladesh’s coastal villages were inundated.
- Fisheries Decline: Warmer waters disrupt fish migration, affecting livelihoods. In 2021, West Africa’s fish stocks declined, impacting economies.
- Mitigation Efforts: Global initiatives, like the 2021 COP26 commitments, aimed to curb SST rise through emissions cuts.
Rising SSTs threaten global stability, requiring urgent climate action, as highlighted in 2021.
Q9: Give a detailed account of the bottom topography of the Pacific Ocean. (2021)
Ans: The Pacific Ocean, the largest and deepest ocean, features a complex bottom topography shaped by tectonic activity, influencing currents and ecosystems, as studied in 2021.
- Mid-Oceanic Ridges: The East Pacific Rise, a divergent boundary, forms elevated ridges, driving currents like the South Equatorial Current in 2021.
- Trenches: The Mariana Trench (11,034 m) and Tonga Trench are subduction zones, causing earthquakes, as monitored in 2021.
- Ocean Basins: The North Pacific Basin and South Pacific Basin, averaging 4,000–5,000 m, accumulate sediments, supporting deep-sea life in 2021.
- Seamounts and Guyots: The Hawaiian-Emperor Seamount Chain rises sharply, hosting coral ecosystems, studied in 2021 for conservation.
- Continental Shelves: Narrow along South America but wider near Australia, these shelves supported fisheries in 2021.
The Pacific’s topography drives ecological and geological processes, requiring sustainable management, as emphasized in 2021.
Q10: Maritime security is being neglected. Indicate the major challenges and suggest solutions in the context of the Law of the Sea. (2021)
Ans: Maritime security, critical for global trade and resource protection, faces neglect, with challenges undermining the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), as evident in 2021.
- Challenges:
- Piracy and Illegal Activities: Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea disrupted shipping in 2021, violating UNCLOS’s freedom of navigation.
- Territorial Disputes: South China Sea conflicts over EEZs, involving China and ASEAN nations, challenged UNCLOS in 2021.
- Illegal Fishing: Overfishing in the Indian Ocean depleted stocks, ignoring UNCLOS regulations in 2021.
- Environmental Threats: Oil spills and pollution, like the 2021 Sri Lanka spill, harmed marine ecosystems.
- Solutions:
- Strengthen UNCLOS Enforcement: Enhance international patrols, as seen in 2021’s EU anti-piracy missions.
- Regional Cooperation: ASEAN’s 2021 maritime dialogues aimed to resolve disputes.
- Technology Use: Satellite monitoring, used in 2021 by India, curbed illegal fishing.
- Sustainable Practices: Global treaties in 2021 promoted marine conservation.
Maritime security demands robust UNCLOS implementation and cooperation, as highlighted in 2021.
|
303 videos|635 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Topic wise Previous Year Questions (Solved) : Oceanography - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the main branches of oceanography? |  |
| 2. How does ocean circulation affect global climate? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of ocean salinity? |  |
| 4. What are the major threats to marine ecosystems? |  |
| 5. How do oceanographic studies contribute to environmental conservation? |  |
















