Science and Technology - 2 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Telescope in Cosmic World
 Why in News?
Why in News?
An Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) is currently being constructed on Cerro Armazones Mountain in the Atacama Desert, Chile. This telescope is set to revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
Key Takeaways
- A telescope enhances the brightness of celestial objects rather than just magnifying them.
- The aperture size of a telescope is crucial for its light-gathering power.
- Different types of telescopes include reflecting and refracting telescopes, each with unique characteristics.
Additional Details
- What are Telescopes?: A telescope is an instrument used by astronomers to observe distant objects. Its primary function is to enhance the brightness of celestial objects, which is quantified by its light-gathering power.
- Types of Telescopes:
- Reflecting Telescope: Utilizes concave mirrors to focus light, producing real, inverted, and smaller images. Most modern telescopes are of this type, employing parabolic mirrors to minimize image blurring.
- Refracting Telescope: Employs lenses and refraction to redirect light for magnification. The maximum lens size achievable is around 1 meter, with the largest being at Yerkes Observatory in the US, measuring 1.02 meters.
- Measuring Brightness: Brightness is quantified using apparent magnitude, a logarithmic scale where lower values indicate brighter objects (e.g., the Sun at -26.78) and higher values denote dimmer ones (e.g., Andromeda Galaxy at +3.44).
- Resolution of Telescopes: The ability to distinguish fine details is defined by resolution. With 20/20 vision, one can see details as small as 60 arcseconds. A toy telescope can resolve details at about 1.47 arcseconds, providing significantly more detail.
- Examples of Largest and Advanced Telescopes:
- Large Binocular Telescope (LBT): The largest telescope to date, featuring two 8.4-meter mirrors and a combined aperture of 11.9 meters, located at Mount Graham International Observatory, Arizona, US.
- Extremely Large Telescope (ELT): Under construction at Cerro Armazones, part of the European Southern Observatory, with five mirrors and a combined aperture of 39.3 meters.
- Subaru Telescope: An 8.2-meter wide telescope at Mauna Kea Observatory, Hawaii.
- International Liquid Mirror Telescope: Asia's largest telescope located in Devasthal, Uttarakhand, India, featuring a 4-meter diameter rotating mirror made of liquid mercury.
In summary, the development of advanced telescopes like the ELT marks a significant milestone in astronomical research, promising to unveil new cosmic phenomena and enhance our understanding of the universe.
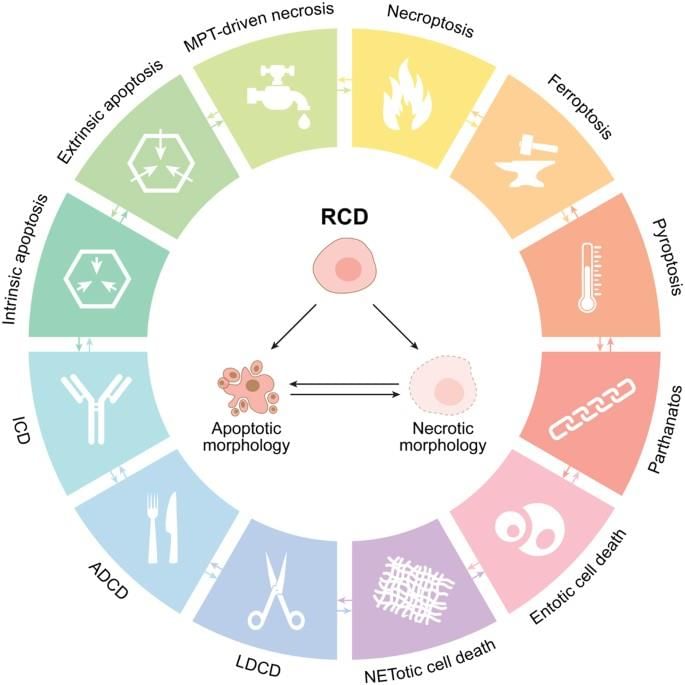
Proposed Cellular Functionality Beyond Mortality
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent research has introduced the idea of a 'third state' that challenges traditional definitions of life and death. This concept suggests that certain cells and tissues may continue to function even after the organism has died, raising intriguing questions regarding cellular capabilities and their implications for biology and medicine.
Key Takeaways
- The 'third state' indicates that death may not mean a complete halt of biological processes.
- Some cells can adapt and operate post-mortem, changing our understanding of life cycles.
Additional Details
- Xenobots: Researchers have discovered that skin cells from deceased frog embryos can spontaneously organize into new multicellular structures known as xenobots. These entities display behaviors that exceed their original biological functions, utilizing tiny hair-like projections called cilia for movement. Unlike living frog embryos, where cilia are primarily used for mucus propulsion, xenobots can engage in kinematic self-replication, effectively duplicating their form without traditional growth processes.
- Anthrobots: Studies indicate that individual human lung cells can create small, multicellular structures termed anthrobots. These bio-robots, formed from human tracheal cells, demonstrate unique behaviors, including movement, self-repair, and the ability to restore damaged neuron cells nearby.
The concept of a third state encourages a reassessment of what constitutes life and death. Understanding how cells can continue to function after death may lead to significant advances in organ preservation and transplantation, ultimately enhancing donor organ viability and improving patient outcomes.
Pager, Walkie-Talkie Blasts in Lebanon
Why in News?
Recently, several people were killed and hundreds injured in Lebanon following explosions of hand-held radios, such as walkie-talkies and pagers, utilized by Hezbollah at multiple locations. These pagers were selected by Hezbollah to evade detection through cell phones and were covertly modified with Pentaerythritol tetranitrate (PETN).
Key Takeaways
- Explosions involved modified communication devices used by Hezbollah.
- Pagers were chosen for their ability to avoid detection.
Additional Details
- What are Walkie-Talkies? They are handheld two-way radios equipped with a microphone and speaker. Walkie-talkies are portable communication devices that transmit and receive messages using radio waves on specific frequency bands.
- History and Invention: First used by the military in the 1930s, walkie-talkies played a crucial role in 20th-century wars. Their invention is credited to Don Hings in 1937, originally created for pilots under various names such as wireless sets and pack sets.
- Components and Operation: A walkie-talkie includes a transmitter-receiver unit, an antenna, and a loudspeaker-microphone combination. The device operates on a single frequency band, allowing users to communicate by pressing a push-to-talk button.
- Applications: Widely used in emergency services, security, military operations, and industries like construction and hospitality, walkie-talkies are invaluable in areas with poor mobile network reception.
- Limitations: Common issues include loss of coverage due to battery depletion, excessive background noise, privacy concerns, and static during transmissions.
What are Pagers?
- Pagers, also known as beepers, are wireless devices that receive and display messages. They were widely used in the 1980s and are still relied upon by specific groups like healthcare and emergency services due to their reliability in low-signal areas.
- Working: Pagers operate using radio signals transmitted by towers that can penetrate areas where cellular signals may be weak.
- Types of Pager:
- One-way pagers: Receive messages from a central transmitter but cannot reply. They alert users through beeps or vibrations.
- Two-way pagers: Allow users to send and receive messages, though they are still less functional than smartphones.
- Pagers Application in Covert Operations:
- Low Susceptibility to Surveillance: Lack of GPS and internet connectivity reduces the risk of location tracking.
- Difficult to Intercept: The use of radio frequencies makes them harder to monitor than cellular or internet-based devices.
- Modifiable for Covert Use: Pagers can be modified to trigger signals for remote detonation or alerts without drawing attention.

What is Hezbollah?
Hezbollah, meaning 'Party of God,' is a Shia militia-cum-political party in Lebanon, recognized as one of the world's most heavily armed non-state actors, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS). Formed during the Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990), Hezbollah emerged largely in response to Israeli invasions of southern Lebanon in 1978 and 1982. Inspired by Iran’s 1979 Islamic revolution, it has received substantial support from Iran and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). It has been designated as a terrorist organization by countries like the US and Israel.
Mains Question: Analyze how electronic devices, such as mobile phones and pagers, have been utilized in modern warfare. What are its implications and strategies to mitigate them?
4 Key Space Projects Receive the Go-Ahead from Cabinet
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved four significant space initiatives to be undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). This decision aligns with the Vision 2047 goals set forth by the agency and includes a financial allocation exceeding ₹22,750 crore for development costs.
Key Takeaways
- Approval of four major space projects by ISRO.
- Overall funding of over ₹22,750 crore sanctioned for these initiatives.
- Projects include Chandrayaan-4, Venus Orbiter Mission, Bharatiya Antariksh Station, and Next Generation Launch Vehicle.
Additional Details
- Chandrayaan-4 Mission: This mission, which is the fourth iteration of India's lunar exploration, has a budget of ₹2,104.06 crore and is set for launch in 2027. Its objectives include conducting a remote mission to collect rock samples from the Moon's surface.
- Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM): Allocated ₹1,236 crore, this mission aims for a March 2028 launch. It will be India's second mission to another planet, focusing on studying Venus’s atmosphere and geology.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS): This ambitious project, with an additional funding of ₹11,170 crore, is set to launch its first module (BAS-1) in 2028, with completion expected by 2035. It aims to establish an Indian space station for research in various fields.
- Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV): A budget of ₹8,240 crore has been approved for this new launch vehicle, which is expected to be cost-effective and reusable, enhancing payload capacity significantly.
These initiatives not only aim to boost India's capabilities in space exploration but also play a crucial role in establishing self-reliance in space technology and fostering innovation.
Night Light Pollution Linked to Alzheimer’s Risk
Why in News?
A recent study published in Frontiers in Neuroscience indicates a significant correlation between exposure to night-time light pollution and the increased incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. This exposure disrupts natural circadian rhythms and negatively affects sleep quality, which may heighten the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Key Takeaways
- Night-time light pollution may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Disruption of circadian rhythms and impaired sleep are contributing factors.
Additional Details
- What is Alzheimer’s Disease? Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that leads to various cognitive impairments, including memory loss, confusion, and behavioral changes. It is characterized by the formation of plaques and tangles in the brain, primarily affecting memory-related neurons.
- Alzheimer's is the most prevalent cause of dementia, responsible for 60-80% of dementia cases worldwide.
- Causes and Risk Factors: Key risk factors include advancing age (primarily affecting those over 65), genetic predispositions, abnormal protein build-up (notably amyloid), and lifestyle factors such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and smoking.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis involves cognitive tests, neuropsychological assessments, imaging techniques like MRI and PET scans, and biomarker tests to detect amyloid plaques.
- Treatment and Management: There is currently no cure for Alzheimer’s, but medications and supportive therapies can help alleviate symptoms temporarily.
- Prevalence: The WHO estimates that as of 2023, over 55 million people globally are affected by Alzheimer’s, with about 75% of these cases occurring in low- and middle-income countries. In India, estimates suggest that between 3 to 9 million individuals are affected, a number expected to rise with an aging population.
This study underscores the growing concern regarding environmental factors, such as light pollution, and their potential implications for public health, particularly in relation to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Stem Cell Transplants
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study published in Science Translational Medicine examined the long-term outcomes of patients who received hematopoietic stem cell transplants (HSCT). The focus was on how these transplanted stem cells evolve and mutate over time.
Key Takeaways
- The research studied 16 pairs of donors and recipients, revealing low mutation rates of approximately 2% per year in donors and 2.6% in recipients.
- This indicates a stable clonal expansion of stem cells over decades.
- While all donors showed some degree of clonal hematopoiesis, the lack of widespread clonal expansion points to a strong regenerative capability of the bone marrow.
Additional Details
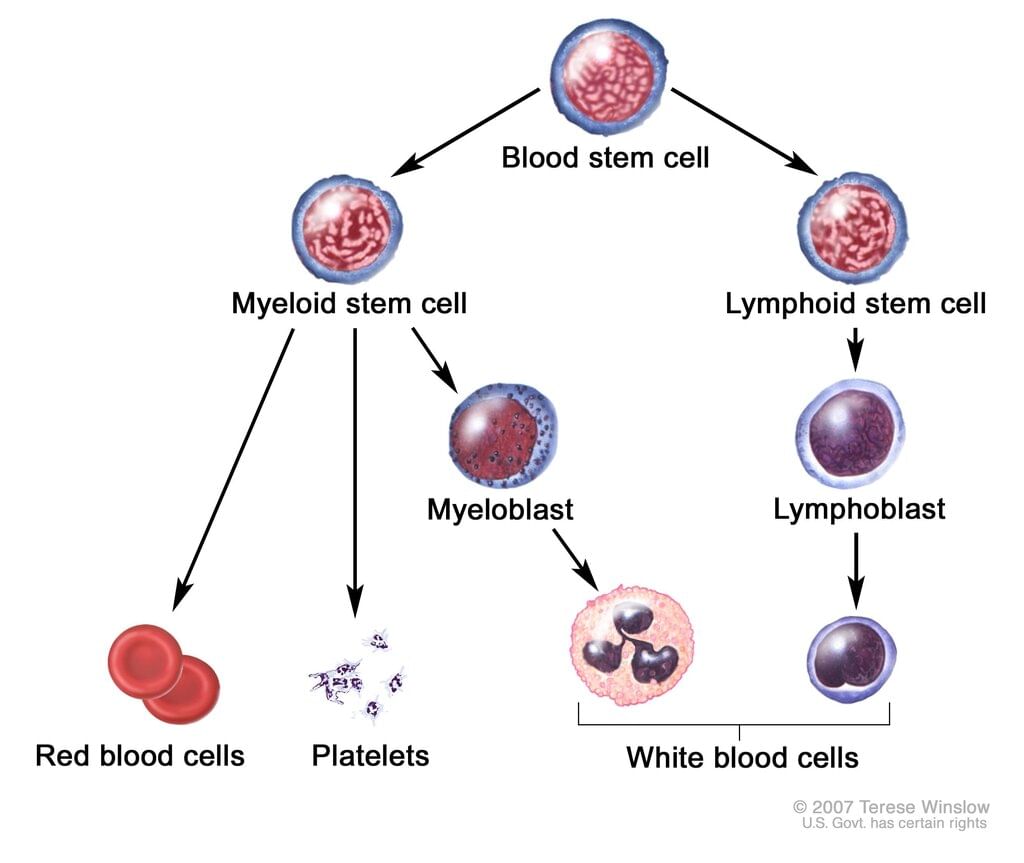
- Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSC): These are immature cells that can develop into all types of blood cells, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. Their potential for use in humans was first explored in the 1950s.
- Hematopoietic stem cells are primarily found in peripheral blood and bone marrow, often referred to as blood stem cells.
- Transplant of HSCs: This process involves administering healthy hematopoietic stem cells to patients whose bone marrow is dysfunctional or depleted. Such transplants can be life-saving for individuals with blood cancers, as the donated stem cells help restore the recipient's blood cell production system.
The findings of this study are crucial for enhancing long-term outcomes in stem cell transplants. However, the presence of clonal hematopoiesis poses a potential risk for recipients, including the development of blood cancers or chronic diseases.
China's JUNO Experiment to Study Neutrinos
 Why in News?
Why in News?
After several years of construction, China's Jiangmen Underground Neutrino Observatory (JUNO) is set to commence its data collection on neutrinos. This advanced particle physics experiment aims to significantly deepen our understanding of these elusive subatomic particles.
Key Takeaways
- JUNO will observe solar neutrinos to provide real-time insights into solar processes.
- The observatory will study neutrinos generated from uranium and thorium decay within the Earth, offering clues about mantle convection and tectonic plate movements.
- JUNO is expected to become operational by late 2025, ahead of the US Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE), which is scheduled for around 2030.
- The project involves a collaborative effort with scientists from multiple countries, including the US, France, Germany, Italy, Russia, and Taiwan.
Additional Details
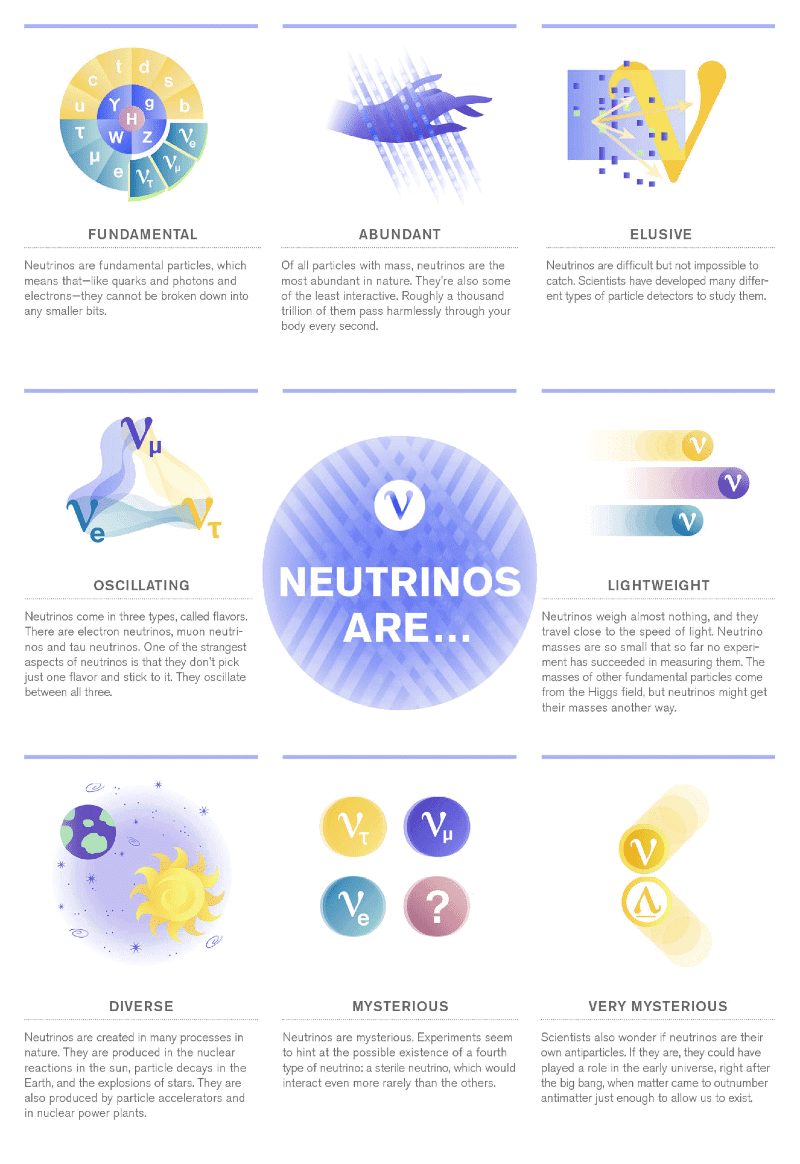
- Neutrinos: Neutrinos are subatomic particles that possess no electric charge, have a minimal mass, and exhibit a left-handed property, meaning their spin direction is opposite to their motion. They are the most abundant massive particles in the universe and are produced in various processes, such as when atomic nuclei fuse (as in stars) or split apart (as in fission reactors or particle accelerators).
- Neutrinos interact only through gravity and the weak nuclear force, making them incredibly difficult to detect. They can oscillate between different types (electron-neutrino, muon-neutrino, tau-neutrino) as they travel and interact with other particles.
- Due to their low interaction rate with matter, neutrinos can carry information over vast distances, potentially offering new ways to communicate, possibly replacing electromagnetic waves in certain applications.
In summary, the JUNO project represents a significant leap in neutrino research, with the potential to unlock new understandings of fundamental processes in both the universe and our planet.
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|
FAQs on Science and Technology - 2 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What are the implications of telescope advancements in studying the cosmic world? |  |
| 2. How does cellular functionality contribute to longevity beyond mortality? |  |
| 3. What are the main features of the communication systems like pagers and walkie-talkies used in Lebanon? |  |
| 4. What are the key objectives of the four space projects approved by the cabinet? |  |
| 5. How is night light pollution linked to Alzheimer’s risk? |  |
















