International Relations - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Quad Foreign Ministers Meeting
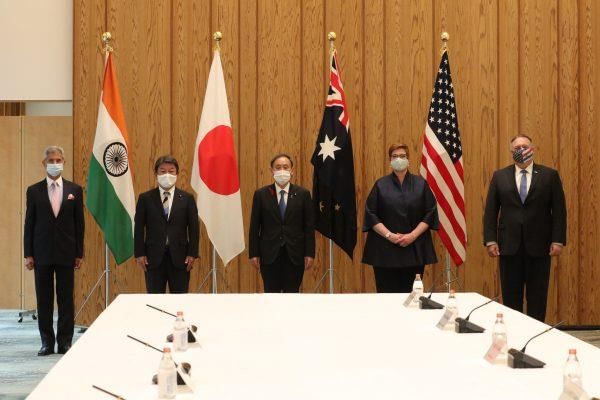 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the foreign ministers' meeting held in Tokyo brought together Australia, India, Japan, and the United States. The ministers emphasized the urgent need to end violence in various global hotspots, including Ukraine, Gaza, and Myanmar. They also expressed their commitment to expanding the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA) into the Indian Ocean Region.
Key Takeaways
- The meeting highlighted the importance of addressing global conflicts.
- There is a clear intention to enhance maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
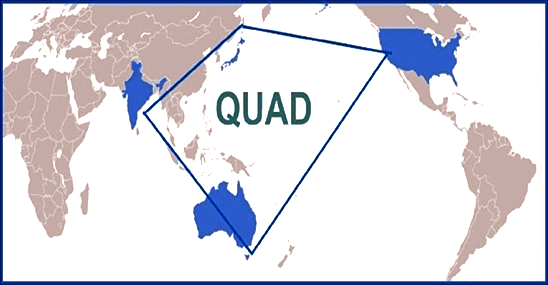
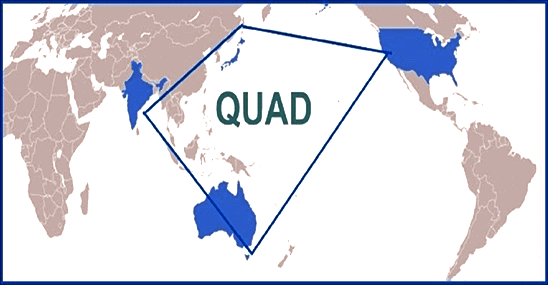
What is QUAD?
- QUAD: An informal diplomatic alliance comprising Australia, India, Japan, and the United States.
- The partnership aims to promote an open, stable, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region that is inclusive and resilient.
- Initially proposed by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe in 2007, it became a formal group in 2017 after overcoming challenges, including Australia's withdrawal due to Chinese influence.
What is the Indo-Pacific Partnership for Maritime Domain Awareness (IPMDA)?
- IPMDA Initiative: Announced during the Quad Leaders' Summit in Tokyo in 2022, this initiative focuses on integrating the Pacific Islands, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- The primary goal is to track ships that disable their Automatic Identification System (AIS) to evade detection.
- It also aims to monitor tactical-level activities to respond to climate and humanitarian crises and to protect fisheries vital to many Indo-Pacific economies.
Significance for India
- The IPMDA is a crucial measure to enhance security and stability in the Indo-Pacific, a region of significant global geopolitical interest.
- India's Navy is expanding from over 140 ships and submarines to a target of 170 to 180 vessels by 2028.
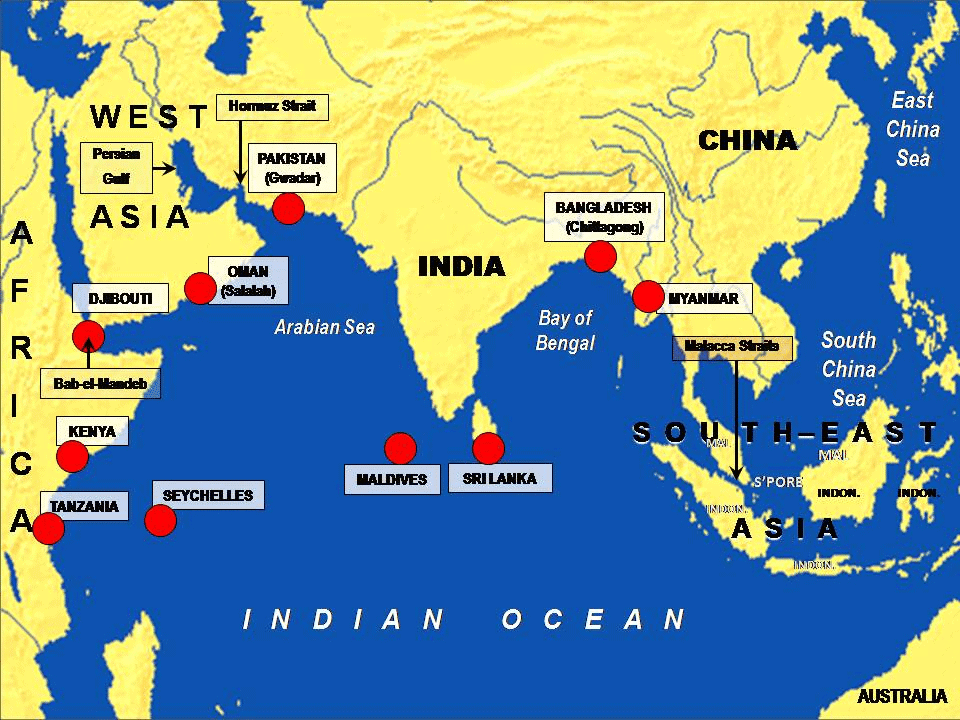
What is the Indian Ocean Region (IOR)?
- IOR: Covers over 36 littoral and island countries, essential for trade routes, natural resources, and geopolitical significance.
- It includes busy sea-lanes such as the Straits of Hormuz and Malacca.
- The region is rich in marine biodiversity but faces challenges like piracy, illegal fishing, and environmental degradation.
- India plays a pivotal role in the IOR, collaborating with China, the US, and regional organizations to address common challenges and promote sustainable development.
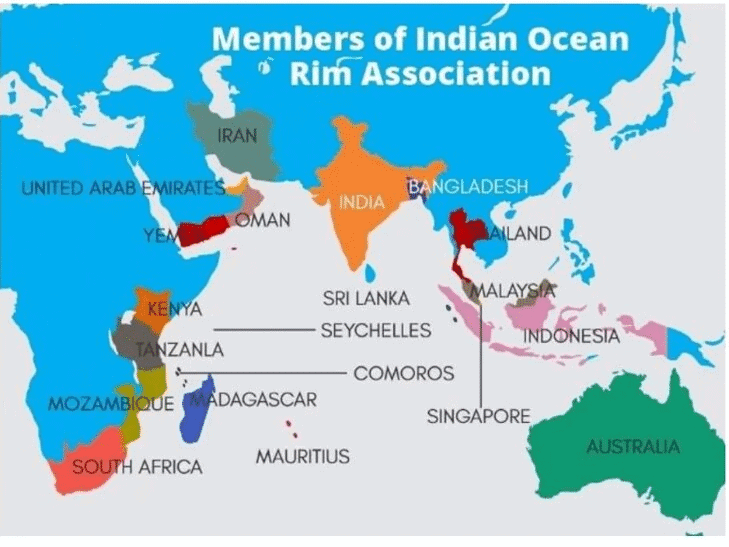
Other Groupings in Indian Ocean Region (IOR)
- Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA): An intergovernmental organization aimed at promoting economic cooperation and regional integration among Indian Ocean bordering nations.
- AUKUS: A trilateral security partnership established in 2021 among Australia, the UK, and the US, focused on the Indo-Pacific. It involves sharing US nuclear submarine technology with Australia and seeks to counterbalance China's influence in the South China Sea. Additionally, it promotes collaboration in emerging technologies such as AI, quantum technologies, and undersea capabilities.
In conclusion, the Quad Foreign Ministers Meeting illustrates the collective commitment of member nations to address pressing global issues and enhance regional security, particularly in the Indo-Pacific and Indian Ocean regions.
2nd Retreat of the Foreign Ministers of the BIMSTEC
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The 2nd Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) was convened in New Delhi, gaining heightened importance amidst rising tensions and significant developments occurring in Myanmar.
Key Takeaways
- The meeting highlighted the urgent need to tackle long-standing objectives such as capacity building and economic cooperation, particularly in light of current global and regional challenges.
- Discussions focused on the ramifications of the Myanmar crisis on regional stability and ongoing developmental initiatives.
- Humanitarian assistance was a key topic, with India currently providing limited help focused on displaced populations within its borders.
- India's cautious approach towards the Myanmar situation, especially regarding the influence of Ethnic Armed Organizations (EAOs), was underscored.
- The importance of cooperation in combating transnational crimes, including cybercrime and narcotics, was reiterated.
Additional Details
- Myanmar Crisis: The ongoing instability in Myanmar poses a serious concern for BIMSTEC, affecting various developmental and connectivity projects that aim to strengthen relationships among member nations including Nepal, Bhutan, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand.
- The discussions included potential avenues for humanitarian aid, although India's current assistance has primarily been directed toward displaced individuals and military personnel seeking refuge in Mizoram.
In conclusion, the BIMSTEC Foreign Ministers' Retreat served as a critical platform for addressing pressing regional issues, particularly the challenges posed by the Myanmar crisis, while also emphasizing the need for enhanced cooperation among member states to promote stability and development.
India Targets Doubling Trade with Africa by 2030
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, at the 19th India-Africa Business Conclave organized by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) in New Delhi, India has unveiled an ambitious plan to double its exports to African countries to USD 200 billion by 2030. This strategic initiative aims to strengthen economic ties and address shared challenges and opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- India plans to significantly increase its exports to Africa, focusing on high-growth sectors.
- Key sectors include agriculture, pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and renewable energy.
- India aims to improve logistics and transportation infrastructure to facilitate trade.
- Collaboration through the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) is vital for mutual growth.
Additional Details
- Agriculture and Agro-Products: Indian firms will assist Africa in enhancing food production through advanced technologies and agro-processing methods.
- Pharmaceuticals: With exports valued at USD 3.8 billion in 2023, India can further supply affordable medicines to African nations.
- Renewable Energy: India and Africa are positioned to lead in solar energy, with initiatives like 'One World, One Grid' aiming to connect energy grids across continents.
- Logistics and Transportation: India plans to share its PM Gati Shakti master plan and Unified Logistics Interface Portal (ULIP) to enhance trade facilitation.
- WTO Reforms: India is advocating for a unified African position on WTO reforms to improve trade conditions for developing nations.
India's current trade with Africa encompasses a diverse range of products, with significant investments in infrastructure projects positively impacting both regions. However, challenges such as non-tariff barriers, rising debt in sub-Saharan Africa, and competition from China's dominance in the region need to be addressed. By focusing on strategic cooperation, trade agreements, and leveraging Africa's critical mineral resources, India aims to enhance its economic position globally.
India and Poland Elevate Bilateral Relations to Strategic Partnership
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The recent visit of the Indian Prime Minister to Poland has marked a significant milestone in bilateral relations, elevating them to a “Strategic Partnership” that aims to enhance cooperation across various sectors, including defense, security, trade, and technology.
Key Takeaways
- This visit was the first by an Indian Prime Minister to Poland in 45 years.
- The meeting coincided with the 70th anniversary of diplomatic relations between India and Poland.
- A five-year Joint Action Plan for 2024-2028 was established to implement the Strategic Partnership.
Additional Details
- Strategic Partnership: This new status reflects a mutual commitment to enhancing cooperation in key areas such as defense, security, and trade.
- Defense and Security Cooperation:
- Both nations agreed to utilize existing bilateral mechanisms to strengthen defense ties, including the Joint Working Group for Defense Cooperation.
- They reiterated their condemnation of terrorism and emphasized the need for countries not to provide safe havens for terrorists.
- Trade and Economic Ties:
- Utilization of the Joint Commission for Economic Cooperation to enhance trade and investment.
- Leaders agreed on the importance of balancing bilateral trade and expanding the trade basket in various sectors.
- Technology and Connectivity:
- Agreed to bolster cooperation in digitalization, including cybersecurity.
- Enhanced connectivity through direct flight connections between India and Poland was emphasized.
- Climate Initiatives: Both countries acknowledged the importance of cooperating on climate action initiatives.
- Multilateral Cooperation:
- They committed to enhancing collaboration at multilateral forums to promote global peace and stability.
- Expressed concern over the ongoing war in Ukraine and its humanitarian consequences.
This partnership not only aims to deepen bilateral ties but also holds potential benefits for broader regional stability and cooperation.
3rd Voice of Global South Summit 2024 (VOGSS)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India hosted the 3rd Voice of Global South Summit (VOGSS) on 17 August 2024 in a virtual format, focusing on the theme, 'An Empowered Global South for a Sustainable Future.' The summit saw participation from 123 countries, although notable absentees included China and Pakistan. Previously, India hosted similar summits on 12-13 January 2023 and in November 2023, both conducted virtually.
Key Takeaways
- The VOGSS aims to unite countries of the Global South to share perspectives on various issues.
- It reflects India's philosophy of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam—'One Earth, One Family, One Future.'
- Recent global events like the Covid pandemic and the Ukraine conflict highlight the need for such a platform.
Additional Details
- Need for the VOGSS: Recent global developments have significantly impacted the developing world, creating a need for a unified platform to address these challenges.
- Key Outcomes:
- A proposal for a comprehensive Global Development Compact (GDC) was put forward, focusing on trade, capacity building, technology sharing, and concessional finance.
- India announced a USD 2.5 million fund to support trade promotion activities and a USD 1 million fund for capacity building in trade policies.
- Healthcare initiatives were introduced to make affordable generic medicines available and to support training for drug regulators.
- India emphasized the need to reform global institutions to prioritize developing countries' concerns.
- Global South Definition: Coined by Carl Oglesby in 1969, it refers to regions like Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Oceania that are often marginalized politically and economically.
The summit highlighted collaborative efforts to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and tackle issues such as climate change, health, and digital transformation, positioning India as a key player in the Global South.
Challenges for India as the “Voice of Global South”
- Geopolitical Competition: India faces competition from China, particularly through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, which enhances China's influence in the Global South.
- Food Security Dilemma: India's decision to restrict rice exports faced criticism, impacting its credibility as a leader in addressing global food challenges.
- Pharmaceutical Challenge: Recent controversies regarding the quality of Indian medicines have raised concerns about maintaining standards in pharmaceutical exports.
- Internal Development Issues: Critics argue that India should first address its domestic challenges, including wealth distribution and access to healthcare and education.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Strategic Partnerships: India should enhance alliances with Global South countries, focusing on collaboration in technology and healthcare to counterbalance China's influence.
- Balanced Development Model: Promoting a sustainable and inclusive development model can position India as a more ethical leader compared to China's debt-trap approach.
- Reassess Export Policies: Balancing domestic needs with international commitments is crucial to maintaining credibility in the Global South.
- Prioritize Domestic Challenges: Addressing issues like poverty and unemployment will strengthen India's position as a leader and enhance its moral authority.
India’s Stance on Fisheries Subsidies
Why in News?
India's proposals at the World Trade Organization (WTO) advocating for the establishment of regulations on fisheries subsidies have garnered substantial backing from numerous developing nations and least developed countries (LDCs). Efforts are currently underway to finalize the second phase of the Fisheries Subsidies Agreement (FSA), which aims to establish regulations on subsidies that contribute to overcapacity and overfishing, thereby promoting sustainable fishing practices.
Key Takeaways
- India's advocacy for regulating fisheries subsidies is supported by many developing nations.
- The FSA aims to combat overfishing and promote sustainable fishing practices.
Additional Details
- Fisheries Subsidies Agreement (FSA): This agreement prohibits subsidies for Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) fishing and for overfished stocks. It was proposed during the WTO's 12th Ministerial Conference and also prevents subsidies for fishing on the high seas.
- Transition Period Allowance: Under the Special and Differential Treatment (S&DT), developing countries and LDCs are granted a two-year transition period from the agreement's enforcement, during which they are not obligated to implement its regulations.
- Exempted Areas: Members may still grant subsidies as long as they are not for IUU fishing or for overfished stocks unless aimed at rebuilding those stocks sustainably.
- Benefits: The FSA will help check large-scale IUU fishing, which significantly impacts coastal nations like India and their fishing communities.
The FSA is critical for addressing global issues of overfishing and ensuring the sustainability of fish stocks, particularly in developing countries, where the livelihoods of small fishermen are often jeopardized by large-scale commercial fishing operations.
Concerns Regarding the Fisheries Subsidies Agreement
- Impact on Small Fishers: Large commercial operations can deplete fish stocks, leading to reduced catches for small fishermen who do not receive equivalent government subsidies.
- Uneven Playing Field: The sustainability exemption in the FSA may allow developed nations to avoid reducing harmful subsidies, disadvantaging poorer countries that fish sustainably.
- Global Overfishing Rates: An estimated 37.7% of global fish stocks are overfished, a sharp rise from 10% in 1974, highlighting the urgency for effective regulations.
- Government Funding: Worldwide, fisheries funding totals USD 35 billion, with about USD 22 billion used for subsidies that encourage unsustainable fishing practices.
India's Stand on the FSA
India positions itself as a low fisheries subsidizer despite its large population and emphasizes its discipline in sustainably managing fish resources. The country advocates for the 'polluter pays principle' and 'common but differentiated responsibilities,' urging that nations with higher subsidies take greater responsibility in prohibiting harmful subsidies.
Way Forward
- Balanced Approach for Negotiations: Future discussions at the WTO should prioritize addressing overcapacity and overfishing while protecting small-scale fishers' interests, particularly in developing countries.
- Leadership Role for India: As a leader of the Global South, India has the opportunity to advocate for coastal nations impacted by foreign industrial fishing fleets, reinforcing its commitment to the welfare of local fishing communities.
India's leadership in these negotiations could greatly benefit its small-scale fishers and coastal communities adversely affected by overfishing, ensuring their needs are central to future agreements.
Global Cybersecurity Index 2024
Why in News?
India has achieved a significant milestone in its cybersecurity initiatives by attaining Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024. This recognition highlights India's commitment to enhancing its cybersecurity framework.
Key Takeaways
- India is now classified in Tier 1, the highest tier in the GCI, indicating a strong dedication to cybersecurity.
- India scored 98.49 out of 100, placing it among 'role-modeling' countries.
- A total of 46 countries are recognized in Tier 1, demonstrating robust cybersecurity practices.
- Many countries remain in Tier 3 ('establishing') or Tier 4 ('evolving') stages of cybersecurity development.
Additional Details
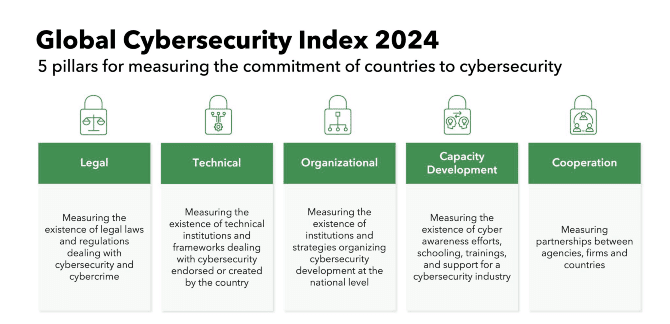
- Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI): A trusted benchmark that evaluates the commitment of nations to cybersecurity across five pillars: Legal Measures, Technical Measures, Organizational Measures, Capacity Development, and Cooperation.
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU): The UN specialized agency for information and communication technologies, established in 1865, which publishes the GCI. It has 193 member countries and plays a crucial role in global telecommunications.
- India and ITU: India has been an ITU member since 1869 and has participated actively in the ITU Council since 1952.
This achievement underscores India's proactive stance in cybersecurity and its commitment to enhancing its cybersecurity capabilities on a global scale.
6th Quad Summit 2024
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The 6th Quad Leaders' Summit was recently held in Delaware, United States. This summit marked the fourth in-person gathering of the Quad leaders, who are driving ambitious projects to assist partner nations in addressing issues such as pandemics, climate change, and cybersecurity.
Key Takeaways
- Quad Health Security Partnership (QHSP) launched to enhance health security in the Indo-Pacific.
- United States pledged USD 84.5 million for infectious disease preparedness across fourteen Indo-Pacific nations.
- Introduction of the Maritime Initiative for Training in the Indo-Pacific (MAITRI) to bolster regional maritime security.
- Quad Ports of the Future Partnership announced to improve port infrastructure and connectivity.
- Investment in undersea cable projects to enhance telecommunications for Pacific island nations.
- Collaboration on semiconductor supply chains and quantum technology initiatives.
Additional Details
- Quad Health Security Partnership (QHSP): Initiated in 2023, this partnership focuses on health security coordination across the Indo-Pacific. A new initiative, the Quad Cancer Moonshot, has been introduced to address cervical cancer treatment.
- Maritime Security Initiatives: The Quad introduced MAITRI to strengthen regional maritime capabilities. Additionally, the Indo-Pacific Logistics Network aims to improve disaster response and airlift capacity.
- Digital Infrastructure Principles: Quad countries have established principles for developing digital public infrastructure that is secure, inclusive, and promotes equitable access.
- Climate and Clean Energy Initiatives: The Quad is enhancing early warning systems and supporting clean energy projects, with India committing USD 2 million to solar projects in various nations.
- Cybersecurity Measures: The Quad's Action Plan focuses on protecting undersea telecommunications cables and promoting a resilient information environment.
The Quad is dedicated to enhancing health security, confronting climate change, and bolstering cybersecurity. Through collaboration and innovation, the Quad aims to ensure a resilient and prosperous Indo-Pacific region, contributing to global stability and sustainable development.
|
52 videos|5374 docs|1136 tests
|





















