International Relations - 2 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
7th Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC) between India and Germany
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The 7th Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC) took place in New Delhi, chaired by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and German Chancellor Olaf Scholz. This meeting addressed several pressing global issues, emphasizing the strengthening of bilateral ties between India and Germany.
Key Takeaways
- Reaffirmation of India's commitment to peaceful resolutions in the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
- Enhancement of the India-Germany strategic partnership, particularly in security and economic cooperation.
- Expansion of annual visas for skilled Indian workers in Germany from 20,000 to 90,000.
- Joint efforts towards clean energy initiatives and sustainable development.
Additional Details
- Russia-Ukraine Conflict: PM Modi reiterated India's dedication to peaceful conflict resolution. Chancellor Scholz recognized India's stabilizing influence in South Asia and urged for support in achieving a political solution to the Ukraine crisis.
- Intergovernmental Consultations (IGC): Established in 2011, this platform allows for comprehensive reviews of cooperation areas, affirming India's position as a key dialogue partner for Germany.
- Indo-Pacific Security: Both leaders emphasized the importance of a rules-based order and pledged to enhance maritime security, including the deployment of a German Liaison Officer at India's Information Fusion Centre.
- Condemnation of Terrorism: A unified stance against terrorism and violent extremism was expressed, advocating for coordinated actions against all terrorist organizations.
- Reform of Global Institutions: A mutual call for reform in multilateral organizations, such as the UN Security Council, was highlighted to better address contemporary global challenges.
In summary, the IGC marked a significant step in strengthening India-Germany relations, focusing on crucial areas such as security, economic cooperation, and sustainable development, thereby positioning both nations as key allies in addressing global challenges.
Nuclear Disarmament
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Nobel Peace Prize 2024 was awarded to Nihon Hidankyo, an organization representing Japanese atomic bomb survivors, in recognition of its dedicated efforts to achieve a nuclear-free world. This award emphasizes the critical importance of advocacy for nuclear disarmament, which is deeply rooted in the catastrophic impacts of nuclear weapons experienced during the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Key Takeaways
- Nihon Hidankyo recognized for its advocacy for a nuclear-free world.
- The impacts of Hiroshima and Nagasaki underscore the need for nuclear disarmament.
Additional Details
- Nuclear Disarmament: This process involves reducing or eliminating nuclear weapons to enhance global security and mitigate the catastrophic risks of nuclear warfare.
- Need for Disarmament:
- Humanitarian Impact: Nuclear explosions cause immediate widespread loss of life, mass destruction, severe burns, and radiation sickness, with long-term effects such as cancer and genetic damage.
- Environmental Consequences: Nuclear detonations can lead to 'nuclear winter,' blocking sunlight and causing global cooling, agricultural collapse, and ecosystem disruptions.
- Ethical Considerations: The destructive nature of nuclear weapons raises significant ethical questions about their use, conflicting with humanitarian law.
- Economic Costs: Maintaining nuclear arsenals diverts substantial resources that could otherwise address pressing issues like poverty and climate change.
Historical Efforts of Nuclear Disarmament
- Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT): Enforced since 1970, this treaty aims to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and promote disarmament, although it faces criticism for being discriminatory.
- Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT): This treaty bans all nuclear explosions, though it is not yet fully in force.
- Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW): Encompasses comprehensive prohibitions on developing, testing, producing, or using nuclear weapons.
Frameworks for Nuclear Proliferation and Disarmament
- Global Framework: The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) monitors compliance with nuclear agreements and ensures nuclear technology is used for peaceful purposes.
- Regional Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zones (NWFZs): These zones prohibit nuclear weapons, with the first established in Latin America (Treaty of Tlatelolco).
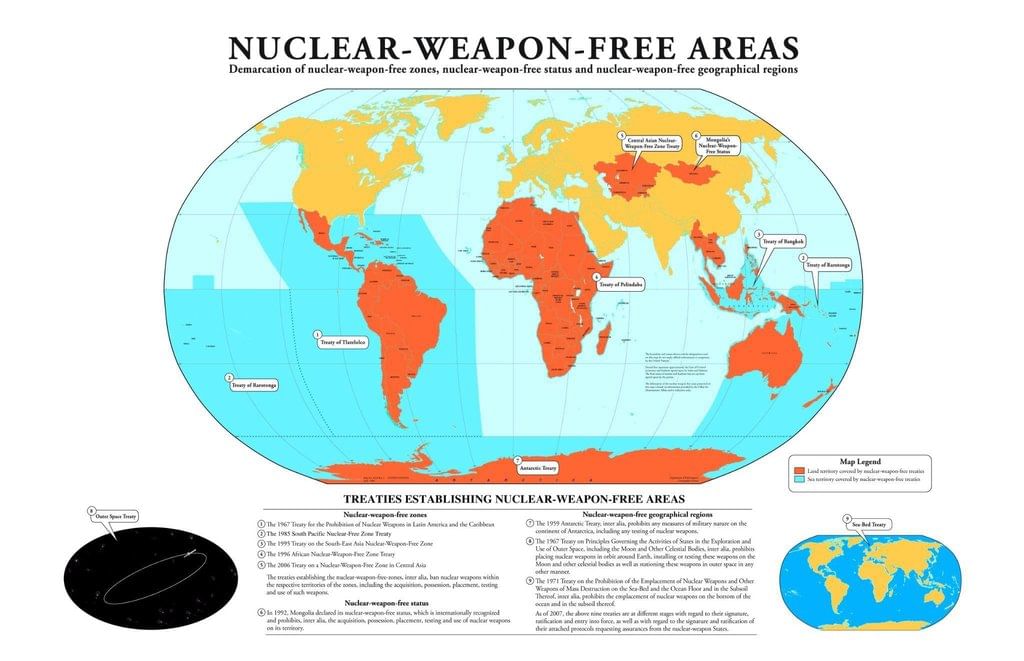
India’s Stance
- No First Use (NFU) Policy: India pledges not to use nuclear weapons first, aiming to reduce nuclear conflict risk while maintaining deterrence.
- Refusal to Join the NPT: India does not sign the NPT, citing its discriminatory nature.
- Promotion of Peaceful Nuclear Energy: India advocates for the peaceful use of nuclear technology under international safeguards.
Challenges Related to Nuclear Disarmament
- Global Scenario:
- Geopolitical Rivalries: Nations view nuclear weapons as deterrents, complicating disarmament.
- Verification Issues: Difficulties in ensuring compliance with disarmament treaties due to the secretive nature of nuclear programs.
- Technological Developments: New technologies complicate disarmament negotiations.
- India’s Scenario:
- China-Pakistan Nexus: China's nuclear modernization and partnership with Pakistan challenge India's strategic balance.
- Dual Approach: India balances between modernizing its nuclear capabilities and advocating for global disarmament.
- Lack of Formal Agreements: Absence of arms control agreements with neighbors complicates trust-building.
Way Forward
- Investing in Peaceful Nuclear Technologies: Promote beneficial uses of nuclear capabilities for energy generation.
- Enhancing Verification Mechanisms: Improve monitoring of disarmament agreements through independent verification bodies.
- Fostering Dialogue: Encourage discussions on nuclear weapons and disarmament among nations.
- Promoting NWFZs: Advocate for the establishment of Nuclear-Weapon-Free Zones in regions like South Asia.
In conclusion, addressing the challenges of nuclear disarmament is crucial for global security. It is equally important to focus on the threats posed by chemical and biological weapons, which can be more lethal and accessible than nuclear arms. Through international cooperation and robust regulatory frameworks, a safer and more secure world can be achieved, minimizing the risks of all forms of warfare.
India - Canada Relations
Why in News?
Recently, India-Canada relations have faced significant setbacks due to allegations of Indian involvement in the assassination of a Khalistani leader in Canada.
Key Takeaways
- The assassination of Hardeep Singh Nijjar has led to accusations against India from the Canadian Prime Minister.
- Both countries have expelled each other’s diplomats, escalating diplomatic tensions.
- Canada has sought support from the Five Eyes intelligence alliance amid the crisis.
Additional Details
- Assassination of Nijjar: The killing of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a prominent Khalistani leader in British Columbia, has prompted Canada to accuse Indian officials of involvement, which India has strongly denied, calling the claims 'absurd.'
- Diplomatic Fallout: The diplomatic relations have deteriorated sharply, with both nations expelling diplomats and halting consular services.
- Political Relations: India and Canada established diplomatic ties in 1947, sharing values such as democracy, human rights, and pluralism, and collaborating in international forums like the Commonwealth, G20, and United Nations.
- Economic Cooperation: Bilateral trade was valued at USD 9.36 billion in 2023, with Canada being the 18th largest foreign investor in India, contributing around USD 3.3 billion from April 2000 to March 2023.
- Diaspora Connections: Canada hosts over 1.8 million people of Indian origin, contributing significantly to cultural exchange and economic activities.
- Education and Space Innovation: Joint research initiatives and space collaborations between ISRO and the Canadian Space Agency have been fruitful, with Indian students making up about 40% of Canada’s international student population.
- Nuclear Cooperation Agreement: Signed in 2010 and effective since 2013, it facilitates uranium supply and establishes a joint oversight committee.
- Strategic Importance: India is key to Canada’s Indo-Pacific strategy, enhancing both economic diversification and regional security dynamics.
Recent challenges include the issue of Khalistani separatism, economic and trade barriers, visa delays, and the geopolitical implications of the diplomatic standoff. Both nations face obstacles in maintaining and enhancing their bilateral relationship amidst rising tensions.
Major Challenges
- Diplomatic Immunity Issue: Canada's invocation of the Vienna Conventions highlights the need to protect diplomatic staff amid rising tensions.
- Khalistan Issue: Canada's tolerance of Khalistani groups is perceived by India as a direct threat to its integrity, exacerbated by the recent assassination investigation.
- Economic and Trade Barriers: Efforts to finalize agreements have stalled, slowing bilateral trade and creating uncertainty for Canadian investments in India.
- Visa and Immigration Issues: Reduced Canadian diplomatic staff has led to significant delays for Indians applying for visas, impacting students seeking education in Canada.
- Geopolitical Implications: The diplomatic impasse could harm India's reputation within the G20 and complicate its relationships with strategic partners like the US and UK.
Way Forward
- Address Khalistan Issue: Open dialogue is essential to resolve concerns regarding the Indian diaspora and Khalistani separatism.
- Strengthen Economic Ties: Revitalize economic partnerships focusing on technology, renewable energy, and infrastructure development.
- Balance Geopolitical Interests: Both nations need to manage their relationships with major powers carefully to enhance strategic partnerships without conflict.
- Leverage Multilateral Forums: Utilize platforms like the G7 and Five Eyes to promote shared values and address global challenges effectively.
In conclusion, addressing the underlying issues and fostering communication between India and Canada is necessary for improving their bilateral ties and navigating the complexities of global politics.

Strengthening India-Pakistan Relations and SCO
Why in News?
Recently, India's External Affairs Minister engaged in an informal interaction with Pakistan's Prime Minister and Foreign Minister during the SCO Council of Heads of Government meeting in Islamabad, Pakistan. The exchanges were noted to have a more positive atmosphere compared to previous encounters.
Key Takeaways
- Both nations avoided contentious language in their statements, steering clear of sensitive issues like Kashmir.
- India acknowledged the productive nature of the SCO meeting organized by Pakistan, indicating a shift towards a more positive rapport.
- Discussions included collaboration on regional issues such as trade, connectivity, and combating terrorism, focusing on cooperation rather than confrontation.
- Proposals for an Economic Dialogue Programme were made, emphasizing cooperation in green development, digital economy, trade, and renewable energy.
Additional Details
- Revocation of Article 370: India's decision to revoke the special status of Jammu and Kashmir in August 2019 worsened relations, with Pakistan viewing it as an illegal annexation.
- Downgrade in Bilateral Relations: Following the revocation, Pakistan downgraded diplomatic ties with India, expelling the Indian High Commissioner.
- Indus Waters Treaty: Tensions have arisen over hydroelectric projects, with India seeking a review of the treaty, which Pakistan opposes.
- Trade between the two countries has significantly decreased since the Pulwama attack in 2019, with India revoking Pakistan's Most Favoured Nation status.
- Accusations of internal interference persist, with Pakistan alleging Indian support for unrest in Balochistan and India accusing Pakistan of radicalizing Kashmiri youth.
The recent informal interactions between India and Pakistan at the SCO meeting, characterized by positive developments and constructive dialogue, highlight the potential of multilateral forums to foster cooperation. By prioritizing regional collaboration and addressing common challenges, these platforms can pave the way for improved bilateral relations and stability.
India and the High Seas Treaty
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India signed the High Seas Treaty, officially known as the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement, in September 2024, representing a significant achievement in international ocean governance. Nevertheless, the implementation of the treaty faces geopolitical challenges that may affect its effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
- The BBNJ Agreement aims to conserve and sustainably use marine biodiversity in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
- High seas encompass 64% of the ocean surface, housing 2.2 million marine species.
- The treaty is crucial for sustainable resource management, biodiversity protection, and accountability for ocean pollution.
Additional Details
- What is the High Seas Treaty? The BBNJ Agreement is developed under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and aims to protect marine ecosystems beyond the 200 nautical miles of Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs). It complements previous agreements such as the 1994 Part XI Implementation Agreement and the 1995 UN Fish Stocks Agreement.
- Need for the Treaty: High seas are vital ecological zones that face threats from pollution and overexploitation, with an estimated 17 million tonnes of plastic entering the oceans annually.
- Objectives of the Treaty: It includes establishing Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), ensuring equitable sharing of marine genetic resources, mandating Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs), and enhancing capacity building for small states.
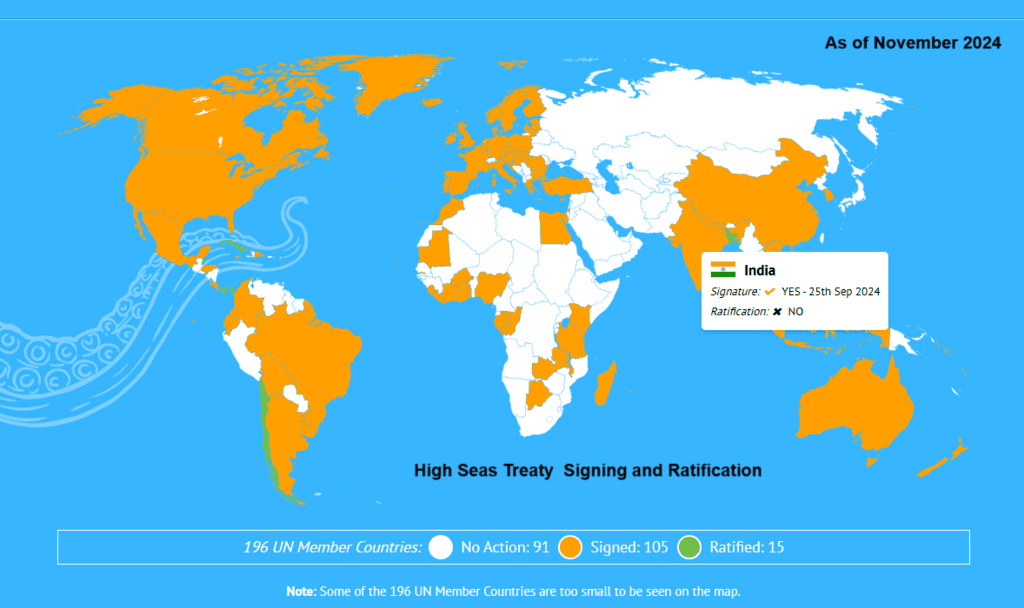
Significance of the High Seas Treaty for India
- Economic Benefits: India's blue economy contributes 4% of its GDP, supporting millions of jobs in coastal regions. The treaty could help regulate fishing and protect fisheries, enhancing sustainable economic activities.
- Addressing Climate Change: The treaty's focus on marine ecosystems as carbon sinks is essential for climate change mitigation, aiding in coastal protection and biodiversity preservation.
- Alignment with Global Commitments: Ratifying the treaty aligns India with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 13 (Climate Action) and SDG 14 (Life Below Water).
Challenges Facing the High Seas Treaty
- Lack of Ratification: Geopolitical tensions slow the ratification process, with only 15 of 105 signatories having approved it.
- Disputes over Maritime Territories: Ongoing territorial disputes complicate the establishment of MPAs, as nations fear loss of sovereignty.
- Implementation Gaps: The treaty lacks clear guidelines and enforceable measures for effective implementation, which may hinder compliance.
Addressing Implementation Gaps
- Integration of Governance: A cohesive framework linking high-seas management with coastal regulations is necessary for effective governance.
- Incentivizing Compliance: Providing technical and financial support to developing nations can enhance capacity-building efforts.
- Strengthening Enforcement: Establishing robust monitoring mechanisms and enhancing transparency can improve accountability.
In summary, the High Seas Treaty represents a pivotal step towards sustainable ocean governance. Its successful implementation is essential for protecting marine biodiversity and ensuring the equitable use of ocean resources, particularly for countries like India that rely on the blue economy for their livelihoods.
11th ADMM Meeting-Plus and Buddhism
Why in News?
India’s Defence Minister recently addressed the ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) forum in Vientiane, Lao PDR. He emphasized the significance of Buddhist principles in conflict resolution and celebrated a decade of India's Act East Policy (AEP).
Key Takeaways
- India highlighted the importance of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), 1982, for freedom of navigation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Advocated for a Code of Conduct that aligns with international law to protect the rights of nations.
- Called for peaceful coexistence in an increasingly polarized world.
- Promoted open communication to foster trust and cooperation in addressing border disputes and trade agreements.
- Described the 21st century as the 'Asian Century,' recognizing ASEAN's economic dynamism.
- Highlighted the success of the Act East Policy in strengthening ties with Indo-Pacific nations.
- Proposed an ADMM-Plus Defence Strategy on Climate Change to address security and environmental challenges.
- Emphasized the importance of safeguarding global commons, including the high seas, atmosphere, Antarctica, and outer space.
What is ADMM-Plus Forum?
- About: A multilateral defence cooperation framework consisting of the defence ministers from the 10 ASEAN member states, 8 Plus countries (dialogue partners), and Timor Leste.
- ASEAN Members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam.
- 8 Dialogue Partners: China, Russia, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, and the US.
- Establishment: The inaugural ADMM-Plus was convened in Ha Noi, Vietnam, on 12 October 2010.
- Focus Area: Currently focuses on maritime security, counter-terrorism, humanitarian assistance and disaster management, peacekeeping operations, military medicine, humanitarian mine action, and cyber security.
What is the Role of Buddhist Ideals in Conflict Resolution?
- Buddhist Perspectives: Key perspectives include the belief that everyone is a Buddha, the power of dialogue for understanding, and the importance of inner transformation to reduce anger, greed, hatred, and delusion.
- Adhikaraṇasamathadhamma: Guidelines for resolving monks' conflicts from the Vinaya Pitaka, applicable to personal and political reconciliation.
- Middle Path (Madhyam Marg): Advocates for balanced policies that cater to all stakeholders, promoting equitable solutions.
- Interdependence (Pratītyasamutpāda): Encourages mutual understanding and shared responsibility among nations for global issues like climate change.
- Karuna (Compassion): Focuses on humanitarian aid and addressing the root causes of suffering in conflict zones.
What is India’s Act East Policy (AEP)?
- It is a strategic initiative aimed at enhancing India's engagement with Southeast Asia, East Asia, and the broader Indo-Pacific region, evolving from the Look East Policy of 1992.
- Strategic Partnerships: India has established strategic partnerships with key countries in the region, including Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Australia, and Singapore.
- Regional Engagement: Actively involved in ASEAN Regional Forum, East Asia Summit, BIMSTEC, Asia Cooperation Dialogue, Mekong Ganga Cooperation, and Indian Ocean Rim Association.
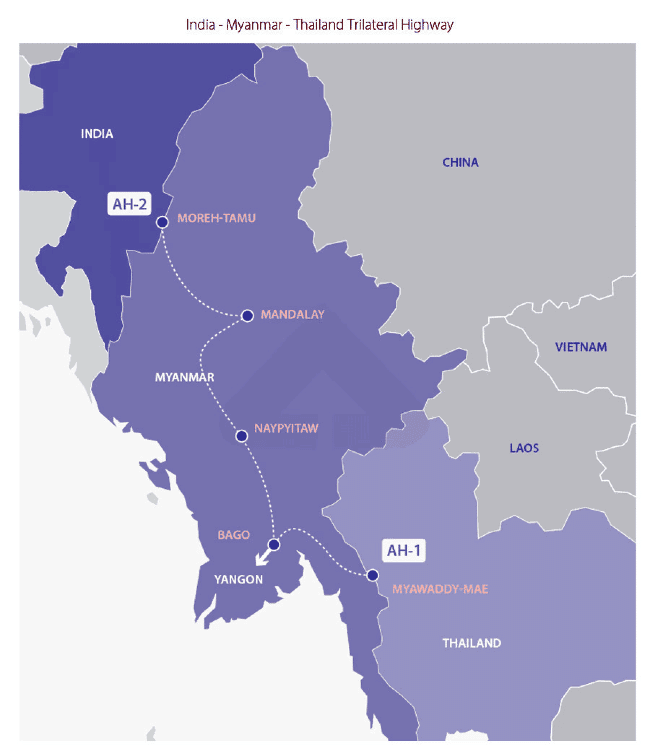
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Major projects include the Kaladan Multi-modal Transit Transport Project and the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway Project.
- Security Cooperation: A shared commitment to uphold international maritime laws and promote regional stability.
- Northeast India: Enhancing connectivity between Northeast India and ASEAN through trade and infrastructure development.
In conclusion, India's participation in the ADMM-Plus underscores its commitment to regional peace, security, and cooperation. The emphasis on Buddhist principles for conflict resolution, the success of the Act East Policy, and strategies to address climate change reflect India's broader vision for a peaceful, integrated, and sustainable Indo-Pacific region.
|
44 videos|5283 docs|1115 tests
|





















