Internal Security - 1 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill 2024
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Maharashtra government proposed a comprehensive new law, the Maharashtra Special Public Security (MSPS) Bill, 2024, which aims to address the increasing presence of Naxalism in urban areas. The Bill has generated significant controversy and debate due to its broad and stringent provisions.
Key Takeaways
- The MSPS Bill is designed to combat the infiltration of Naxalism into urban settings.
- It allows the government to declare any organization unlawful based on its activities.
- Penalties for violations include imprisonment for 2-7 years and fines ranging from Rs 2-5 lakh.
- The Bill facilitates faster prosecution by enabling district magistrates or police commissioners to grant permissions.
Additional Details
- Background: The government asserts that Naxalism, previously limited to remote regions, is now using urban organizations for logistics and safe havens for armed cadres. Existing laws, such as the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA) and the Maharashtra Control of Organised Crime Act (MCOCA), are considered insufficient to counter this evolving threat. The MSPS Bill is modeled after similar legislation in states like Chhattisgarh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Odisha.
- Comparison with UAPA: While the UAPA targets unlawful activities, the MSPS Bill broadens the definition of 'unlawful activity' to include actions that disrupt public order and generate fear. The prosecution process is simplified under the MSPS Bill, which the government argues will reduce delays.
- Criticisms: Critics highlight the vagueness of terms like 'menace to public order,' which could lead to misuse. Concerns have been raised about potential threats to civil liberties, particularly regarding the targeting of activists and journalists.
- Judicial Oversight: Unlike the UAPA, which requires a High Court judge-led tribunal to confirm declarations of unlawful organizations, the MSPS Bill's process relies on an advisory board of former judges, raising issues about adequate judicial oversight.
- Social Implications: The broad definitions could criminalize legitimate protests and criticism of the government, potentially leading to increased activism from human rights organizations.
The Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, represents a significant shift in the state's approach to combating Naxalism. While the government defends it as a necessary measure against urban Naxalism, its broad provisions raise serious concerns regarding civil liberties and potential for misuse. Balancing public security with democratic freedoms will be essential in determining the Bill's future and its impact on Maharashtra's legal and social landscape.
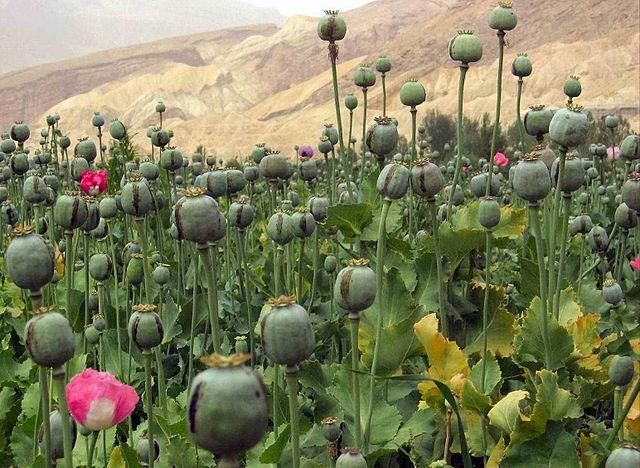
Opium Stockpiles in Afghanistan: Current Concerns
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent reports from the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) reveal serious issues regarding Afghanistan's large stockpiles of opium, despite the Taliban's prohibition on poppy cultivation.
Key Takeaways
- Afghanistan still possesses significant opium stockpiles, even after the Taliban's ban on poppy cultivation in April 2022.
- The full impact of this ban may take years to evaluate due to the existing stockpiles.
- No substantial decrease in drug exports has been observed, according to seizure data.
- Senior Taliban officials and influential traders, including the Haqqani Network, continue to profit from the narcotics trade.
- Key Taliban figures oversee various routes for narcotics trafficking.
- Production of methamphetamine has increased sharply, with notable amounts of fentanyl also being reported.
- Major production sites for methamphetamine are located in Farah, Herat, and Nimroz, with operational labs in Bahramcha, Dishu district, and Helmand province.
Additional Details
- Trafficking Networks: A significant portion of drugs trafficked to India originates from Afghanistan, with the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) of Pakistan controlling these networks.
- Terrorism Funding: The profits from drug sales are increasingly being utilized to fund anti-India terrorist groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT).
- Narcotics shipped from Afghanistan are processed in clandestine laboratories in Balochistan before being smuggled into India.
- Significant Seizures: Indian security agencies have established direct links between drug cartels based in Kandahar and smuggling operations. A notable seizure involved the National Investigation Agency (NIA) intercepting 3,000 kg of heroin at Mundra port in September 2021.
- Government Response: The Union Home Minister has called for a stringent approach against smuggling networks. The central government is also working on installing container scanners at all ports and border crossings to combat drug trafficking.
The ongoing challenges presented by Afghanistan's opium trade have serious implications for India's security and socio-economic stability. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive strategy that includes strengthening border security, enhancing international cooperation, and bolstering anti-narcotics efforts.
Rise in Militancy in Jammu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) has experienced a significant uptick in militant attacks since mid-2021. This escalation has included recent ambushes on Army vehicles in Kathua district and targeted strikes in other areas. This resurgence represents a departure from historical patterns and raises concerns regarding security vulnerabilities and the implications for regional stability.
Key Takeaways
- Notable increase in militant activities since 2021.
- Shift in security dynamics with implications for regional stability.
Additional Details
- Strategic Shift: The implementation of a zero terror policy in Kashmir has inadvertently allowed militants to operate more freely in Jammu. Troop redeployments in response to perceived low militancy in Jammu have provided militants opportunities to relocate.
- Strategic Importance of Jammu: Jammu is a critical gateway to the rest of India, making it a prime target for militants aiming to disrupt normalcy.
- Geostrategic Considerations: The proximity to the Line of Control (LoC) facilitates easier access for militants from Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, aiding infiltration and logistical support.
- Economic Disparities: Limited economic opportunities in remote areas contribute to recruitment by militant groups.
- Political Alienation: Perceived alienation among certain communities, fueled by historical grievances, can lead to sympathy for militant ideologies.
- Lack of Human Intelligence: Aging local informants and a disconnect with younger generations hinder effective intelligence gathering.
Challenges in addressing the rise in militancy include:
- Geographical Terrain: The difficult terrain along the 192-km international border in Jammu complicates security efforts.
- Community Relations: Building trust with local communities is crucial for effective intelligence gathering but remains a challenge due to historical grievances.
- Intelligence Gathering: The sophistication of militant communication methods complicates intelligence operations.
- External Support: Allegations of cross-border support from Pakistan, including weapons supply via drones, further complicate the situation.
- Communal Fault Lines: The demographic diversity in Jammu can lead to communal tensions, especially during periods of violence.
Way Forward
- Border Security Measures: Enhancing surveillance and fortifying vulnerable points along the border is essential to curb infiltration.
- Technological Advancements: Utilizing advanced surveillance technologies can improve monitoring of militant activities.
- Legal and Political Frameworks: Strengthening laws against terrorism financing and expediting the judicial process for terror cases are vital for effective counter-terrorism.
- Community Engagement: Socio-economic development initiatives and youth empowerment can help mitigate support for extremism.
- Diplomatic Outreach: Strengthening international cooperation on counter-terrorism can disrupt external support networks.
- Policy Review: Continuous evaluation and adaptation of security policies are necessary to address evolving militant tactics.
In summary, addressing the rise in militancy in Jammu requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses security enhancements, community engagement, and international cooperation. This comprehensive strategy is crucial to restoring stability in the region.
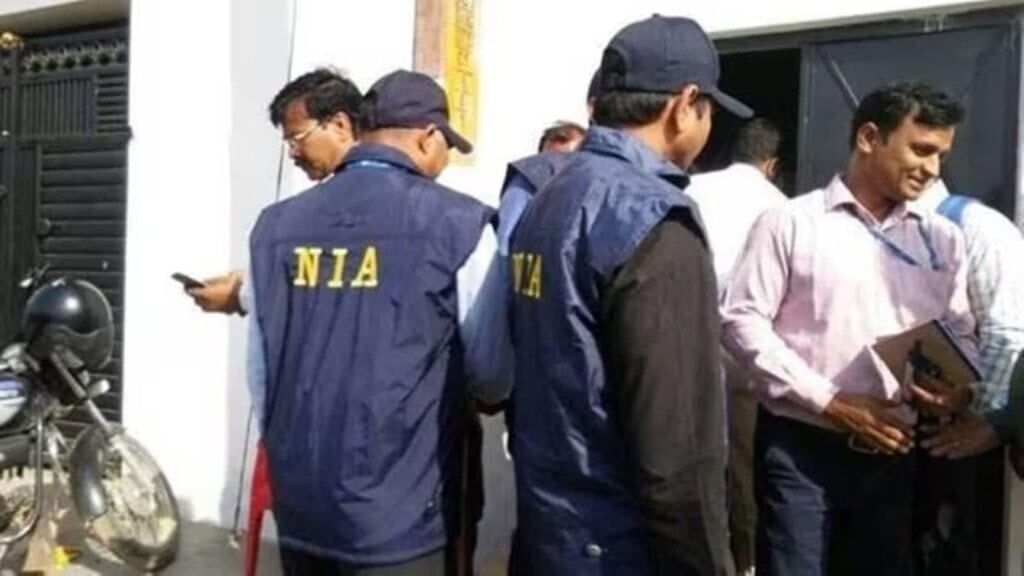
NIA's Combat Against the Terror-Gangster Nexus
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The National Investigation Agency (NIA) recently held its first meeting with police officials from Punjab, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Delhi to address the alarming issue of the terror-gangster nexus. This meeting follows a rise in organized crime connected to terrorist groups, especially those associated with Pro-Khalistan Elements (PKEs) and networks originating from Pakistan.
Key Takeaways
- The meeting aimed to map extortion calls from gangsters linked to terror syndicates.
- Discussions included the use of cyberspace for evasion and the involvement in drug smuggling.
- Central-state coordination was emphasized to create effective action plans and standard operating procedures (SOPs).
- The meeting aligns with directives from the Union Home Minister to enhance anti-terrorism structures under the NIA.
Additional Details
- Terror-Gangster Nexus: This term describes the collaboration between organized crime groups and terrorist organizations, sharing resources and tactics to achieve their objectives.
- Such alliances benefit both terrorism and organized crime, often involving international elements that facilitate their activities.
- In India, key conflict zones include Jammu and Kashmir, Northeastern states, Western India, and Punjab, where various groups exploit local conditions for criminal and terror-related activities.
- The NIA, established in 2008, is responsible for investigating terrorism-related offenses and operates independently across states without needing special permissions.
The rise of the terror-gangster nexus poses significant challenges to national security and law enforcement. Efforts to combat this issue require comprehensive legislative reforms, enhanced cooperation among agencies, and advanced technology to track and dismantle these networks effectively.
Supreme Court Halts Criminal Proceedings Against 30 Army Personnel in Nagaland
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has recently closed all criminal proceedings against 30 army personnel involved in a controversial operation in Nagaland that resulted in the deaths of 13 civilians. This decision follows the denial of prosecution sanction under the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA), which is required to pursue legal action against military personnel in such cases.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court ruled that without the necessary sanction, criminal proceedings could not continue.
- The incident in question involved a mistaken identity shooting by army commandos in December 2021.
- The court's order does not prevent the Army from taking disciplinary actions against the personnel involved.
Additional Details
- Background of the Incident: In December 2021, army personnel mistakenly opened fire on coal mine workers in Nagaland, killing six. This triggered violent protests, resulting in additional civilian casualties.
- Special Investigation Team (SIT): Formed to investigate the incident, the SIT indicted all involved personnel but could not proceed with prosecution due to the lack of sanction from the central government under AFSPA.
- Prosecution Sanction Requirement: Under AFSPA, prosecution of armed forces personnel requires prior approval from the Central Government, leading to the closure of the case when such approval was denied.
This ruling highlights the complex legal framework surrounding military operations in conflict zones and the challenges faced in seeking accountability for actions taken by armed forces personnel.
7th National Security Strategies Conference 2024
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Home Minister inaugurated the National Security Strategies Conference (NSSC) 2024 in New Delhi. The conference focused on addressing emerging national security challenges through discussions among top police leadership.
Key Takeaways
- The NSSC was conceived by the Prime Minister during the DGsP/IGsP Conference to find solutions to major national security challenges.
- The conference features a diverse group of participants, including young police officers and domain experts.
- A new dashboard by the National Crime Records Bureau was launched to aid in implementing decisions from the annual conference.
- Discussions emphasized a non-colonial approach to tribal issues, advocating for respect, inclusion, and empowerment.
- Multiple security challenges, including youth radicalization, narcotics trafficking, and security at non-major ports, were addressed.
Additional Details
- Diversity of Participants: The conference brought together young police officers and experts to tackle national security issues collaboratively.
- Focus on Tribal Issues: A non-colonial perspective on tribal grievances was discussed, moving away from Western models that historically marginalized these communities.
- Emerging Security Challenges: Key topics included the rise of fintech fraud, countermeasures against rogue drones, and the exploitation of mobile apps for criminal activities.
The NSSC 2024 has initiated crucial dialogues on how to better address national security challenges while ensuring the rights and dignity of tribal communities are respected. The conference underlines the necessity for a holistic approach in formulating strategies that not only focus on security but also emphasize civil rights and community empowerment.
Joint Doctrine for Amphibious and Cyberspace Operations
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, Chief of Defence Staff (CDS) General Anil Chauhan unveiled the Joint Doctrine for Amphibious Operations during the Chiefs of Staff Committee (COSC) meeting. This follows the earlier release of the Joint Doctrine for Cyberspace Operations by the CDS.
Key Takeaways
- The Joint Doctrine for Amphibious Operations serves as a keystone publication for military leaders.
- The doctrine enhances the Armed Forces' operational capabilities within the Indian Ocean Region.
- The Joint Doctrine for Cyberspace Operations addresses the complexities of modern warfare in the cyberspace domain.
Additional Details
- Joint Doctrine for Amphibious Operations: This doctrine provides essential guidance to commanders for conducting amphibious operations in a multifaceted military landscape. It facilitates the Armed Forces' ability to engage in a broad spectrum of operations during both wartime and peacetime situations.
- Joint Doctrine for Cyberspace Operations: This doctrine outlines the military aspects of cyberspace, emphasizing the need for strategic planning in a domain that includes various Information and Communication Technology (ICT) systems. It aims to raise awareness and provide direction for military personnel involved in cyberspace operations.
In conclusion, the release of these joint doctrines marks a significant step in enhancing the operational readiness and strategic capabilities of the Armed Forces, especially in the context of multi-domain military engagements.
Cyberfraud Costs 0.7% of GDP
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), operating under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), released significant projections regarding the impact of cyber frauds in India.
Key Takeaways
- Indians are projected to lose over Rs 1.2 lakh crore to cyber fraud by 2025, accounting for 0.7% of the nation's GDP.
- From January to June 2024, financial fraud led to losses of Rs 11,269 crore.
Additional Details
- Contributors to Cyber Fraud: Approximately 4,000 mule bank accounts are identified daily by I4C. Additionally, 18 ATM hotspots across the country have been pinpointed for fraudulent withdrawals. A mule account is a bank account used to facilitate illegal activities such as money laundering and fraudulent transactions.
- Origin of Scam: The government has located “scam compounds” in Southeast Asian countries like Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, with many scams traced back to China or Chinese-linked entities.
- Modus Operandi: International scam compounds operate similarly to call centers, targeting individuals through investment scams and duping them via methods like lottery schemes.
- Illegal Activities: Cyber scams can also facilitate terror financing and money laundering. For example, between March and May 2024, cryptocurrency worth Rs 5.5 crore was laundered using Indian accounts.
Cyber fraud represents a significant and growing threat, impacting various sectors of society, from individuals to businesses and government entities.
What is Cyberfraud?
Cyber fraud is a form of cyber crime aimed at stealing money or valuable assets from individuals or organizations through online methods.
Types of Cyberfraud
- Phishing: Involves deceptive emails that appear to come from trusted sources, tricking users into revealing sensitive information.
- Malware: Software designed to steal personal information, allowing cyber criminals to control a victim's computer.
- Ransomware: Encrypts files and demands payment for decryption, as seen in the 2016 WannaCry attack.
- Cyberbullying: Threats or coercion targeting an individual's safety.
- Cyber Spying: Unauthorized access to networks for classified data or private information.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Hacking legitimate email accounts to impersonate others for financial gain.
- Dating Hoodwinks: Exploiting dating platforms to access personal data by posing as potential partners.
Consequences of Cyber Fraud
- For Individuals: May lead to unauthorized purchases, financial account access loss, and personal distress due to data misuse.
- For Businesses: Companies risk heavy fines and legal repercussions if they fail to protect client data, which can also affect firm value and stock prices.
- For Government: Cyber breaches can endanger national defense and security by corrupting sensitive information.
What is the Scenario of Cyber Fraud in India?
India, with around 658 million internet users, boasts the world's second-largest internet population. According to the “ThreatLabz 2024 Phishing Report” by Zscaler, India ranks third globally for phishing attacks, following the US and UK.
Commitment to Cybersecurity
India has achieved Tier 1 status in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2024 by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) with a score of 98.49 out of 100, showcasing a strong commitment to global cybersecurity practices.
Notable Cyberfraud Incidents
- Aadhar Data Breach (2018): Compromised personal data of 1.1 billion Aadhar cardholders.
- Canara Bank ATM Attack (2018): Hackers utilized skimming devices on 300 debit cards, stealing over Rs 20 lakh.
- Pegasus Spyware: This tool was used to collect data from devices without user consent, impacting over 300 verified Indian phone numbers.
What can be Done to Address Cyber Fraud?
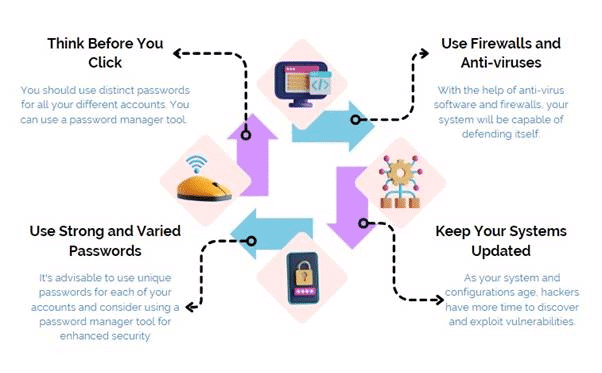
- Adopt Cybersecurity Best Practices: Implement firewalls, keep software updated, and be cautious of unsolicited communications.
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Role of Banks: Banks should monitor for unusual transactions and alert authorities to prevent money laundering.
- System Upgrades Needed: Banks should enhance systems to detect multiple logins from a single IP address, especially from abroad.
- For Content Creators: Invest in creator insurance to protect against potential financial losses due to data breaches.
|
38 videos|5314 docs|1124 tests
|





















