Ethics: Public Infrastructure and Public Service Delivery | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Public Service Delivery |

|
| Measures for Good Governance |

|
| Characteristics of New Public Management (NPM) |

|
Introduction
Bihar has recently witnessed the collapse of over 15 bridges, leading to the suspension of around 15 engineers due to negligence and poor monitoring. This incident raises concerns about the quality of public infrastructure and the government's ability to ensure effective public service delivery.
The collapse of bridges in Bihar is not an isolated incident. It echoes previous failures like the Morbi bridge collapse in Gujarat in 2022, roof collapses at airports in Delhi, Rajkot, and Jabalpur, and the railway collision involving the Kanchanjunga Express and a container freight train.
These incidents highlight a troubling trend of compromised quality in public infrastructure across the country.
The government’s role in providing quality public services is crucial, and these failures raise questions about its effectiveness in fulfilling this responsibility.
Public Service Delivery
Public service delivery refers to the process through which various services are provided to the public by the government at different levels, including local, municipal, and federal.
Examples of public services include sewage and trash disposal, public education, and health services.
This mechanism serves as a tangible link between the government and citizens, fostering national values and ensuring the well-being of the population.
Significance of Public Service Delivery
- Economic Growth: Effective public service delivery is crucial for poverty alleviation, human capital formation, and reducing corruption. These factors are essential for driving economic growth and development.
- Equitable Resource Distribution: Public service delivery helps reduce inequalities based on gender, caste, and other factors. For example, targeted service delivery through the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS) ensures food security for vulnerable populations.
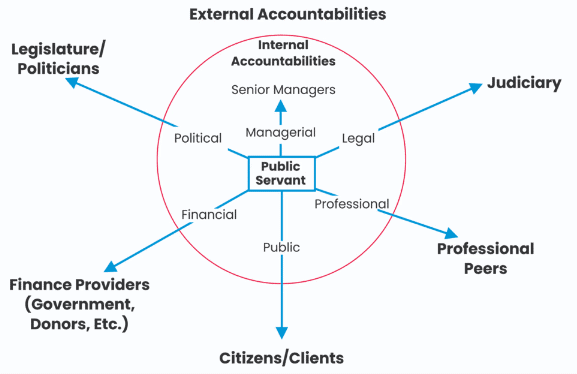
Ethical Issues in Infrastructure Development
- Inefficient Administrative Machinery:. weak administrative setup hinders the effective implementation of development plans, leading to negligence of responsibilities.
- Policy Issues: There is often a neglect of service delivery quality, with a focus on merely completing the minimum requirements of assigned duties.
- L1 Contract Method: This approach, which prioritizes the lowest bidder, compromises quality and safety in infrastructure projects.
- Corruption: Misuse of discretion by public officials creates a nexus between officials, contractors, and other stakeholders, undermining the integrity of service delivery.
- Lack of Probity: Mechanisms for ensuring accountability and transparency are either lacking or poorly implemented. Public servants often evade responsibility for ensuring quality service delivery.
- Attitudinal Issues: Indifference and lack of motivation among public servants contribute to poor service delivery and a lack of commitment to excellence.
Ethical Issues in Public Service Delivery
- Lack of Professional Ethics: Public servants may lack the necessary managerial skills and ethical values to ensure effective service delivery.
- Public Service Attitude: Some public servants prioritize personal gains over their duty to serve the public, leading to favoritism and patronage based on social status.
- Corruption: Unethical use of power and discretion, such as leakages in the Public Distribution System (PDS) and errors in scheme inclusions and exclusions, undermine service delivery.
- Accountability and Transparency: Inconsistent treatment of malafide errors weakens deterrence against corrupt practices, allowing unethical behavior to persist.
ARC Seven Step Model for Citizen Centricity
- Define Services and Clients: Clearly outline the services provided and identify the target clients.
- Set Standards and Norms: Establish benchmarks for each service to ensure quality and consistency.
- Develop Capability: Build the necessary capacity to meet the established standards.
- Performance Achievement: Strive to meet and exceed the set standards in service delivery.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly monitor performance against the established standards to ensure accountability.
- Impact Evaluation: Assess the impact of services through an independent mechanism to ensure objectivity.
- Continuous Improvement: Use monitoring and evaluation results to drive continuous improvement in service delivery.
Case Studies in Public Service Delivery
- Commission for Right to Services: States like Maharashtra, West Bengal, and Punjab have established commissions to ensure the right to services for citizens.
- Right to Public Services Legislations: More than 20 states, including Haryana, have passed legislation to guarantee timely public services to citizens.
Reasons for Persistent Issues in Public Service Delivery
- Lack of Effective Implementation: Various service improvement systems and regulations for civil servants are not effectively implemented, leading to persistent issues.
- Rigidity in Administration: There is a resistance to reforms and change within the administration, hindering progress.
- Political Constraints: Political interests often take precedence over public interests, affecting equitable public service delivery.
- Neglect of Grassroot Bureaucracy Reforms: Most reforms focus on higher levels of bureaucracy, neglecting the need for ethical improvements at the grassroots level.
Measures for Good Governance
- Administrative Reforms: Implement measures like Citizen's Charters, responsive grievance redressal mechanisms, and accountability frameworks for public servants.
- New Public Management (NPM): Adopt efficient practices from the private sector in public sector management, focusing on results and citizen-centric approaches.
- Human Capital Development: Recruit and train capable public servants with a focus on ethical values and public service commitment.
- Grassroot Bureaucracy Sensitization: Sensitize grassroots bureaucrats, who are the direct link to public service delivery, to ethical and effective service standards.
- E-Governance: Optimize technology adoption to enhance service quality, public fund utilization, and citizen access to services. Examples include SMART governance and the 'Aaple Sarkar' App in Maharashtra.
- Project Implementation Monitoring: Conduct regular audits at multiple levels to ensure project quality and accountability, as seen in initiatives like PRAGATI.
Characteristics of New Public Management (NPM)
- Strategic Policy and Operational Management Separation: Distinguish between strategic policy formulation and operational management to enhance efficiency.
- Result Orientation: Focus on achieving results while maintaining attention to processes and procedures.
- Citizen-Centric Orientation: Prioritize the interests of citizens over those of organizations or bureaucrats in service delivery.
- Provider to Enabler Shift: Increase the involvement of private and voluntary sectors in service delivery and strategic decision-making, such as contracting-out and public-private partnerships (PPPs).
- Entrepreneurial Management Culture: Foster an entrepreneurial culture in public management, adopting practices like Total Quality Management (TQM) and quality standards such as IS 15700:2005.
Conclusion
The role of government in service delivery is increasingly vital in a rapidly changing world. To meet the evolving needs of citizens, governance structures must transition from rigid bureaucratic hierarchies to flexible, multi-level institutions.
These institutions should integrate civil society and bridge the gap between government and citizens, ensuring responsive and effective public service delivery.
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|
FAQs on Ethics: Public Infrastructure and Public Service Delivery - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is public service delivery and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the key measures for good governance in public service delivery? |  |
| 3. How does New Public Management (NPM) influence public service delivery? |  |
| 4. What role do ethics play in public infrastructure and service delivery? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of effective public service delivery systems? |  |















