Lenz's Law | Physics Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Lenz’s Law? |

|
| Lenz’s Law Formula |

|
| Lenz’s Law Applications |

|
| Lenz’s Law Experiment |

|
What is Lenz’s Law?
Lenz’s law states that
The induced electromotive force with different polarities induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux through the loop in order to ensure that the original flux is maintained through the loop when current flows in it.
Named after Emil Lenz, Lenz’s law depends on the principle of conservation of energy and Newton’s third law. It is the most convenient method to determine the direction of the induced current. It states that the direction of an induced current is always such as to oppose the change in the circuit or the magnetic field that produces it.
Lenz’s Law Formula
Lenz’s Law is reflected in the formula of Faraday’s law. Here the negative sign is contributed by Lenz’s law. The expression is –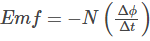
Where,
Emf is the induced voltage (also known as electromotive force).
N is the number of loops.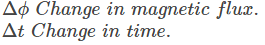
Lenz’s Law Applications
Lenz’s law applications are plenty. Some of them are listed below-
- Eddy current balances
- Metal detectors
- Eddy current dynamometers
- Braking systems on train
- AC generators
- Card readers
- Microphones
Lenz’s Law Experiment
To find the direction of the induced electromotive force and current we look to Lenz’s law. Lenz proved some experiments in accordance with his theory.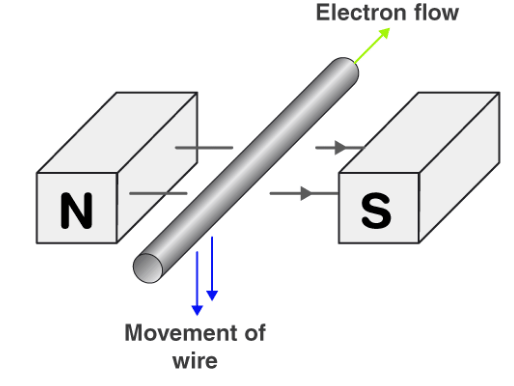
First Experiment
In the first experiment, he concluded that when the current in the coil flows in the circuit, the magnetic field lines are produced. As the current flow through the coil increases, the magnetic flux will increase. The direction of the flow of induced current would be such that it opposes the increase in magnetic flux.
Second Experiment
In the second experiment, he concluded that when the current-carrying coil is wound on an iron rod with its left end behaving as N-pole and is moved towards coil S, an induced current will be produced.
Third Experiment
In the third experiment, he concluded that when the coil is pulled towards the magnetic flux, the coil linked with it decreases, which means that the area of the coil inside the magnetic field decreases. According to Lenz’s law, the motion of the coil is opposed when the induced current is applied in the same direction.
To produce the current, force is exerted by the magnet in the loop. To oppose the change, the current on the magnet must exert a force on the magnet.
FAQs on Lenz's Law - Physics Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is Lenz's Law and how does it relate to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 2. What is the formula associated with Lenz's Law? |  |
| 3. What are some practical applications of Lenz's Law? |  |
| 4. Can you describe a simple experiment to demonstrate Lenz's Law? |  |
| 5. How is Lenz's Law relevant in the context of UPSC examinations? |  |



















