UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR) Portal
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The state of Telangana has been recognized as the leading state in India for the recovery of stolen and lost mobile phones through the Central Equipment Identity Register (CEIR) portal. This achievement highlights the effectiveness of the CEIR system in combating mobile phone theft.
Key Takeaways
- The CEIR portal was developed by the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Ministry of Communications.
- It serves as a central database for tracking lost or stolen mobile devices in India.
- The CEIR maintains records of all International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) numbers and Electronic Serial Numbers (ESN).
Additional Details
- IMEI Number: This is a unique 15-digit number assigned to every mobile handset, which is crucial for identification.
- Tracking Mechanism: Users can track their mobile devices by entering the IMEI number and providing details such as a copy of the First Information Report (FIR) on the CEIR portal.
- The CEIR is designed to work across all network operators, allowing for comprehensive tracking of devices even if the Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) is changed.
- Database Categories:
- White List: Contains authorized IMEI numbers permitted to access the network.
- Grey List: Holds IMEI numbers under observation.
- Black List: Lists unauthorized IMEI numbers that are blocked from network registration.
- Objectives of CEIR:
- To discourage mobile theft and protect consumer interests.
- To centralize the database for identifying and blocking lost or stolen devices.
- To track mobile phones via IMEI numbers, even when SIM cards are changed or deactivated.
- To establish infrastructure for mobile device tracking services.
- To connect with GSMA’s database for authenticating mobile devices.
- To identify duplicate, cloned, reprogrammed, or stolen devices.
The CEIR portal represents a significant advancement in mobile security and recovery efforts in India, aiming to enhance consumer protection and reduce mobile theft incidents.
GS1/Indian Society
International Booker Prize 2025
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
Banu Mushtaq, an accomplished Indian writer, lawyer, and activist, has made history by becoming the first author to win the International Booker Prize for her remarkable short story collection, Heart Lamp, written in Kannada.
Key Takeaways
- Banu Mushtaq is the first Kannada author to receive the International Booker Prize.
- The prize is awarded annually for outstanding works of fiction translated into English.
- Heart Lamp highlights the struggles faced by Muslim women in southern India.
Additional Details
- About the International Booker Prize: This prestigious award celebrates the best long-form fiction or collections of short stories translated into English and published in the UK and/or Ireland.
- History: Founded in 2005, it initially recognized works irrespective of their original language. In 2015, the rules changed to focus specifically on translations from other languages into English.
- Prize Money: The total prize fund of £50,000 is split equally between the author and the translator, with shortlisted candidates receiving £2,500 each.
- 2025 Winner: Heart Lamp, translated by Deepa Bhasthi, is notable for being the first collection of short stories to win this award, encompassing stories written between 1990 and 2023.
Banu Mushtaq's achievement not only underscores her literary talent but also brings attention to the vital narratives surrounding Muslim women in India. The International Booker Prize continues to highlight the essential role of translators in making world literature accessible to English-speaking audiences.
GS2/Polity
The Justice Yashwant Varma Case and the Legacy of the Veeraswami Judgment
Source: The Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent inquiry into Justice Yashwant Varma by the Supreme Court has sparked controversy. Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar has raised concerns about the constitutional validity of this in-house inquiry and has called for a reevaluation of the K Veeraswami judgment, reigniting discussions on judicial accountability and the potential for criminal prosecution of judges.
Key Takeaways
- Unaccounted cash was discovered at Justice Yashwant Varma's residence in March 2024.
- The Supreme Court's in-house inquiry found him culpable, but it dismissed calls for an FIR and criminal investigation.
- The Vice President criticized the inquiry as lacking legal foundation and urged for an FIR based on the findings.
Additional Details
- Judicial Independence vs Accountability: The Constitution protects judicial independence, allowing removal of judges only through impeachment (Article 124(4) for Supreme Court judges and Article 217 for High Court judges) for proven misbehavior or incapacity.
- In-house Inquiry Mechanism: Established by the Supreme Court to handle complaints against judges without resorting to impeachment, this mechanism has limitations, including the inability to enforce removal, only recommending action.
- The Veeraswami Judgment (1991): This landmark ruling addressed whether judges could be prosecuted under the Prevention of Corruption Act, concluding that while judges can be treated as public servants, prosecution requires sanction from the Chief Justice of India to prevent executive overreach.
- Post-Veeraswami, sanctions for criminal proceedings against judges are rare, with notable instances such as the 2019 FIR against Justice S N Shukla for misconduct.
The case of Justice Yashwant Varma highlights ongoing tensions between judicial independence and public accountability. While internal mechanisms exist to maintain judicial integrity, their effectiveness and transparency are often questioned. There is a growing call for reforms that allow for responsible criminal investigations without executive interference to foster a better balance.
GS1/History & Culture
INSV Kaundinya: A Symbol of Ancient Maritime Heritage
Source: The Indian Express
Why in News?
The Indian Navy has welcomed the INSV Kaundinya, a reconstructed ship inspired by 5th-century designs depicted in the Ajanta Cave paintings. This initiative aims to celebrate India's historic shipbuilding practices and enhance awareness of its maritime legacy.
Key Takeaways
- INSV Kaundinya was launched in July 2023 under a tripartite agreement involving the Ministry of Culture and Hodi Innovations.
- The ship will navigate an ancient maritime trade route from Gujarat to Oman in 2025.
Additional Details
- Traditional Shipbuilding Techniques: The ship employs ancient “stitched ship” methods, where wooden planks are secured with coir ropes, coconut fibers, and natural resin, eliminating the need for metal nails.
- The design process involved interpreting 2D representations from the Ajanta murals through archaeological and naval architectural analyses, as there are no existing blueprints.
- Symbolism and Cultural Integration: The ship’s sails feature motifs such as the 'Gandabherunda' (a mythical two-headed eagle) and the Sun, symbolizing strength and vitality. The bow is adorned with a 'Simha Yali' (a mythical lion-like figure), reflecting traditional South Indian maritime art.
- A Harappan-style stone anchor on the deck links the ship to India’s Indus Valley maritime heritage.
- The name 'Kaundinya' honors a legendary Indian sailor known for reaching Southeast Asia, underscoring India's historical role in transoceanic trade and cultural interchange.
The INSV Kaundinya not only represents India's ancient shipbuilding tradition but also serves as a vessel for promoting maritime heritage and cultural pride.
GS2/Governance
DoT Introduces Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI)
Source: The Indian Express
Why in News?
In a significant effort to combat cyber fraud and financial crimes, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has launched the Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI) as part of its Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP).
Key Takeaways
- The FRI is designed to assess the risk level of mobile numbers for financial fraud.
- DIP facilitates real-time information sharing among various stakeholders.
- Access to the DIP is restricted to authorized entities only.
Additional Details
- Digital Intelligence Platform (DIP):This integrated platform allows for secure, real-time intelligence sharing among various stakeholders, including:
- Telecom Service Providers (TSPs)
- Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs)
- Banks and Financial Institutions
- Social Media Platforms
- Identity Document Issuers
- Financial Fraud Risk Indicator (FRI):A risk-based tool that categorizes mobile numbers into Medium, High, or Very High risk based on potential for financial fraud. It utilizes data from:
- National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP)
- DoT's Chakshu Platform
- Banking institutions
- The system enhances security measures for Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and UPI service providers by identifying high-risk numbers.
- Through its Digital Intelligence Unit (DIU), the system shares a Mobile Number Revocation List (MNRL) for reasons such as cybercrime and failed verification, allowing for prompt action against fraudulent activities.
PhonePe's adoption of the FRI system exemplifies its effectiveness in preventing fraud. The platform allows PhonePe to block transactions linked to Very High-risk numbers and issue proactive warnings for Medium-risk numbers. The accuracy of this tool has been validated through its successful identification of fraud-related mobile numbers.
GS2/International Relations
Water, Warfare, and the Future of Bilateral Diplomacy
Source: Times of India
Why in News?
The recent suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) between India and Pakistan, following the Pahalgam terrorist attack, has sparked renewed discussions on the use of shared natural resources like water as geopolitical tools. This situation raises significant concerns regarding legality, sustainability, and India's international credibility.
Key Takeaways
- The Indus Waters Treaty is central to India-Pakistan water relations.
- India's hydropower projects have become points of contention amid rising tensions.
- Unilateral withdrawal from the treaty poses legal and diplomatic risks for India.
Additional Details
- Background of the Indus Waters Treaty: Established in 1960, the IWT was brokered by the World Bank to manage water distribution between India and Pakistan after the 1947 partition. It allocates the eastern rivers (Ravi, Beas, Sutlej) to India and the western rivers (Indus, Jhelum, Chenab) to Pakistan, allowing India limited uses for hydropower generation under strict conditions.
- Durability of the Treaty: The IWT has endured despite multiple conflicts, including three wars and various diplomatic crises, owing to its technical structure and the establishment of the Permanent Indus Commission for dispute resolution.
- India's Hydropower Projects: The Kishanganga and Ratle projects have become contentious as Pakistan accuses India of treaty violations, while India maintains compliance. Legal disputes are ongoing, with differing preferences for arbitration methods complicating resolution.
- Risks of Unilateral Withdrawal: Exiting the treaty would harm India's reputation as a responsible power, trigger potential World Bank interventions, and alarm neighboring countries. Legally, the IWT lacks a withdrawal clause, making any exit difficult and ethically problematic due to the humanitarian implications for Pakistan's downstream communities.
In conclusion, while it is crucial to consider strategic interests in geopolitics, the Indus Waters Treaty illustrates the necessity for shared responsibility regarding natural resources. India's strength lies in demonstrating moral and legal leadership by prioritizing cooperation over coercive measures.
GS3/Environment
International Day for Biological Diversity (IDB)
Source: World Economic Forum
 Why in News?
Why in News?The International Day for Biological Diversity is observed annually on May 22 to raise awareness of the critical need to take action to protect biodiversity.
Key Takeaways
- IDB is celebrated every year on May 22.
- The theme for IDB 2025 is “Harmony with nature and sustainable development.”
- The day emphasizes the connection between biodiversity and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Additional Details
- 2025 Theme: The theme highlights the importance of aligning the efforts to protect biodiversity with the global agenda outlined in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- History of IDB: The United Nations designated May 22 as IDB to commemorate the adoption of the Convention on Biological Diversity on May 22, 1992. This change from the original date of December 29 was made to facilitate better planning for celebrations, considering the number of holidays during that period.
This year's observance aims to reinforce the linkages between the SDGs and the goals of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, advocating for their simultaneous advancement as part of a broader commitment to sustainable development.
GS3/Science and Technology
SWOT Satellite: Measuring River Flood Waves
Source: Frontiners
Why in News?
In a groundbreaking achievement, NASA and Virginia Tech researchers have successfully utilized data from the SWOT satellite to measure the speed and height of flood waves on U.S. rivers.
Key Takeaways
- The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite was launched in 2022 as a collaborative mission between CNES (French Space Agency) and NASA.
- SWOT employs a specialized instrument known as the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) to accurately measure the height, width, and elevation of various surface water bodies.
- The satellite can monitor over 55% of large-scale global floods during their lifecycle through its frequent Earth orbits.
Additional Details
- What are River Waves? River waves, also called flood or flow waves, are temporary surges in water flow typically triggered by intense rainfall, snowmelt, ice jams, or dam breaches.
- Unlike ocean waves, which are driven by wind and tides, river waves are transient phenomena that can span tens to hundreds of kilometers.
- These waves are ecologically significant, as they transport nutrients and organisms, but they also present flood risks to downstream communities.
- Previously, the detection of such large-scale waves was limited to local ground stream gauges, which are sparse in many regions around the world.
This innovative use of SWOT satellite data enhances our understanding of river dynamics and flood management, providing crucial insights for environmental monitoring and disaster preparedness.
GS2/Governance
Key Facts about Polavaram Project
Source: Finshots
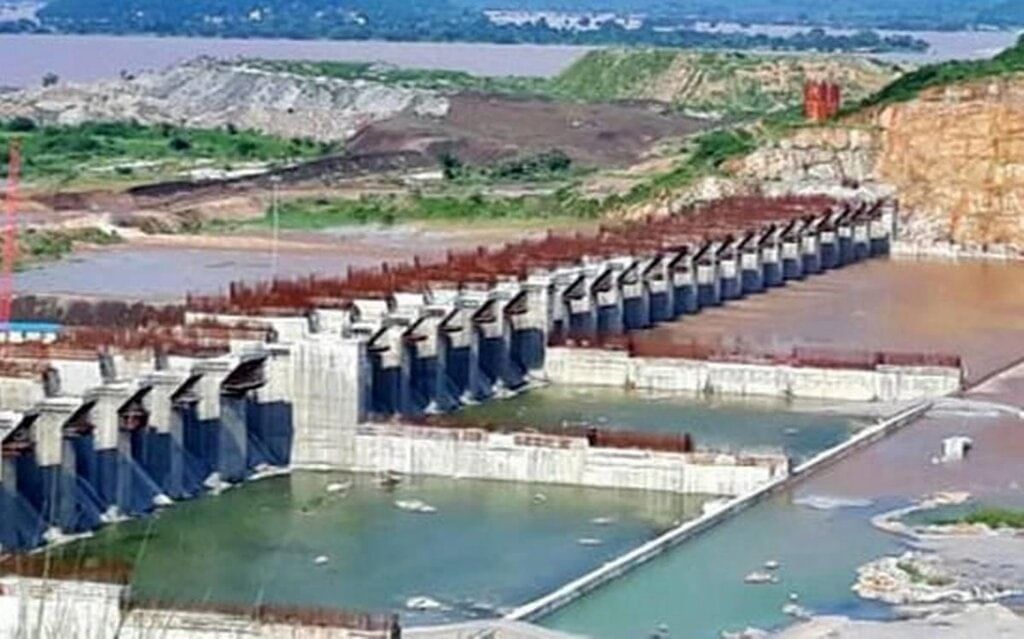 Why in News?
Why in News?The Prime Minister is set to chair a crucial meeting with the Chief Ministers of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh to discuss the ongoing developments and implications of the Polavaram project.
Key Takeaways
- The Polavaram project is a multi-purpose irrigation initiative located on the Godavari River.
- Conceived in 1980, it aims to enhance agricultural productivity and address water scarcity.
- The project has been accorded national project status by the central government.
- The dam will be constructed near Polavaram village in the West Godavari district of Andhra Pradesh.
- It is designed to manage significant floodwaters and has a discharge capacity set to surpass the 3 Gorges Dam in China.
Additional Details
- Dam Specifications: The dam spans approximately 1.2 km with a pier height of 54 m and features 48 radial gates (16m x 20m).
- Flood Management: The Polavaram Spillway is engineered to withstand massive floods occurring once in a 1000-year cycle, boasting the highest discharge capacity in the world at 50 lakh cusecs.
- Concrete Usage: The project set a world record by pouring 32,315.5 cubic metres of concrete into the spillway channel.
- The project aims to develop an irrigation potential of 4,36,825 hectares, generate 960 MW of hydropower, and provide drinking water to approximately 28.50 lakh people across 611 villages.
- Additionally, it seeks to transfer 80 TMC (Thousand Million Cubic Feet) of water from the Godavari to the Krishna river basin, helping manage floodwaters from the Godavari River and mitigating risks to nearby communities.
The Polavaram project represents a significant step towards improving irrigation and water management in the region, with wide-ranging benefits for agriculture and local communities.
GS3/Environment
Kākāpō Conservation Efforts
Source: DTE
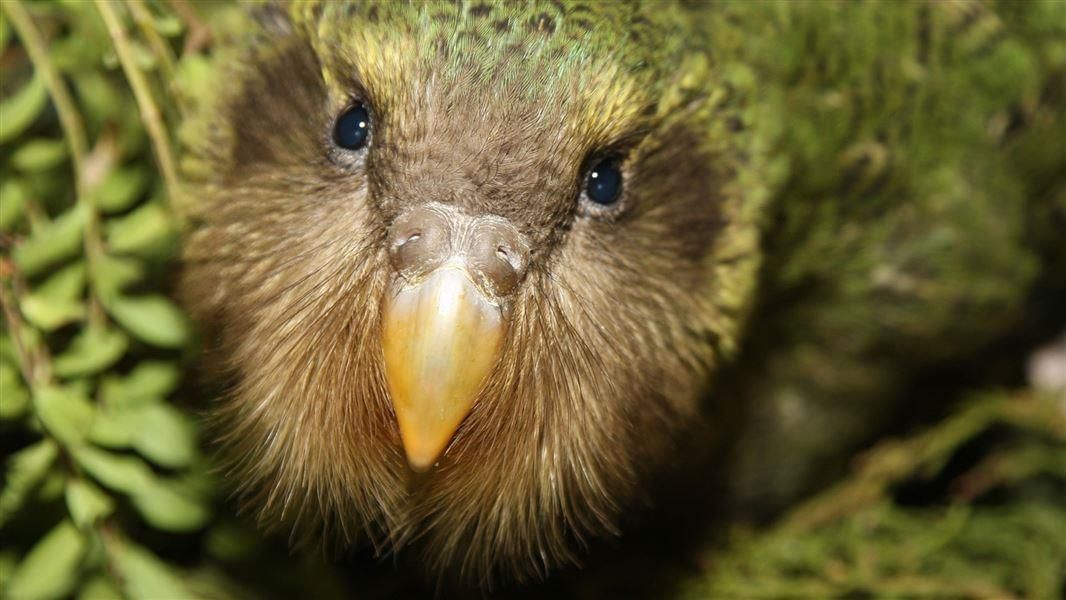 Why in News?
Why in News?A collaborative team from Justus Liebig University Giessen (Germany), New Zealand’s Department of Conservation, Kakapo Recovery, and the University of Otago has successfully employed artificial insemination (AI) to aid in the breeding of the critically endangered Kākāpō.
Key Takeaways
- The Kākāpō is the largest flightless parrot in the world.
- This species is native to New Zealand and is known for its nocturnal and herbivorous behavior.
- The Kākāpō exhibits unique lek-breeding behavior.
Additional Details
- Kākāpō (Strigops habroptilus): The Kākāpō is characterized by its owl-like face, moss-green plumage mottled with yellow and black, a grey bill, and grey legs with pale soles.
- Reproductive patterns: Kākāpō breed infrequently, typically only during years when certain native fruits, such as rimu berries, are plentiful.
- Lek-breeding behavior: Males create bowl-shaped depressions in the ground to amplify their mating calls over long distances.
- Threats to Survival: The Kākāpō faces several threats including predation from invasive mammals (like rats and stoats), infertility issues leading to high embryo mortality, and susceptibility to diseases such as aspergillosis.
- Due to these challenges, the Kākāpō is classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
The implementation of artificial insemination represents a significant step forward in the conservation efforts for this species, highlighting the importance of innovative solutions in wildlife preservation.
GS3/Science and Technology
Observation of Liquid Carbon's Atomic Structure
Source: Nature
 Why in News?
Why in News?For the first time, scientists have successfully observed the atomic structure of liquid carbon using the high-power DIPOLE 100-X laser alongside ultrashort X-ray pulses from the European XFEL (X-ray Free Electron Laser) in Germany. This breakthrough has significant implications for various scientific fields.
Key Takeaways
- Liquid carbon exists in a transient state, which is not stable under normal conditions.
- The study enhances understanding of planetary cores and high-energy astrophysical processes.
- Liquid carbon's formation requires extreme temperatures and pressures that are challenging to replicate in a laboratory.
Additional Details
- Liquid Carbon: This refers to carbon in a liquid state, which typically cannot exist naturally at standard temperature and pressure. It usually transitions from solid forms like graphite and diamond directly to gas.
- Challenges in Study: Carbon does not melt under normal pressure; instead, it sublimates, making laboratory studies of its liquid phase nearly impossible. Liquid carbon can only be formed under extreme conditions, such as temperatures around 4500°C and very high pressures.
- Experimental Technique: The DIPOLE 100-X laser was utilized to generate compression waves, briefly liquefying solid carbon for a billionth of a second. During this moment, the ultrashort X-ray pulse from the European XFEL irradiated the sample, allowing scientists to examine the atomic arrangement through the diffraction pattern.
- Findings: The study revealed that liquid carbon has a water-like structure with four nearest atomic neighbors, similar to solid diamond. This confirmed earlier theoretical simulations and helped to determine carbon's melting point under high pressure.
- Significance of Research: Understanding liquid carbon is crucial for planetary science, as it may exist in the interiors of planets, and for nuclear fusion technology, where carbon-based materials are often subjected to extreme conditions.
This groundbreaking research not only deepens our understanding of carbon's properties but also opens new pathways for advancements in planetary science and materials under extreme conditions.
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
















