Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Infographics: Metals and Non-metals
Infographics: Metals and Non-metals | Science Class 10 PDF Download
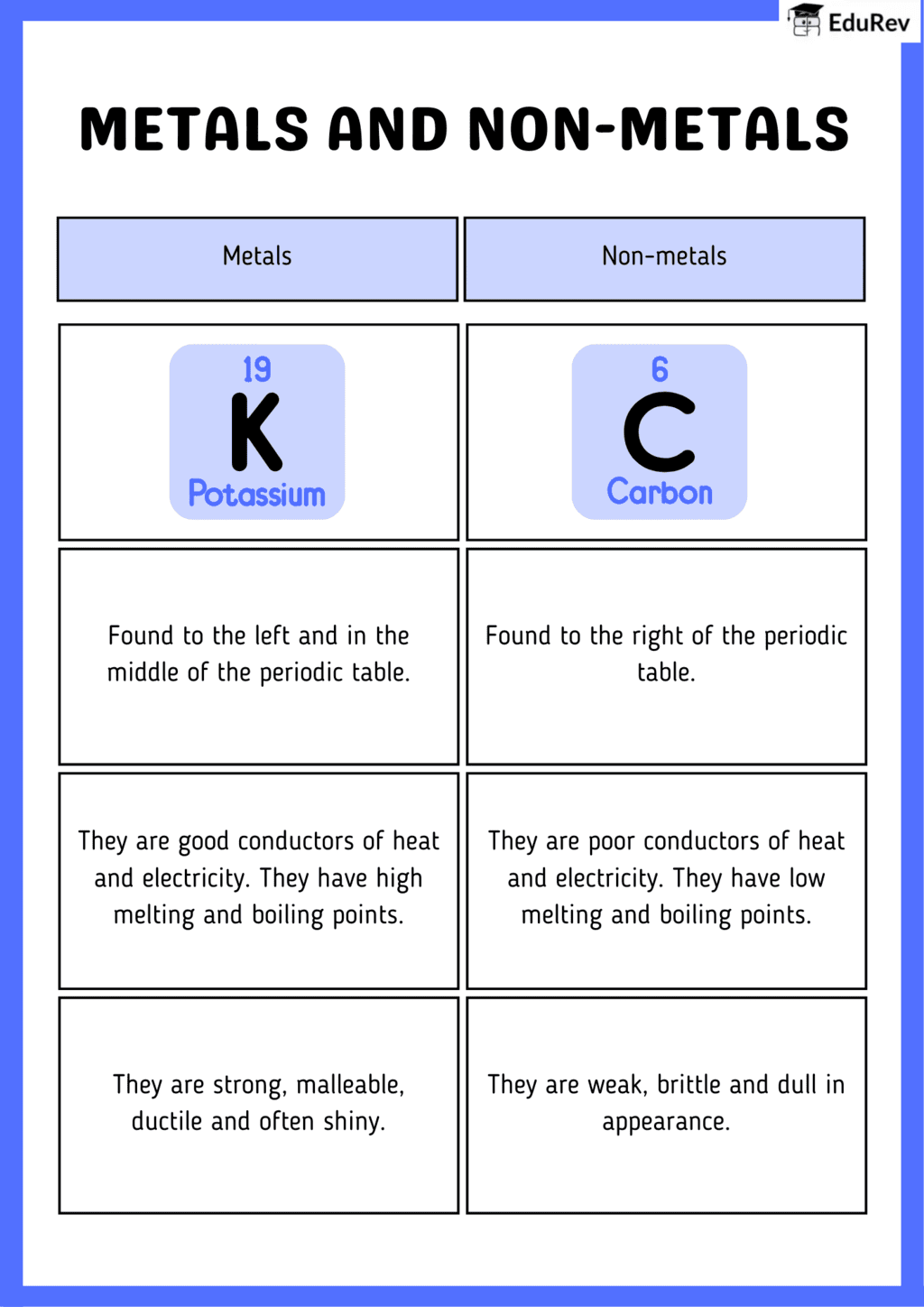
The document Infographics: Metals and Non-metals | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|567 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Infographics: Metals and Non-metals - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
Ans. The main differences between metals and non-metals are their physical and chemical properties. Metals are typically solid at room temperature (except mercury), have high melting and boiling points, are good conductors of heat and electricity, and are malleable and ductile. In contrast, non-metals can be gases, liquids, or solids, usually have lower melting and boiling points, are poor conductors of heat and electricity, and are more brittle in solid form.
| 2. How do metals and non-metals react with acids? |  |
Ans. Metals generally react with acids to produce hydrogen gas and a salt. For example, when zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, it forms zinc chloride and hydrogen. Non-metals, on the other hand, do not typically react with acids in the same way. Some non-metals can form acids when combined with oxygen (like sulfur forming sulfuric acid), but they do not release hydrogen gas when reacting with acids.
| 3. Can you give examples of common metals and non-metals? |  |
Ans. Common metals include iron, copper, aluminum, gold, and silver. These are widely used in construction, electrical wiring, and jewelry. Common non-metals include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and chlorine. Non-metals are essential for life and are found in various chemical compounds.
| 4. What are the uses of metals and non-metals in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Metals are used in a variety of applications, including construction (steel and aluminum), electronics (copper and gold for wiring), and transportation (aluminum and iron for vehicles). Non-metals are crucial for life and are used in products such as water (H2O), fertilizers (nitrogen and phosphorus), and disinfectants (chlorine).
| 5. How do metals and non-metals form compounds? |  |
Ans. Metals and non-metals form compounds through ionic or covalent bonding. Metals tend to lose electrons and form positively charged ions, while non-metals gain electrons to form negatively charged ions in ionic bonds. In covalent bonds, non-metals share electrons with each other or with metals. These interactions lead to the formation of various compounds, such as sodium chloride (table salt) and water.
Related Searches
















