Class 3 Exam > Class 3 Notes > Science Class 3 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Plants in the Surroundings
Plants in the Surroundings Chapter Notes | Science Class 3 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Inroduction |

|
| Parts of a Plant |

|
| Structure of a Seed |

|
| Kinds of Seeds |

|
| Germination |

|
| Care of Plants |

|
Inroduction
Plants play an important role in our lives as we depend on them for food, clothing, timber, medicine and other things. They also give out oxygen which we need for breathing. Hence, we can say that life would not be possible on the earth without plants.
There is a large variety of plants on our planet like trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers, creepers and aquatic plants. However, the basic structure/parts of majority of plants remain the same. Let's learn about the structure and various parts of plants.
Parts of a Plant
- Plants have two main systems: the root system and the shoot system.
- The root system grows below the ground and anchors the plant in the soil.
- The shoot system includes parts above the ground, such as the stem, branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
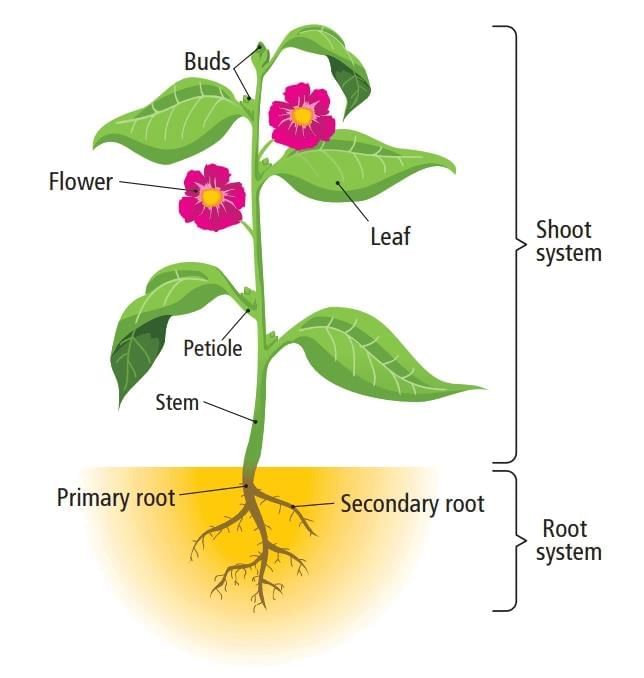
1. Root
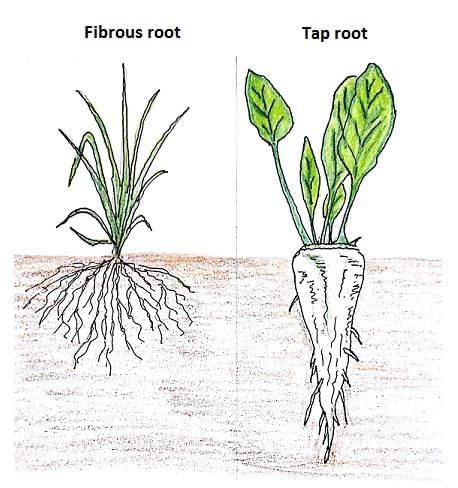
Types of Roots- Taproot: A single main root that grows straight down from the stem, with smaller roots branching out. Examples include bean, mustard, and carrot.
- Fibrous root: Many thin roots growing in all directions from the base of the stem, looking like a mass of fibers. Examples include grass, wheat, and onion.
Functions of the Root
- Anchors the plant firmly in the soil.
- Holds the soil together to prevent erosion.
- Absorbs water and minerals from the soil for the plant's growth.
- Some roots, like carrot, radish, and turnip, store food that we can eat.
- Banyan trees have special roots that grow from branches down to the ground.
2. Stem
- Trees have a strong, woody stem called a trunk.
- Shrubs have several thin, woody stems.
- Herbs have soft, thin stems.
- Climbers and creepers have weak, soft stems.
Functions of the Stem
- Keeps the plant upright and supports its parts.
- Carries branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Transports water and minerals from roots to other parts.
- Moves food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Some stems, like sugarcane, potato, and ginger, store food that we can eat.
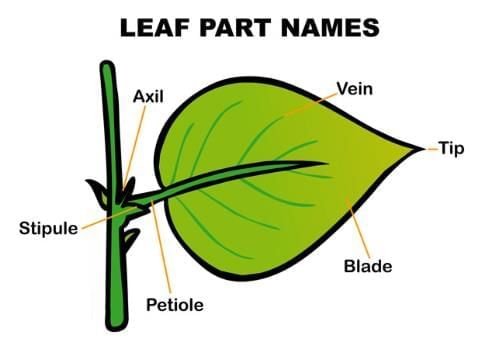
3. Leaf
- Lamina: The flat, broad part of the leaf, also called the leaf blade.
- Petiole: The stalk that connects the leaf to the stem, helping transport water and minerals. Some leaves do not have a petiole.
- Veins: Tiny channels that spread across the leaf, carrying water and minerals. The main vein, called the midrib, runs from the stalk to the leaf tip and divides the leaf into two parts.
- Stomata: Small openings on the leaf’s underside that allow gas exchange and release extra water.
Features of Leaves
- Leaves vary in color (green, red, purple, yellow, or orange).
- Leaves differ in size (large like banana, small like rose).
- Leaves vary in shape (long like Ashoka, needle-shaped like pines).
Functions of the Leaf
- Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that helps leaves absorb sunlight to make food through photosynthesis.
- Acts as the plant’s "food factory" by producing food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Helps exchange gases between the plant and the environment.
- Some leaves, like cabbage, lettuce, and spinach, store food that we can eat.
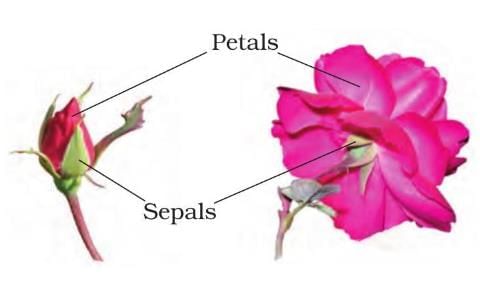
4. Flowers
- Petals: Soft, brightly colored parts that produce scent to attract or repel insects.
- Sepals: Green parts under the petals that protect the flower when it is a bud.
Functions of the Flower
- Develops into a fruit in most plants.
- Makes the plant attractive with its color, smell, and nectar, drawing birds, bees, and insects.
- Helps the plant reproduce.
- Pitcher plants have special trumpet-shaped leaves that trap insects.
5. Fruit
- Fruits develop from flowers and are the fleshy, edible parts of plants.
- Fruits contain seeds, which vary in number and size (e.g., few small seeds in an apple, one large seed in a mango, many small seeds in a pomegranate).
Functions of the Fruit
- Protects and encloses the seeds.
- Many fruits, like oranges, mangoes, and apples, are edible for humans.
6. Seed
- Seeds are small, hard structures usually found inside fruits.
- Seeds vary in size (small like grains, large like some seeds), shape (oval, spherical, kidney-shaped), and color (yellow, green, white, brown, etc.).
Functions of the Seed
- Gives rise to a new plant.
- Some seeds, like wheat, rice, corn, and gram, are edible and called edible seeds.
- Not all plants grow from seeds (e.g., banana).
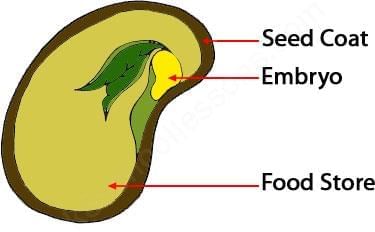
Structure of a Seed
- Seed coat: Hard outer covering with a tiny hole for water to enter, protecting the embryo.
- Embryo: The baby plant inside the seed that grows into a seedling with sunlight, air, food, and water.
- Cotyledons: Seed leaves inside the seed that store food for the new plant.
Kinds of Seeds
- Monocot seeds: Have one cotyledon, like corn, wheat, and rice. They produce plants with long, narrow leaves.
- Dicot seeds: Have two cotyledons, like beans, peas, and pulses. They produce plants with varied leaf shapes and sizes.

Germination
Process of Germination
- Germination is when a seed begins to grow into a new plant.
- Requires good soil, oxygen, water, warm temperature, and sunlight.

Steps:
- Seed absorbs water through a hole in the seed coat, causing it to swell and split.
- A tiny root grows downward, and a shoot grows upward toward light.
- A seedling with tiny leaves emerges from the soil.
- The seedling grows into a new plant.
- Some seeds need light to germinate, while others need darkness.
- Not all seeds germinate due to factors like flooding, heat, or being eaten by animals.
- Some seeds take longer to grow, and some are carried to new places by wind or rain.
Care of Plants
At Home
- Plant where they get enough sunlight.
- Water plants daily.
- Avoid stepping on young plants.
- Add manure to improve soil quality.
- Keep enough space between plants for growth.
At Public Places
- Do not pluck flowers or leaves.
- Do not scratch or write on tree trunks.
- Taking care of plants ensures they support our survival and environment.
Terms to Know
- Taproot: Single main root growing straight down from the stem’s base.
- Fibrous root: Many thin roots growing in all directions from the stem’s base.
- Shoot: Parts of the plant growing above the ground.
- Lamina: Flat, broad part of a leaf.
- Veins: Tiny channels on a leaf’s surface that carry water and minerals.
- Petiole: Stalk connecting the leaf to the stem or branch.
- Petal: Soft, colorful part of a flower.
- Sepal: Green part under petals that protects the flower bud.
- Seed coat: Hard outer covering of a seed.
- Embryo: Baby plant inside the seed.
- Cotyledons: Seed leaves that store food for the new plant.
- Monocot seed: Seed with one cotyledon.
- Dicot seed: Seed with two cotyledons.
- Germination: Process of a seed growing into a new plant.
The document Plants in the Surroundings Chapter Notes | Science Class 3 ICSE is a part of the Class 3 Course Science Class 3 ICSE.
All you need of Class 3 at this link: Class 3
|
44 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Plants in the Surroundings Chapter Notes - Science Class 3 ICSE
| 1. What are the main parts of a plant? |  |
Ans. The main parts of a plant include the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Stems provide support and transport nutrients and water between the roots and leaves. Leaves are the site of photosynthesis, where plants make their food. Flowers are involved in reproduction, and fruits contain seeds.
| 2. What is the structure of a seed? |  |
Ans. A seed typically consists of three main parts: the seed coat, the embryo, and the food storage. The seed coat protects the seed. The embryo is the young plant that will grow when conditions are favorable. The food storage provides nutrients to the embryo until it can produce its own food through photosynthesis.
| 3. What are the different kinds of seeds? |  |
Ans. There are various kinds of seeds, including monocot seeds and dicot seeds. Monocot seeds, such as rice and corn, have one seed leaf (cotyledon). Dicot seeds, like beans and sunflowers, have two seed leaves. Seeds can also be classified based on their size, shape, and the type of plant they come from.
| 4. What is germination, and how does it occur? |  |
Ans. Germination is the process by which a seed develops into a new plant. It occurs when the seed absorbs water, swells, and breaks through the seed coat. This process requires warmth, moisture, and sometimes light. The embryo begins to grow, and the roots and shoots emerge from the seed.
| 5. How can we take care of plants? |  |
Ans. Taking care of plants involves providing them with the right amount of water, sunlight, and nutrients. Regularly check for pests and diseases, and prune when necessary to promote healthy growth. It's also important to plant them in suitable soil and ensure they receive adequate air circulation.
Related Searches















