Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st May 2025) - 2 | Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
Early Monsoon Onset 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
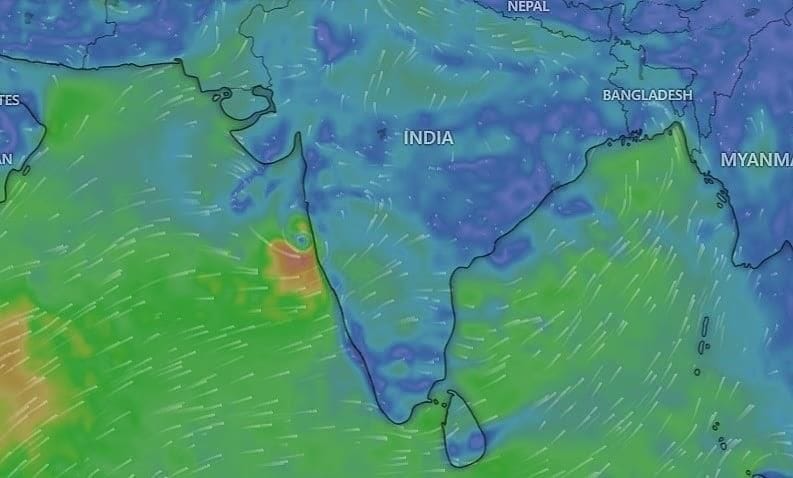
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has declared the southwest monsoon onset over Kerala earlier than usual. This early arrival is significant as the monsoon accounts for over 70% of India's annual rainfall, which is crucial for agriculture and the economy. The last early onset before 2025 occurred in 2009.
Key Takeaways
- The southwest monsoon has begun earlier than the typical timeline.
- This onset is vital for agricultural productivity and economic stability in India.
Additional Details
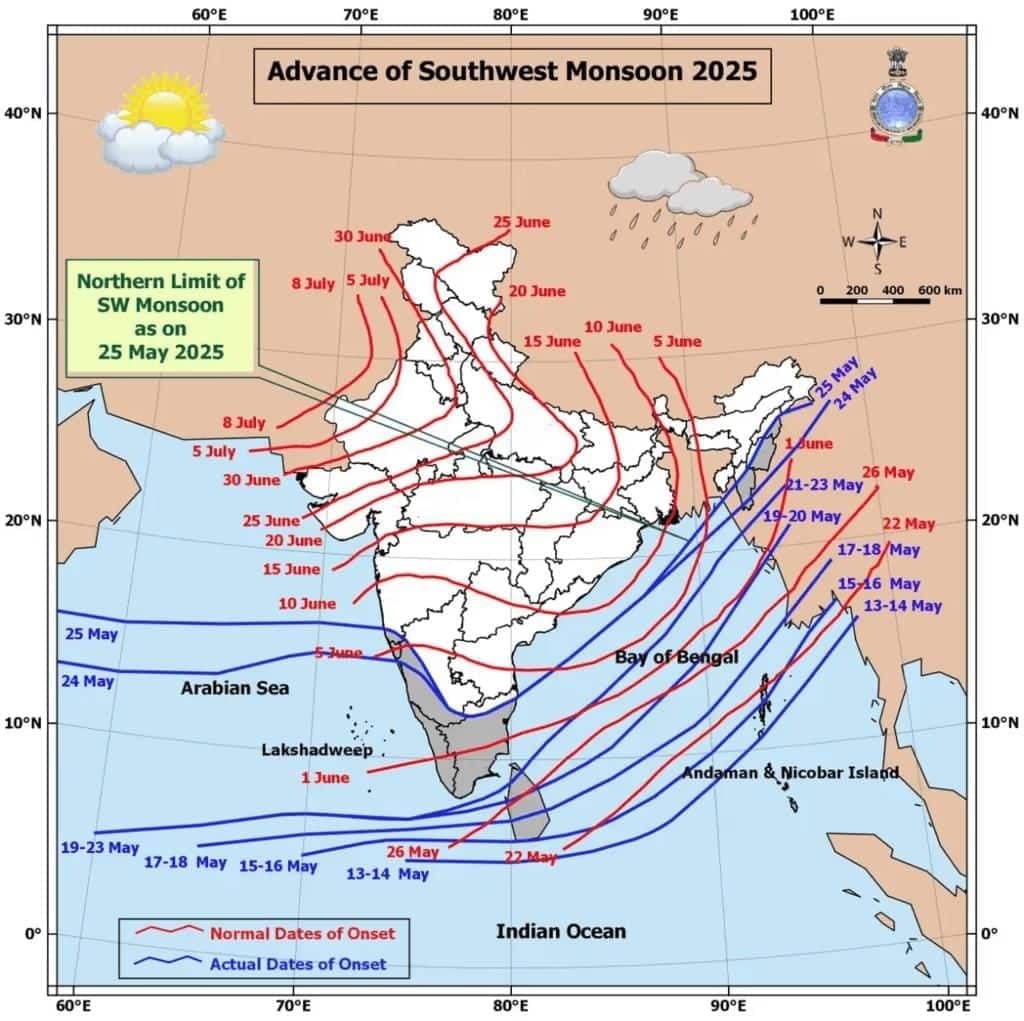
- Criteria for Declaring the Onset:The IMD declares monsoon onset after May 10 based on specific criteria:
- Rainfall Criteria: If 60% of 14 designated weather stations in Kerala record ≥2.5 mm of rainfall for two consecutive days, the onset is announced on the second day.
- Wind Field: Westerly winds must be maintained at up to 600 hPa, with wind speeds between 15-20 knots (27-37 km/hr).
- Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR): OLR values should be below 200 W/m² in specific latitude and longitude coordinates, indicating conducive conditions for rainfall.
- Factors Causing Early Onset:The early onset is influenced by several atmospheric systems including:
- Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO): A weather pattern affecting tropical regions that can enhance rainfall.
- Mascarene High: A high-pressure area affecting rainfall along India's west coast.
- Convection: Increased convective activity contributes to rainfall.
- Somali Jet: A wind band that strengthens monsoon winds upon reaching the Arabian Sea.
- Heat-low: A low-pressure zone that draws moist air, enhancing rainfall.
The early onset of the monsoon has several implications:
- Boost to Kharif Crop Sowing: Early rains allow timely sowing of Kharif crops like rice and maize, leading to higher yields.
- Water Resource Management: Early rainfall helps recharge groundwater and fill reservoirs, crucial for agriculture.
- Increased Spoilage & Inflation Pressure: Unanticipated rains can lead to spoilage and increased prices for vegetables.
What is the Impact of Climate Change on Indian Monsoon?
- Increasing Extreme Rainfall Events: There is a rising trend in extreme rainfall occurrences attributed to climate change.
- Overall Monsoon Rainfall Decline: A 6% decline in summer monsoon precipitation has been noted over the last 50 years.
- Warming Atmosphere and Moisture Capacity: Higher temperatures increase the atmosphere's moisture capacity, resulting in more intense rainfall events.
In conclusion, the early onset of the southwest monsoon in 2025 has significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and the economy, while also raising concerns about the effects of climate change on rainfall patterns.
India’s AMR Crisis
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The launch of Nafithromycin (Miqnaf) — India’s first indigenously developed antibiotic in over 30 years — marks a significant advancement in the fight against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). However, the scale and urgency of the AMR crisis necessitate broader and sustained efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Overuse of antibiotics is prevalent, with improper prescriptions leading to resistance.
- India faces inadequate healthcare infrastructure, contributing to AMR.
- There is a lack of new antibiotics due to the pharmaceutical industry's focus on chronic diseases.
- Unregulated use of antibiotics in agriculture and animal husbandry exacerbates the issue.
- Environmental contamination from pharmaceutical waste and inadequate sewage management creates resistance hotspots.
Additional Details
- Overuse of Antibiotics: Inappropriate prescriptions often include antibiotics for viral infections like influenza. Despite only 30% of antibiotics being used in humans, as of 2022, 59% of India's antibiotic consumption came from the "Watch" group, which is intended for severe infections.
- Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: The absence of diagnostic tools leads to the empirical prescription of broad-spectrum antibiotics, while overcrowded and unhygienic hospitals promote resistant bacteria and hospital-acquired infections.
- Environmental Factors: Pharmaceutical factories discharge antibiotic residues into water bodies, contaminating the environment and allowing resistant microbes to spread.
- Health Catastrophe: AMR complicates the treatment of common illnesses, leading to increased mortality and morbidity.
- Economic Cost: The World Bank estimates that AMR could increase healthcare costs by USD 1 trillion by 2050 and cause significant GDP losses.
- Food Security Crisis: With 70% of antibiotics used in farming, the situation threatens food availability and safety.
While the launch of Nafithromycin represents a critical milestone, effectively combating AMR requires a comprehensive and sustained strategy. This includes strengthening regulations, enhancing antibiotic stewardship, promoting domestic antibiotic development, and expanding public awareness initiatives.
Urban Flooding in India
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- Bengaluru has recently faced intense pre-monsoon rains that resulted in significant waterlogging, lake overflows, and considerable damage to life and property. With the early onset of the monsoon this year, the risk of urban flooding in the city is anticipated to increase further.
Key Takeaways
- Severe pre-monsoon rains in Bengaluru have led to major urban flooding concerns.
- Urban flooding disrupts daily life, damages infrastructure, and poses health risks.
Additional Details
- What is Urban Flooding: Urban flooding refers to the inundation of land or property in densely populated areas due to heavy rainfall, overflowing rivers, poor drainage systems, or other water-related incidents. It disrupts transportation, damages infrastructure, and poses health hazards.
- Examples: Notable instances include the floods in Bengaluru (2024), Delhi (2023), Mumbai (2020), and Chennai (2015).
Key Reasons for Urban Flooding in India
- Natural Causes:
- Heavy Monsoon Rainfall: India experiences intense monsoon precipitation, particularly in the Western Ghats and northeastern regions, overwhelming drainage systems.
- Topography: Many cities are situated in floodplains or low-lying areas, which naturally accumulate runoff, exacerbating flooding.
- Climate Change: Increased frequency and intensity of rainfall due to climate change leads to flash floods.
- Anthropogenic Causes:
- Rapid Urbanization: Unplanned growth results in the loss of natural drainage channels and wetlands.
- Inadequate Drainage Infrastructure: Many cities rely on outdated systems that cannot handle heavy rainfall.
- Solid Waste Mismanagement: Blocked drains due to waste contribute to flooding, as seen in various recent floods.
- Deforestation: Improper land use increases surface runoff, leading to urban flooding.
Major Impacts of Urban Flooding
- Economic Loss: Flooding damages critical infrastructure leading to significant repair costs and economic disruption.
- Public Health Crisis: Stagnant water increases the risk of diseases like malaria and cholera.
- Displacement: Vulnerable groups face severe displacement, losing homes and access to services.
- Ecological Degradation: Floods carry pollutants, harming aquatic ecosystems and reducing biodiversity.
- Overburdened Infrastructure: Recurring floods expose failures in drainage systems and city planning.
Measures to Enhance Resilience Against Urban Floods
- Integrated Watershed Management: Comprehensive management of river basins can control flooding at the source.
- Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS): Incorporating permeable surfaces and rain gardens can effectively manage runoff.
- Sponge City Concept: Designing urban landscapes to absorb and purify rainwater helps reduce flooding.
- Restoration of Water Bodies: Reviving lakes and wetlands improves flood absorption capacity.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in flood preparedness enhances resilience.
In conclusion, urban flooding in India, driven by unplanned urban growth and climate change, poses a significant threat to life, property, and infrastructure. A resilient approach that integrates sustainable practices, community involvement, and effective planning is essential for long-term flood mitigation.
Mains Question:
Discuss the key factors contributing to urban flooding and suggest measures for effective flood management.
Revisiting NGO Regulatory Framework
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has recently announced new amendments to the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011, which will affect how non-governmental organizations (NGOs) operating in India can receive and utilize foreign funds.
Key Takeaways
- New certificates required for NGOs engaged in publication activities.
- Mandatory financial disclosures for FCRA registration.
- NGOs must declare adherence to FATF guidelines.
- Commitment letters from foreign donors are now necessary.
- Obligations for previously registered NGOs to submit affidavits.
Additional Details
- Ban on Publication Activities: NGOs engaged in publication-related activities must obtain a certificate from the Registrar of Newspapers for India, confirming compliance with media regulations and declaring they are "Not a Newspaper."
- Financial Disclosure: NGOs applying for FCRA registration must provide financial statements and audit reports for the past three years, including details on assets and liabilities, income and expenditure, and receipts and payments.
- FATF Compliance: NGOs are required to declare adherence to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) Good Practice Guidelines, supporting India's efforts to oversee foreign financial flows.
- New Requirements for Receiving Foreign Contributions: NGOs must submit a commitment letter from foreign donors that matches the donation with a detailed project report, including an expense breakdown.
- Obligations for Previously Registered NGOs: NGOs whose FCRA registration has expired or been cancelled must submit an affidavit detailing the receipt and utilization of previously received foreign contributions.
NGOs in India are defined as non-profit entities that operate independently of the government, focusing on humanitarian, social, or developmental goals. They can be formed as:
- Societies: Registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- Trusts: Private Trusts registered under the Indian Trusts Act, 1882, and Public Trusts registered under respective state laws.
- Charitable Companies: Registered as non-profit companies under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010 governs NGOs receiving foreign contributions, aiming to prevent foreign funds from undermining India's sovereignty and security. Key amendments in the FCRA Amendment Act, 2020 include:
- Mandating that all foreign contributions be received only through a designated "FCRA Account" at a specified bank.
- Prohibiting the transfer of foreign contributions to any other entity.
- Reducing the permissible limit for administrative expenses from 50% to 20% of foreign funds received.
- Empowering the Central Government to restrict or suspend further receipt or utilization of foreign contributions.
- Requiring identification documents for NGO office bearers and directors.
Key Roles and Responsibilities of NGOs
- Governance: NGOs promote transparency and accountability, exemplified by organizations like the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR).
- Social Reforms: NGOs work to protect human rights, empower women, and represent marginalized groups.
- Disaster Relief and Rehabilitation: NGOs provide immediate aid and long-term support during natural disasters.
- Environmental Conservation: Many NGOs focus on protecting natural resources and promoting sustainable development.
Key Challenges Related to NGOs in India
- Regulatory Restrictions: Strict FCRA regulations have led to the cancellation of NGO licenses, limiting access to foreign donations.
- Trust Deficits: NGOs face accusations of "anti-national" activities, resulting in audits and closures.
- Lack of Transparency: Criticisms arise from poor accountability and non-compliance with reporting requirements.
Key Reforms Needed to Strengthen NGO Regulation in India
- Implement 2nd ARC Recommendations: Decentralizing FCRA implementation to ease bureaucratic hurdles.
- Stronger Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Checks: Linking NGO funding regulations to FATF guidelines and enhancing measures to block shell NGOs.
- Encourage Domestic Funding: Providing tax incentives for Indian donors and promoting CSR partnerships with credible NGOs.
The new FCRA amendments aim to regulate foreign-funded NGOs to ensure national security. However, balanced reforms including digital audits and domestic funding incentives are essential to support development work while ensuring compliance. Stricter FATF compliance and expedited blacklisting of rogue entities will enhance oversight without stifling NGO activities.
Mains Question:
Examine the reforms needed for better regulation of NGOs receiving foreign funding in India.
Inter-Services Organisations Rules 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- India has officially notified the Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Rules, 2025 under the Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Act, 2023. These rules are designed to enhance the command, control, and administrative efficiency of Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs), particularly following the coordinated tri-service response during Operation Sindoor.
Key Takeaways
- ISOs facilitate integrated planning and operations across the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- The ISO Act 2023 empowers commanders with administrative and disciplinary authority over personnel from multiple services.
- The ISO Rules 2025 ensure effective management of discipline across joint commands and theatre commands.
Additional Details
- Inter-Services Organisations (ISOs): These are units or commands composed of personnel from two or more branches of the Armed Forces, aimed at enhancing operational efficiency. Examples include the Andaman and Nicobar Command and upcoming theatre commands.
- ISO Act 2023: This act addresses challenges from existing separate service laws that can hinder coordination and discipline in joint-service contexts. It allows for the creation of new ISOs and authorizes Commanders-in-Chief to exercise command over personnel from any service.
- ISO Rules 2025: Notified under Section 11, these rules govern the operational discipline and administration within ISOs, specifying command structures and protocols for absence or emergencies.
- Significance of ISOs: The integration under unified commands enhances operational synergy, reduces redundancy in resource allocation, improves combat readiness, and aligns India’s military structure with modern warfare needs.
The establishment of ISOs represents a significant step towards modernizing India’s military framework, ensuring better coordination among the armed forces, and preparing for contemporary geopolitical challenges.
Mains Question: Discuss the significance of the Inter-Services Organisations in the context of India's military reforms.
WHO Endorses Global Pandemic Agreement
 Why in News?
Why in News?
- The World Health Organization (WHO), during its 78th World Health Assembly, has adopted the world’s first global Pandemic agreement under Article 19 of the WHO Constitution. This landmark agreement aims to strengthen health security and ensure equitable pandemic responses, representing the second legal instrument following the 2003 Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
Key Takeaways
- The WHO's Global Pandemic Agreement was adopted in May 2025.
- This treaty focuses on enhancing international cooperation for timely access to diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics during pandemics.
- The agreement will become binding once ratified by 60 countries.
Additional Details
- Background: Negotiations began in December 2021 amid the rise of the Omicron variant of Covid-19, which highlighted vaccine hoarding by wealthier nations that limited access for poorer countries. Equitable vaccine distribution could have saved over a million lives.
- Key Provisions:
- Pathogen Access & Equitable Sharing: Pharmaceutical companies will gain access to pathogen samples and data in exchange for sharing 10% of their pandemic-related vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics with WHO, along with another 10% at affordable prices.
- Technology & Knowledge Transfer: Member states are urged to promote the sharing of technology and expertise to facilitate local production of vaccines and drugs in developing countries.
- Global Supply Chain and Logistics Network (GSCL): This network aims to eliminate barriers and ensure equitable, timely, safe, and affordable access to pandemic-related health products during public health emergencies.
- Research Funding & Access Rights: Countries must ensure that publicly funded research includes provisions for timely access to resultant medical products, intervening if life-saving medicines are unaffordable or unavailable.
- Sovereignty Preserved: The WHO cannot override national laws or mandate measures like travel bans or vaccination requirements, ensuring countries maintain authority over their pandemic responses.
- Key Concerns:
- Limited WHO Authority: The treaty does not grant WHO the power to direct national laws, which may hinder compliance during crises.
- Intellectual Property & Innovation: Pharmaceutical companies demand strong IP protections, which may conflict with equitable access initiatives.
- Unclear Benefit-Sharing Mechanism: The Pathogen Access and Benefit-Sharing System (PABS) aims to ensure fair sharing but lacks clarity in its implementation, with final details expected at the 2026 World Health Assembly.
- US Exit from WHO: The withdrawal of the US, a significant player in global pharmaceutical manufacturing, may weaken the treaty’s effectiveness since its companies are not obligated to share data or comply with treaty provisions.
The WHO Pandemic Agreement signifies a pivotal shift towards a more equitable and coordinated global health structure. It institutionalizes lessons learned from Covid-19, promoting faster responses, fair vaccine access, and stronger health systems. For countries like India, swift adoption and effective implementation of this agreement will be essential in safeguarding against future health emergencies and enhancing global health security.
TR1 Cells Lead the Fight Against Malaria
Why in News?
- A recent study has highlighted that Type-1 Regulatory T-cells (TR1 cells) are the primary drivers of the immune response to malaria, which challenges the previous understanding that relied on other T-cells.
Key Takeaways
- TR1 cells play a crucial role in regulating the immune response to malaria.
- These cells help maintain a balance between fighting the malaria parasite and preventing excessive immune reactions.
Additional Details
- What are T1 Cells? T1 cells are a specialized group of CD4+ helper T-cells that are essential for regulating the immune system. Unlike traditional T-cells that primarily attack pathogens, TR1 cells help control and balance immune responses by reducing inflammation and preventing excessive immune reactions.
- Role Against Malaria: When the body is infected by Plasmodium falciparum, it must navigate the dual challenge of combating the parasite while avoiding immune damage. TR1 cells promote immune tolerance, allowing coexistence with the parasite and aiding in the development of clinical immunity, which prevents severe illness.
- Components of the Human Immune System: The immune system comprises various components including physical barriers (skin, mucous membranes), innate immunity (immediate, non-specific responses), and adaptive immunity (specific responses that create memory). Key players include white blood cells, lymphocytes (B-cells and T-cells), and the lymphatic system that houses immune cells.
In conclusion, understanding the role of TR1 cells in malaria could lead to new strategies for treatment and prevention, enhancing the body's ability to combat this life-threatening disease.
China's Tianwen-2 Mission

Why in News?
China is preparing to launch the Tianwen-2 mission, which will focus on surveying and sampling the near-Earth asteroid 469219 Kamo‘oalewa. This mission builds on the success of Tianwen-1, which was China's first mission to Mars that included an orbiter, a lander, and a rover to explore the Martian surface.
Key Takeaways
- The Tianwen-2 mission aims to collect samples from the near-Earth asteroid Kamo‘oalewa.
- This mission will enhance China's reputation as a leader in complex deep space operations.
- China will join the US and Japan in successfully retrieving asteroid samples and returning them to Earth.
Additional Details
- Near-Earth Asteroids (NEAs): These are asteroids with orbits that bring them close to Earth. Those that cross Earth's path are termed Earth-crossers.
- Significance: The mission will investigate Kamo‘oalewa’s unusual orbit, exploring its potential lunar origin and testing the hypothesis that it may be a fragment from a historic Earth-Moon collision.
- Kamo‘oalewa was discovered in 2016 and is classified as one of only seven known quasi-satellites of Earth, which are influenced gravitationally by our planet.
- Quasi-satellites like Kamo‘oalewa can shift their orbits over a period of 100-300 years.
- Sampling Techniques: The mission will utilize a “touch-and-go” technique, where a robotic arm collects fragments of the asteroid and propels them into a sample chamber. An optional “anchor and attach” method may be used for drilling if necessary.
- Future Plans: Following the Kamo‘oalewa mission, Tianwen-2 will analyze asteroids in the main asteroid belt (located between Mars and Jupiter) and set the stage for the planned Tianwen-3 mission in 2028, which aims to return samples to Earth for the first time.
In summary, the Tianwen-2 mission represents a significant step for China in advancing its capabilities in space exploration, particularly in understanding the origins and compositions of near-Earth objects.
|
287 docs|142 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (22nd to 31st May 2025) - 2 - Weekly Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What is the significance of the early monsoon onset in 2025 for India? |  |
| 2. How does India's Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) crisis affect public health? |  |
| 3. What measures can be taken to mitigate urban flooding in India? |  |
| 4. What changes are proposed in the NGO regulatory framework in India? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the WHO endorsing a global pandemic agreement? |  |





















