Important Questions: Chemical Reactions and Equations | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Balancing of Chemical Equations |

|
| Combination Reaction |

|
| Decomposition Reaction |

|
| Displacement and Double Displacement Reactions |

|
| Redox Reactions |

|
| Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions |

|
Welcome to this carefully curated document designed to prepare you for your board exams. The questions included here are highly significant, frequently asked in previous exams, and crafted to boost your confidence and performance.
Balancing of Chemical Equations
Q1. Consider the following chemical equation:
a Al + b CuSO₄ → c Al₂(SO₄)₃ + d Cu
In order to balance this chemical equation, the values of the coefficients a, b, c, and d must be:
(a) 2, 3, 1, 3
(b) 1, 3, 1, 2
(c) 2, 1, 1, 3
(d) 3, 2, 1, 1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1. Write the unbalanced equation
Al + CuSO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + Cu
2. Balance Aluminum (Al)
On the right, Al₂(SO₄)₃ has 2 Al atoms.
So, put 2 before Al on the left:
2Al + CuSO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + Cu
3. Balance Sulfate (SO₄)
On the right, Al₂(SO₄)₃ contains 3 sulfate groups.On the left, each CuSO₄ has 1 sulfate group.
So, put 3 before CuSO₄:
2Al + 3CuSO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + Cu
4. Balance Copper (Cu)
On the left: 3 Cu atoms (from 3CuSO₄).
On the right: each Cu represents 1 atom, so put 3 before Cu:
2Al + 3CuSO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3Cu
5. Verify
Al: 2 (LHS) = 2 (RHS)
Cu: 3 (LHS) = 3 (RHS)
S: 3 (LHS) = 3 (RHS)
O: 12 (LHS) = 12 (RHS)
Balanced.
Final Answer
The coefficients are a = 2, b = 3, c = 1, d = 3 → Option (a).
Q2. To balance the following chemical equation:
xFeS₂ + yO₂ → zFe₂O₃ + wSO₂
The values of the coefficients x, y, z, and w must be, respectively:
(a) 4, 11, 2, 8
(b) 2, 7, 1, 4
(c) 4, 7, 2, 4
(d) 2, 11, 1, 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Step 1: Write the unbalanced equation.
FeS₂ + O₂ → Fe₂O₃ + SO₂
Step 2: Balance iron (Fe).
On the right, Fe is in Fe₂O₃ (2 atoms).
So, put coefficient 4 before FeS₂ and 2 before Fe₂O₃.
4FeS₂ + O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃ + SO₂
Now Fe is balanced (4 on each side).
Step 3: Balance sulfur (S).
On the left: 4FeS₂ = 8 sulfur atoms.
So, put coefficient 8 before SO₂.
4FeS₂ + O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃ + 8SO₂
Now S is balanced (8 on each side).
Step 4: Balance oxygen (O).
On the right:
From 2Fe₂O₃ → 2 × 3 = 6 oxygen atoms
From 8SO₂ → 8 × 2 = 16 oxygen atoms
Total = 22 oxygen atoms.
On the left: O₂ molecule contains 2 oxygen atoms.
So, coefficient before O₂ must be 11.
4FeS₂ + 11O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃ + 8SO₂
Step 5: Verify.
Fe: 4 (LHS) = 4 (RHS)
S: 8 (LHS) = 8 (RHS)
O: 22 (LHS) = 22 (RHS)
Balanced.
Final Answer: (a) x = 4, y = 11, z = 2, w = 8
Q3: What is a balanced chemical equation?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The equation which contains an equal number of atoms of each element on both sides of the arrow is called a balanced chemical equation.
Q4: Assertion (A): The following is a balanced chemical equation for the action of steam on iron:
3Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Reason (R): The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical equation.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
In this question, both the Assertion (A) and the Reason (R) are true.
The balanced chemical equation 3Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g) correctly represents the reaction of steam with iron, forming iron(II,III) oxide (Fe3O4) and hydrogen gas (H2).
The Reason (R) states that the law of conservation of mass holds, meaning that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, which is indeed reflected in the balanced equation. Therefore, option (a) is correct, as the Reason accurately explains the Assertion.
Q5: Lead nitrate solution is added to a test tube containing potassium iodide solution. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
Combination Reaction
Q1: Select from the following a process in which a combination reaction is involved:
(a) Black and White photography
(b) Burning of coal
(c) Burning of methane
(d) Digestion of food
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Burning of coal involves the reaction of carbon (coal) with oxygen to form carbon dioxide: C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g). This is a combination reaction as two substances (carbon and oxygen) combine to form a single product (carbon dioxide).
Q2: Which of the following reactions is different from the remaining three?
(a) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(b) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(c) KNO3 + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HNO3
(d) ZnCl2 + H2S → ZnS + 2HCl
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In the reactions listed, options (a), (c), and (d) involve double displacement or exchange of ions between reactants, where compounds are formed by swapping partners. However, option (b) is a combination reaction, where calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with water (H2O) to form calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) without exchanging ions. This makes (b) different from the others.
Q3: Which of the following is a redox reaction, but not a combination reaction?
(a) C + O2 → CO2
(b) 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O
(c) 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO
(d) Fe2O3 + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
A redox reaction involves both oxidation and reduction, where electrons are transferred between substances. In option (d), iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3) is reduced to iron (Fe), while carbon monoxide (CO) is oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO2). Unlike the other options, which are combination reactions, this one shows the reduction and oxidation of different substances, making it a redox reaction but not a combination reaction.
Q4: Name the type of chemical reaction in which calcium oxide reacts with water. Justify your answer by giving a balanced chemical equation for the chemical reaction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Combination reaction – Single product is formed (or any other)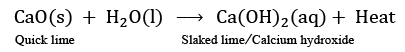
Q5: When magnesium ribbon is burnt in the air, an ash of white colour is produced. Write the chemical equation for the reaction giving the chemical name of the ash produced. State the type of chemical reaction justifying your answer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 2 Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Magnesium oxide
Type – Combination reaction
Reason: Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
Q6: Name the type of chemical reaction that takes place when quicklime is added to water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The reaction between CaO and H2O to form Ca(OH)2 is an exothermic and combination reaction.
Decomposition Reaction
Q1: Select from the following a decomposition reaction in which the source of energy for decomposition is light:
(a) 2FeSO4 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
(b) 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
(c) 2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2
(d) CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
A decomposition reaction is when a compound breaks down into simpler substances. Option (c) 2AgBr → 2Ag + Br2 is the correct answer because it requires light energy to break down silver bromide (AgBr) into silver (Ag) and bromine (Br2). The other options do not use light for decomposition.
Q2: (i) Define a decomposition reaction. How can we say that (I) electrolysis of water, and (II) blackening of silver bromide when exposed to sunlight, are decomposition reactions? Mention the type of energy involved in each case.
(ii) The type of reactions in which (I) calcium oxide is formed, and (II) calcium hydroxide is formed, are opposite reactions to each other. Justify this statement with the help of chemical equations.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) A reactant breaks down to give two or more products. A reaction which requires energy to split a compound or reactant in two or more simple substances.
(I) Water splits into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
Type of Energy: Electrical energy
(II) Silver bromide decomposes into silver and bromine
Type of Energy: Light energy
(ii) (I) Formation of calcium oxide:
CaCO₃ + Heat → CaO + CO₂
It is an endothermic reaction/decomposition reaction.
(II) Formation of calcium hydroxide: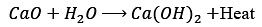 It is exothermic/combination reaction
It is exothermic/combination reaction
Q3: (A) Write the essential conditions for the following reaction to take place and name its types:
2AgCl → 2Ag + Cl2
(B) Complete the following chemical reaction in the form of a balanced equation: 
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) 
Sunlight is essential for the above reaction to take place. This is a decomposition reaction. Such reactions require energy either in the form of heat, light or electricity for breaking down the reactants. Silver chloride turns grey after its decomposition into silver and chlorine by sunlight. This reaction is used in black and white photography.
(B) 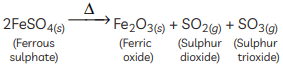
Q4: What is observed when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight? Give the type of reaction involved.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When silver chloride is exposed to sunlight, it decomposes to form silver metal and chlorine gas. 2AgCl(s) → 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) This is a photochemical decomposition reaction.
Q5: The emission of brown fumes in the given experimental set-up is due to:
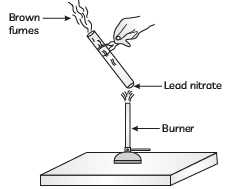
(a) thermal decomposition of lead nitrate, which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
(b) thermal decomposition of lead nitrate, which produces brown fumes of lead oxide.
(c) oxidation of lead nitrate, forming lead oxide and nitrogen dioxide.
(d) oxidation of lead nitrate forming lead oxide and oxygen.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
When lead nitrate is heated, it undergoes thermal decomposition, resulting in the formation of lead oxide,PbO (a yellow solid), nitrogen dioxide NO2 (a brown gas), and oxygen, O2. The brown fumes observed in this setup are due to the release of nitrogen dioxide gas.
The reaction is as follows: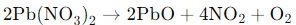
Thus, the correct answer is (a) thermal decomposition of lead nitrate which produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide.
Q6: When lead nitrate powder is heated in a boiling tube. we observe
(a) Brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide
(b) Brown fumes of lead oxide
(c) Yellow fumes of nitrogen dioxide
(d) Brown fumes of nitric oxide.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
When lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) is heated, it decomposes and produces brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide (NO2). This happens because the lead nitrate breaks down into lead oxide (PbO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and oxygen (O2). The brown color of the fumes is characteristic of nitrogen dioxide, making option (a) the correct answer.
Q7: Assertion (A): Silver salts are used in black-and-white photography.
Reason (R): Silver salts do not decompose in the presence of light.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: Silver salt (AgCl) are used in black and white photography. Silver salt (AgCl) is photosensitive compound, it decomposes into elemental chlorine (Cl2) and Ag(metal).
AgBr is also used as black and white photography.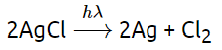
Q8: Study the figure given below and answer the following questions:
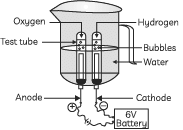 (A) Name the process depicted in the diagram.
(A) Name the process depicted in the diagram.
(B) Write the composition of gases collected at the anode and cathode.
(C) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction taking place in this case.
(D) The reaction does not take place if a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid are not added to water. Why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (A) Electrolytic decomposition of water/ electrolysis of water.
(B) The gas collected at cathode is hydrogen which is double the volume of oxygen collected at anode.
(C) The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: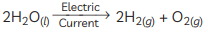
(D) The reaction does not occur without dilute sulphuric acid because:
- Water is a poor conductor of electricity.
- Adding sulphuric acid improves conductivity, allowing the reaction to proceed.
Q9: In the electrolysis of water
(a) Name the gases liberated at the anode and cathode.
(b) Why is it that the volume of gas collected on one electrode is two times that on the other electrode?
(c) What would happen if dil. H2SO4 is not added to water? (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) At anode: Oxygen gas is liberated. At cathode: Hydrogen gas is liberated.
(b) In the test tube covering the cathode, the amount of gas collected is double than that of the gas collected in the test tube covering the anode due to stochiometry.
2H2O → 2H2 + O2
(c)Without adding dilute sulphuric acid, water would not conduct electricity effectively, which would hinder the electrolysis process. As addition of a few drops of sulphuric acid make water a good conductor of electricity.
Displacement and Double Displacement Reactions
Q1: Which of the following reactions is different from the remaining three?
(a) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(b) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(c) KNO3 + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HNO3
(d) ZnCl2 + H2S → ZnS + 2HCl
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In the reactions listed, options (a), (c), and (d) involve double displacement or exchange of ions between reactants, where compounds are formed by swapping partners. However, option (b) is a combination reaction, where calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with water (H2O) to form calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) without exchanging ions. This makes (b) different from the others.
Q2: Zn + 2CH3COOH → Zn(CH3COO)2 + H2
The above reaction is a:
(a) Decomposition reaction
(b) Displacement reaction
(c) Double displacement reaction
(d) Combination reaction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
In the given reaction, zinc (Zn) replaces hydrogen in acetic acid (CH3COOH) to form zinc acetate (Zn(CH3COO)2) and hydrogen gas (H2). This type of reaction, where one element displaces another from a compound, is called a displacement reaction. Therefore, option (b) is correct.
Q3: Study the experimental set-up shown in the diagram and write a chemical equation for the chemical reaction involved. Name and define the type of reaction. List two other metals that can be used in place of iron to show the same type of reaction with copper sulphate solution. 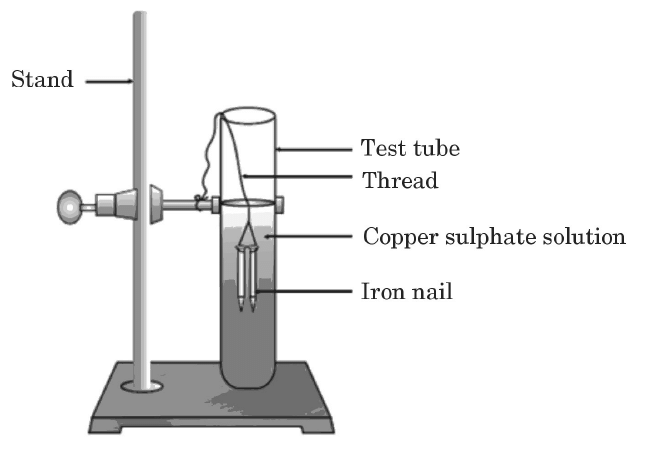
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Displacement reaction: A reaction in which a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Other metals that can be used in place of iron to show the same type of reaction with copper sulphate solution: Zinc, Aluminium, Calcium, Magnesium
Q4: (a) Define a double displacement reaction.
(b) Write the chemical equation of a double displacement reaction which is also a (i) Neutralisation reaction and (ii) Precipitation reaction. Give justification for your answer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) The chemical reaction in which two reactants exchange ions to form two new compounds is called a double displacement reaction.
(b) (i) When an aqueous solution of an acid reacts with a base (alkali) by exchanging their ions/radicals to form salt and water as the only products, the reaction which takes place is called neutralisation reaction.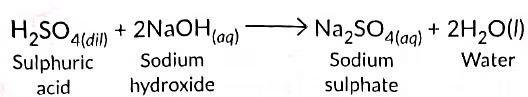
(ii) When the aqueous solutions of two ionic compounds react by exchanging their ions/radicals, to form two or more new compounds such that one of the products formed is an insoluble salt, and hence forms precipitate, the double displacement reaction is said to be precipitation reaction. When lead nitrate solution is mixed with potassium iodide solution, a yellow precipitate is formed. This reaction is a precipitation reaction and can be expressed as follows:
Q5: When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction
(d) Double displacement reaction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
When hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is passed through a blue solution of copper sulfate (CuSO4), it forms a black precipitate of copper sulfide (CuS) while sulfuric acid (H2SO4) remains in the solution. This process involves the exchange of ions between the reactants, characteristic of a double displacement reaction. In this type of reaction, the ions from both compounds swap partners, which makes option (d) the correct answer.
Q6: In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution:
(A) Exchange of atoms takes place
(B) Exchange of ions takes place
(C) A precipitate is produced
(D) An insoluble salt is produced
The correct option is
(a) (B) and (D)
(b) (A) and (C)
(c) Only (B)
(d) (B), (C) and (D)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In a double displacement reaction, like the one between sodium sulfate and barium chloride, the ions in the reactants swap places. This results in the formation of an insoluble salt (barium sulfate), which is a solid that separates out (precipitate) from the solution. So, options (B), (C), and (D) are all correct because they describe the ion exchange and the formation of a precipitate.
Q7: What is observed after about 1 hour of adding the strips of copper and aluminium separately to the ferrous sulphate solution filled in two beakers? Name the reaction if any change in colour is noticed. Also, write a chemical equation for the reaction.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Cu(s) + FeSO₄(aq) → No change will take place
Copper is less reactive than Fe, so Cu cannot displace iron from a ferrous sulphate solution. Hence, No reaction will take place.
2 Al(s) + 3 FeSO₄(aq) → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3 Fe(s) (Displacement reaction)
When Al is added to a FeSO₄(aq) solution, the green colour of FeSO₄(aq) disappears and the Fe is seen setting down as the reaction occurs. Al being higher in the reactivity series displaces the Fe in FeSO₄.
Q8: Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The type of reaction taking place is a single displacement reaction. Zinc (Zn) displaces silver (Ag) from silver nitrate (AgNO3) to form zinc nitrate (Zn(NO3)2) and silver (Ag). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
(b) The type of reaction taking place is a double displacement reaction or a precipitation reaction. Potassium iodide (KI) reacts with lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) to produce potassium nitrate (KNO3) and lead iodide (PbI2). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) → 2KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s)
Q9: When potassium iodide solution is added to a solution of lead (II) nitrate in a test tube, a precipitate is formed.
(a) What is the colour of this precipitate? Name the compound precipitated.
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(c) List two types of reactions in which this reaction can be placed.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The color of the precipitate formed is yellow. The compound precipitated is lead iodide (PbI2)
(b) The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
2KI(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
(c) The two types of reactions in which this reaction can be placed are a double displacement reaction and a precipitation reaction. In a double displacement reaction, the positive and negative ions of two compounds switch places to form new compounds. In a precipitation reaction, a solid precipitate is formed when two solutions are mixed together.
Redox Reactions
Q1: (a) Can a displacement reaction be a redox reaction? Explain with the help of an example.
(b) Write the type of chemical reaction in the following:
(i) Reaction between an acid and a base
(ii) Rusting of iron.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Consider the following displacement reaction:
Zn(s)+ CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Here, Zn has changed into ZnSO4 (i.e., Zn2+ ions) by loss of electrons. Hence, Zn has been oxidised. CuSO4 (i.e., Cu2+) has changed into Cu by gain of electrons. Hence, CuSO4 has been reduced. Thus, the above reaction is a displacement reaction as well as a redox reaction.
(b) (i) Neutralisation reaction
(ii) Oxidation reaction.
Q2: Define a redox reaction in terms of gain or loss of oxygen.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The reaction in which one element gets oxidised or addition of oxygen occurs and other element gets reduced or removal of oxygen occurs in other element is called redox reaction.
Example: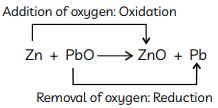
Q3: Assertion (A): In the following reaction ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ZnO undergoes reduction.
Reason (R): Carbon is a reducing agent that reduces ZnO to Zn.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is False.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Sol: The reaction in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed or loss of electrons takes place is called an oxidation reaction. In the reaction,
(i) Carbon is getting oxidised to carbon monoxide.
(ii) Zinc oxide is getting reduced to zinc.
Carbon is a reducing agent that reduces ZnO to Zn.
Q4: A shining metal ‘M’, on burning gives a dazzling white flame and changes to a white powder ‘N’.
(a) Identify ‘M’ and ‘N’.
(b) Represent the above reaction in the form of a balanced chemical equation.
(c) Does ‘M’ undergo oxidation or reduction in this reaction? Justify.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(a) 'M' is (Mg) Magnesium and 'N' is (MgO) Magnesium Oxide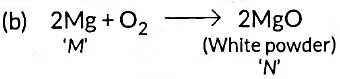
(c) 'M' undergoes oxidation in this reaction because Mg gain oxygen to form MgO.
Q5: Mention with reason the colour changes observed when copper powder is strongly heated in the presence of oxygen.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 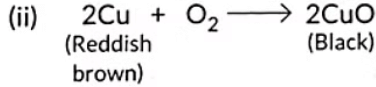
Copper metal undergoes oxidation.
Q6: 1 g of copper powder was taken in a China dish and heated. What change takes place in healing? When hydrogen gas is passed over this heated substance, a visible change is seen in it. Give the chemical equations of reactions, the name and the colour of the products formed in each case.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: When copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance which is copper oxide.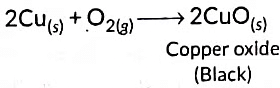
When hydrogen gas is passed over CuO, the black coating on the surface turned reddish brown due to the formation of Cu.
Q7: What is a reduction reaction? Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions. (A) Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
(B) 2PbO + C → 2Pb + CO2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A reduction reaction is a reaction in which hydrogen is added to a substance or oxygen is removed from a substance.
(A) In this reaction, Fe2O3 is losing oxygen and forming Fe, whereas Al is gaining oxygen and forming Al2O3. Therefore, Fe2O3 is getting reduced and Al is getting oxidised.
(B) In this reaction, PbO is losing oxygen and forming Pb whereas C is gaining oxygen and forming CO. Therefore, PbO is getting reduced and C is getting oxidised.
Q8: You might have noted that when copper powder is heated in a China dish, the reddish-brown surface of copper powder becomes coated with a black substance.
(a) Why has this black substance formed?
(b) What is the black substance?
(c) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place.
(d) How can the black coating on the surface be turned reddish-brown?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) The black substance is formed because copper reacts with oxygen in the air to form copper oxide.
(b) The black substance is copper oxide (CuO).
(c) The chemical equation for the reaction is:
2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
(d) The black coating on the surface can be turned reddish-brown by reducing it back to copper. This can be done by passing hydrogen gas over the hot copper oxide. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(g)
The reduction reaction converts the black copper oxide back to reddish-brown copper.
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Q1: Assertion (A): The reaction of quick lime with water is an exothermic reaction.
Reason (R): Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A)
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A)
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is False
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Sol: Reaction of quick lime (CaO) with water is an exothermic reaction because CaO reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
CaO(s) + H2O(I) → Ca(OH)2(ag) + Heat
Q2: C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(I)
The above reaction is a/an
(a) Displacement reaction
(b) Endothermic reaction
(c) Exothermic reaction
(d) Neutralisation reaction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: In the process of respiration, glucose combines with oxygen in cells of our body and provides energy. Thus, respiration is an exothermic process.
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(I) + Energy
Q3: Consider the following processes
I. Dilution of sulphuric acid
II. Sublimation of dry ice
III. Condensation of water vapours
IV. Dissolution of ammonium chloride in water
The endothermic process(es) is/are
(a) I and III
(b) Il only
(c) Ill only
(d) Il and IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Sol: During sublimation of dry ice, heat is absorbed, so, it is an endothermic process. Dissolution of NH4CI in water is also an endothermic process.
Q4: Assertion (A): Burning of natural gas is an endothermic process.
Reason (R): Methane gas combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Assertion (A): Burning of natural gas is an endothermic process. This is incorrect. Burning (or combustion) of natural gas, which mainly consists of methane, is an exothermic process, meaning it releases heat.
Reason (R): Methane gas combines with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. This statement is correct. During combustion, methane reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as products.
Since the assertion is false, but the reason is true, the correct answer is (d) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Q5: A compound 'A' is used in the manufacture of cement. When dissolved in water, it evolves a large amount of heat and forms compound 'B'.
(i) Identify A and B.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction of A with water.
(iii) List two types of reactions in which this reaction may be classified.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Compound A is calcium oxide (CaO) and compound B is calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
(ii) The chemical equation for the reaction of A (calcium oxide) with water is:
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
(iii) The reaction can be classified as a combination reaction and an exothermic reaction. It is a combination reaction because two substances combine to form a new compound, and it is exothermic because it evolves a large amount of heat.
Q6: Identify the type of each of the following reactions. Also, write a balanced chemical equation for each reaction:
A reaction in which the reaction mixture becomes warm.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The type of reaction in which the reaction mixture becomes warm is an exothermic reaction. An example of such a reaction is the combustion of methane (CH4):
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Chemical Reactions and Equations - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the different types of chemical reactions? |  |
| 2. How can I balance a chemical equation? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of balancing chemical equations? |  |
| 4. What are some common indicators of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 5. What role do catalysts play in chemical reactions? |  |
















