Class 3 Exam > Class 3 Notes > Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) > Chapter Notes: Perimeter and Area
Perimeter and Area Chapter Notes | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Perimeter |

|
| Finding Perimeter Using a Square Grid |

|
| Area |

|
| Area of Irregular Plane Figures |

|
Introduction
Imagine you're building a fence around your favorite park or coloring a picture within its lines! The concepts of perimeter and area help us understand the boundaries and space of shapes in a fun and practical way. In this chapter, we'll explore how to measure the distance around shapes (perimeter) and the space they cover (area). From fencing a garden to calculating the space on your desk, these ideas are like magic tools for everyday math adventures!
Perimeter
- Perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a closed shape.
- It is found by adding up the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
- You can measure it using tools like a ruler, measuring tape, or even a rope!
- The word "perimeter" comes from Greek words meaning "around" and "measure."
- Example: Mr. Verma wants to fence his garden. He uses a rope, tying knots at each corner, and measures the total length as 20 meters. This 20 meters is the perimeter of his garden.

Finding Perimeter Using a Square Grid
- A square grid is made of small squares, each with a side of 1 cm.
- Draw the shape on the grid and count the number of unit lengths along its boundary.
- Add up these lengths to find the perimeter.
- Example: For a shape ABCDEFGH on a square grid (each square side is 1 cm), the perimeter is calculated as:
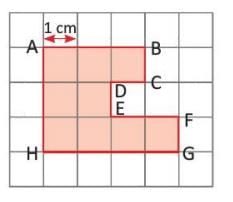 AB = 3 cm, BC = 1 cm, CD = 1 cm, DE = 1 cm, EF = 2 cm, FG = 1 cm, GH = 4 cm, HA = 3 cm. Total = 3 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 1 + 4 + 3 = 16 cm.
AB = 3 cm, BC = 1 cm, CD = 1 cm, DE = 1 cm, EF = 2 cm, FG = 1 cm, GH = 4 cm, HA = 3 cm. Total = 3 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 1 + 4 + 3 = 16 cm.
Area
- Area is the amount of space inside the boundary of a closed shape.
- It is measured in square units, like square centimeters (sq. cm) or square meters (sq. m).
- You can find the area by covering the shape with unit squares and counting them.
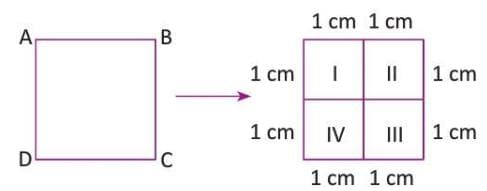
- Example: A figure ABCD is made of 4 equal squares, each with an area of 1 square unit. The total area is 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4 square units.
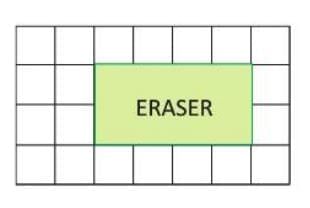
Finding Area by Counting Squares
- Place the shape on a square grid where each square has an area of 1 sq. cm.
- Trace the shape’s outline and count the number of squares it covers.
- The total number of squares gives the area in square units.
- Example: An eraser covers 8 complete squares on a grid where each square is 1 sq. cm. So, the area of the eraser is 8 × 1 sq. cm = 8 square centimeters.
Area of Irregular Plane Figures
- Irregular shapes don’t have a fixed shape, so we find their approximate area.
- Trace the shape on a square grid (each square = 1 square unit).
- Count squares as follows:
- Whole squares covered = 1 square unit each.
- Half squares covered = ½ square unit each.
- Squares covered more than half = 1 square unit each.
- Squares covered less than half = ignore them.
- Add up the areas to get the approximate total area.
Example: For an irregular shape:
- Whole squares = 4 (4 × 1 = 4 square units).
- Half squares = 2 (2 × ½ = 1 square unit).
- More than half squares = 2 (2 × 1 = 2 square units).
- Less than half squares = 4 (ignore).
- Total approximate area = 4 + 1 + 2 = 7 square units.
The document Perimeter and Area Chapter Notes | Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3 is a part of the Class 3 Course Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 3 at this link: Class 3
|
65 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Perimeter and Area Chapter Notes - Year 3 Mathematics IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 3
| 1. What is the difference between perimeter and area? |  |
Ans. The perimeter is the total distance around the outside of a shape, while the area is the amount of space inside that shape. For example, if you have a rectangle, the perimeter is calculated by adding up all its sides, and the area is calculated by multiplying its length by its width.
| 2. How do you calculate the perimeter of a rectangle? |  |
Ans. To calculate the perimeter of a rectangle, you can use the formula: Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width). Simply add the length and width of the rectangle together and then multiply the sum by 2.
| 3. What is the formula for calculating the area of a square? |  |
Ans. The formula for calculating the area of a square is Area = Side × Side or Area = Side². You simply multiply the length of one side by itself to find the area.
| 4. Can the perimeter and area be the same for different shapes? |  |
Ans. Yes, different shapes can have the same perimeter and area. For example, a square and a rectangle can have the same perimeter, but their areas may differ, or vice versa. It's important to analyze both dimensions separately to understand their properties.
| 5. Why is it important to know how to calculate perimeter and area? |  |
Ans. Knowing how to calculate perimeter and area is important for various practical applications such as construction, landscaping, and design. It helps in determining the amount of materials needed, understanding space usage, and planning layouts effectively.
Related Searches