History, Art and Culture: May 2025 UPSC Current Affairs | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Satavahana Dynasty and Culture

Why in News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has documented 11 ancient inscriptions in Peddapalli, Telangana, belonging to the Satavahana dynasty. Written in Brahmi script and Prakrit language, these BCE 6-CE inscriptions offer key insights into the Satavahana era and early Deccan politics and culture. The inscriptions confirm Asmaka as part of one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas, highlighting its historic role and early ties to major dynasties.
Key Takeaways
- The Satavahana dynasty thrived from the 1st century BC to the early 3rd century AD.
- Known for their contributions to trade, agriculture, and cultural developments in ancient India.
Additional Details
- About the Satavahanas: They succeeded the Mauryas in central India, initially ruling from north Maharashtra and later expanding into Karnataka and Andhra.
- The Satavahanas are associated with the Andhras mentioned in the Puranas, although inscriptions do not explicitly use this name.
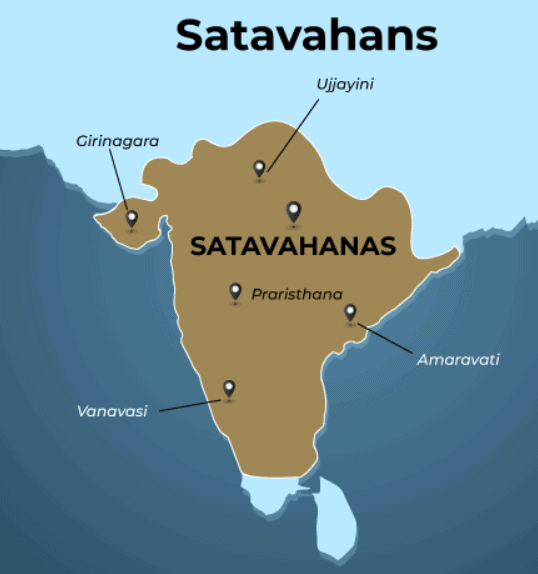
Important Rulers
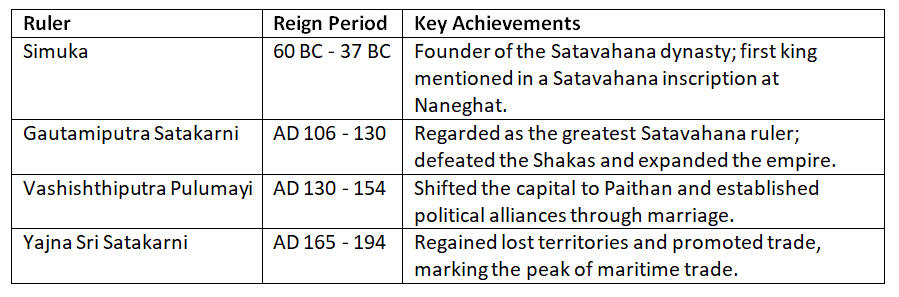
Material Culture
- Agriculture: Iron tools such as hoes and ploughshares facilitated farming, especially in the fertile Krishna-Godavari delta.
- Urbanization: Significant urban developments included brick structures, wells, and drainage systems.
- Trade: Roman coins found in the region indicate extensive trade networks.
Social Organization
- The Satavahanas initially emerged as a Deccan tribe and later became brahmanized, re-establishing the varna system.
- Craft and commerce flourished, with merchants and artisans actively contributing to society.
Administration
- The administration was organized into a three-tier feudal system, consisting of the Raja (king), Mahabhoja (second-rank rulers), and Senapati (military chiefs).
- Districts were governed by Mahamatras who acted as officials.
Religion
- The Satavahana rulers promoted Brahmanism while supporting Buddhism, granting land to monks and fostering its growth.
- They were known for their rock-cut architecture and patronage of Buddhist art, as seen in the Ajanta Caves.
Language
- The official language was Prakrit, with significant literary contributions such as the Gathasattasai attributed to King Hala.
Conclusion
The discovery of Satavahana inscriptions provides valuable insights into the dynasty’s political and cultural impact. Renowned for their support for matrilineal influences, the Satavahanas significantly contributed to the development of urbanization and the shaping of early Deccan history. After their decline, the Ikshvakus emerged as successors in the eastern Deccan, continuing many administrative and cultural traditions, especially in the patronage of Buddhism.
Mains Question
Q: Examine the socio-political structure of the Satavahana dynasty, focusing on their administration, military system, and feudal relationships.
Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025
Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025 will be observed on May 28, 2025, marking the 142nd birth anniversary of Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, popularly known as "Veer Savarkar." On this day, people across India pay tribute to his sacrifice and commitment to the country's freedom. Various cultural programs, seminars, essay competitions, and events are organized to honor his memory.
Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, affectionately called Veer Savarkar, was a revolutionary freedom fighter, poet, writer, and political thinker. His bold ideas and fierce patriotism made him one of the most controversial yet influential figures in India’s struggle for independence. Every year, his birth anniversary is celebrated with pride and remembrance throughout the country.
- On Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025, government officials, students, and members of civil society participate in floral tributes and remembrance events. His portrait is garlanded, and discussions about his contributions take place in schools and universities.
- Cultural programs, seminars, and essay competitions are organized to honor his memory and promote awareness about his role in India’s freedom struggle.
Biography of Veer Savarkar
Veer Savarkar was born on May 28, 1883, in Bhagur village, near Nashik, Maharashtra. His full name was Vinayak Damodar Savarkar. From a young age, he was deeply inspired by stories of Indian resistance against British rule. He founded a revolutionary group called Mitra Mela, which later evolved into the Abhinav Bharat Society.
Savarkar was a brilliant student. He attended Fergusson College in Pune and later moved to London in 1906 on a scholarship to study law at Gray’s Inn. While in London, he joined India House and became a prominent figure in the Indian revolutionary movement abroad.
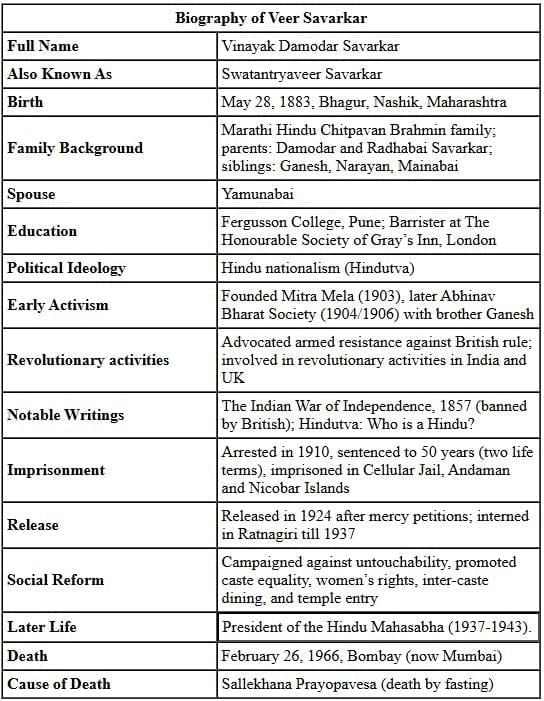
Veer Savarkar’s Contribution to National Freedom Movements
Veer Savarkar played a pivotal role in shaping the revolutionary phase of India’s struggle for independence. His ideas were radical and differed from the moderate and Gandhian approaches. He believed that freedom could not be achieved through petitions and non-violence alone. Here are the key contributions of Veer Savarkar to India’s freedom movement:
- Founded the Abhinav Bharat Society to train youth in revolutionary ideas.
- Authored ‘ The Indian War of Independence 1857, ’ which presented the 1857 uprising as a national struggle rather than a mutiny.
- Promoted armed resistance against British rule while in London.
- Became the first political prisoner to be sentenced to two life terms (total 50 years) and was sent to Cellular Jail in the Andaman Islands.
- Inspired many revolutionaries, including Bhagat Singh, Subhas Chandra Bose, and Lala Hardayal.
- After his release, he actively promoted Hindu unity and nationalist thought through speeches and writings.
- Advocated social reforms like ending caste discrimination and promoting widow remarriage.
- Though his ideology was not aligned with the Congress, his contributions to India’s independence were significant. He focused on cultural nationalism and encouraged Indians to take pride in their heritage.
Veer Savarkar’s Books
Veer Savarkar was not only a revolutionary but also a prolific writer. His books, essays, and poems played a crucial role in awakening patriotic feelings among Indians. He used his writing to challenge colonial narratives and promote nationalist ideology. Some of his most famous works include:
- The Indian War of Independence 1857: One of the first books to portray the 1857 uprising as a national struggle.
- Hindutva: Who is a Hindu? In this book, Savarkar explained his concept of cultural nationalism and defined the term Hindutva.
- The Story of My Transportation for Life:. powerful autobiographical account of his experiences in the Andaman Cellular Jail.
- Six Glorious Epochs of Indian History:. historical analysis showcasing India’s resistance against invaders throughout history.
- Some of his other notable works include Letters from Andamans, Historic Statements by Savarkar, Hindu Rashtra Darshan, Inside the Enemy Camp, Hindu Pad Padashahi, and काला पानी.
Veer Savarkar’s Death and Legacy
Veer Savarkar passed away on February 26, 1966, in Mumbai. He had voluntarily chosen atmaarpan (self-willed death) by giving up food and medicines, declaring that his mission was complete. His death marked the end of an era, but his legacy continues to influence India’s political and cultural discussions today.
- He is considered a pioneer of Hindutva ideology, which influences current political thought.
- Honoured posthumously by the Government of India, with the airport at Port Blair named Veer Savarkar International Airport.
- His life story is taught in schools, and his works are studied in colleges.
- He inspires discussions on nationalism, social reform, and civil liberties.
- Regarded as a bold reformer, a strong critic of untouchability, and an advocate of women's rights in Hindu society.
Veer Savarkar was a man of rare courage, vision, and determination. His role in India’s freedom struggle, his writings, and his ideas continue to influence generations. On his Jayanti, let us remember his sacrifice and learn from his life.
Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025
Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025 will be observed on May 28, 2025, marking the 142nd birth anniversary of Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, popularly known as "Veer Savarkar." On this day, people across India pay tribute to his sacrifice and commitment to the country's freedom. Various cultural programs, seminars, essay competitions, and events are organized to honor his memory.
Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, affectionately called Veer Savarkar, was a revolutionary freedom fighter, poet, writer, and political thinker. His bold ideas and fierce patriotism made him one of the most controversial yet influential figures in India’s struggle for independence. Every year, his birth anniversary is celebrated with pride and remembrance throughout the country.
- On Veer Savarkar Jayanti 2025, government officials, students, and members of civil society participate in floral tributes and remembrance events. His portrait is garlanded, and discussions about his contributions take place in schools and universities.
- Cultural programs, seminars, and essay competitions are organized to honor his memory and promote awareness about his role in India’s freedom struggle.
Biography of Veer Savarkar
Veer Savarkar was born on May 28, 1883, in Bhagur village, near Nashik, Maharashtra. His full name was Vinayak Damodar Savarkar. From a young age, he was deeply inspired by stories of Indian resistance against British rule. He founded a revolutionary group called Mitra Mela, which later evolved into the Abhinav Bharat Society.
Savarkar was a brilliant student. He attended Fergusson College in Pune and later moved to London in 1906 on a scholarship to study law at Gray’s Inn. While in London, he joined India House and became a prominent figure in the Indian revolutionary movement abroad.

Veer Savarkar’s Contribution to National Freedom Movements
Veer Savarkar played a pivotal role in shaping the revolutionary phase of India’s struggle for independence. His ideas were radical and differed from the moderate and Gandhian approaches. He believed that freedom could not be achieved through petitions and non-violence alone. Here are the key contributions of Veer Savarkar to India’s freedom movement:
- Founded the Abhinav Bharat Society to train youth in revolutionary ideas.
- Authored ‘ The Indian War of Independence 1857, ’ which presented the 1857 uprising as a national struggle rather than a mutiny.
- Promoted armed resistance against British rule while in London.
- Became the first political prisoner to be sentenced to two life terms (total 50 years) and was sent to Cellular Jail in the Andaman Islands.
- Inspired many revolutionaries, including Bhagat Singh, Subhas Chandra Bose, and Lala Hardayal.
- After his release, he actively promoted Hindu unity and nationalist thought through speeches and writings.
- Advocated social reforms like ending caste discrimination and promoting widow remarriage.
- Though his ideology was not aligned with the Congress, his contributions to India’s independence were significant. He focused on cultural nationalism and encouraged Indians to take pride in their heritage.
Veer Savarkar’s Books
Veer Savarkar was not only a revolutionary but also a prolific writer. His books, essays, and poems played a crucial role in awakening patriotic feelings among Indians. He used his writing to challenge colonial narratives and promote nationalist ideology. Some of his most famous works include:
- The Indian War of Independence 1857: One of the first books to portray the 1857 uprising as a national struggle.
- Hindutva: Who is a Hindu? In this book, Savarkar explained his concept of cultural nationalism and defined the term Hindutva.
- The Story of My Transportation for Life:. powerful autobiographical account of his experiences in the Andaman Cellular Jail.
- Six Glorious Epochs of Indian History:. historical analysis showcasing India’s resistance against invaders throughout history.
- Some of his other notable works include Letters from Andamans, Historic Statements by Savarkar, Hindu Rashtra Darshan, Inside the Enemy Camp, Hindu Pad Padashahi, and काला पानी.
Veer Savarkar’s Death and Legacy
Veer Savarkar passed away on February 26, 1966, in Mumbai. He had voluntarily chosen atmaarpan (self-willed death) by giving up food and medicines, declaring that his mission was complete. His death marked the end of an era, but his legacy continues to influence India’s political and cultural discussions today.
- He is considered a pioneer of Hindutva ideology, which influences current political thought.
- Honoured posthumously by the Government of India, with the airport at Port Blair named Veer Savarkar International Airport.
- His life story is taught in schools, and his works are studied in colleges.
- He inspires discussions on nationalism, social reform, and civil liberties.
- Regarded as a bold reformer, a strong critic of untouchability, and an advocate of women's rights in Hindu society.
Veer Savarkar was a man of rare courage, vision, and determination. His role in India’s freedom struggle, his writings, and his ideas continue to influence generations. On his Jayanti, let us remember his sacrifice and learn from his life.
|
110 videos|653 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on History, Art and Culture: May 2025 UPSC Current Affairs - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What was the significance of the Satavahana Dynasty in ancient Indian history? |  |
| 2. What were the major contributions of the Satavahana Dynasty to art and culture? |  |
| 3. How did the Satavahana Dynasty influence trade in ancient India? |  |
| 4. What role did the Satavahana Dynasty play in the spread of Buddhism? |  |
| 5. What were the socio-political structures of the Satavahana Dynasty? |  |





















