UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Coins in Ancient and Medieval India
Mind Map: Coins in Ancient and Medieval India | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
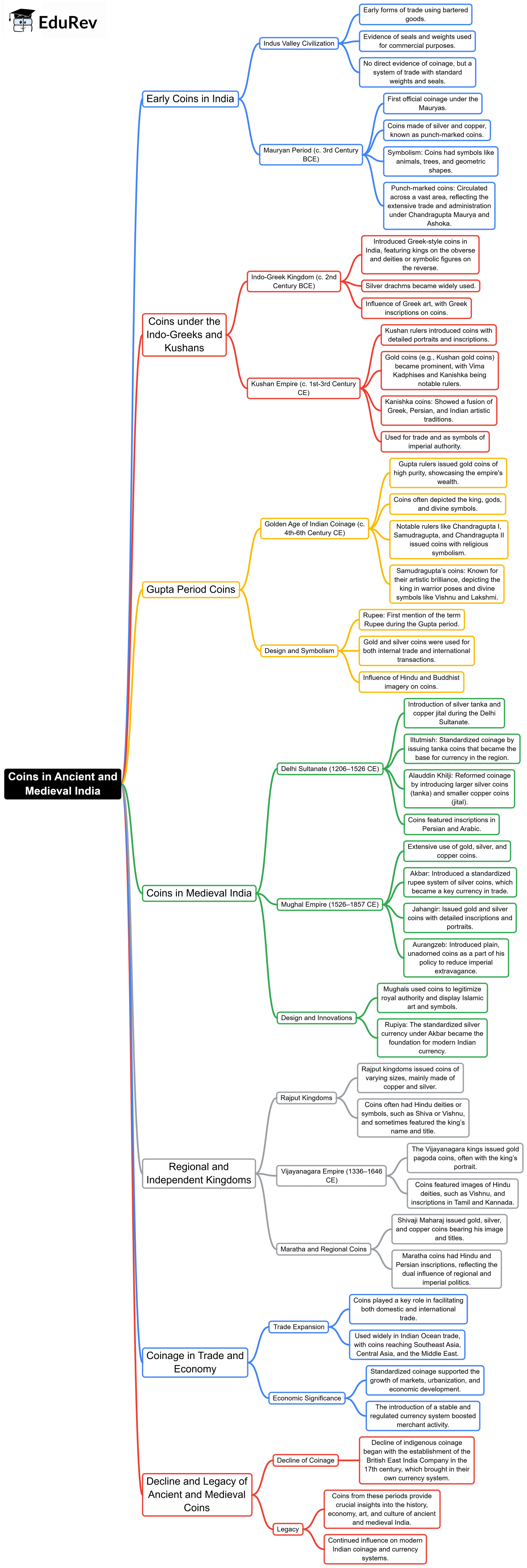
The document Mind Map: Coins in Ancient and Medieval India | History for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course History for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
110 videos|653 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Coins in Ancient and Medieval India - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the main types of coins used in Ancient and Medieval India? |  |
Ans. In Ancient and Medieval India, the main types of coins included punch-marked coins, cast coins, and minted coins. Punch-marked coins, made from silver or copper, were among the earliest forms used, featuring various symbols punched onto them. Cast coins, made by pouring molten metal into molds, were prevalent in regions like Magadha. Minted coins, which were produced by official mints, showcased intricate designs and were often used by various dynasties, such as the Gupta and Maurya empires.
| 2. How did the coinage system evolve in Ancient India? |  |
Ans. The coinage system in Ancient India evolved from the use of barter and commodity money to the introduction of metal coins. Initially, the Indus Valley Civilization used various objects for trade. By the 6th century BCE, with the rise of Mahajanapadas, coinage became standardized, particularly with punch-marked coins. Over time, as trade expanded and empires grew, the need for a more sophisticated currency system led to the minting of coins with specific weights and designs, reflecting the political and economic conditions of the time.
| 3. What role did coins play in trade and economy during Medieval India? |  |
Ans. During Medieval India, coins played a crucial role in facilitating trade and shaping the economy. They served as a medium of exchange, enabling merchants and traders to conduct transactions more efficiently than barter systems. The introduction of standardized weights and measures in coinage improved trade relations across regions. Additionally, coins often bore inscriptions that reflected the authority of the ruling dynasties, which helped in establishing trust and credibility in commerce.
| 4. What are some notable dynasties that issued coins in Medieval India? |  |
Ans. Some notable dynasties that issued coins in Medieval India include the Gupta Empire, which is renowned for its gold coins called "dinar," and the Mughal Empire, known for its silver coins known as "rupiya." The Chola and Vijayanagara empires also minted distinctive coins that depicted their rulers and deities, contributing to the rich numismatic history of India during the medieval period.
| 5. How did the metal composition of coins reflect the socio-economic conditions of Ancient and Medieval India? |  |
Ans. The metal composition of coins in Ancient and Medieval India often reflected the socio-economic conditions of the time. For instance, gold coins were typically issued during prosperous periods, indicating wealth and stability, while copper coins were more common during times of economic challenges. The shift in metal usage also indicated trade relations, with certain regions favoring specific metals based on availability and demand. Additionally, the quality and purity of the metal used in coins could signify the authority of the issuing power and its economic policies.
Related Searches
















