UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Environment for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Indian Forest
Mind Map: Indian Forest | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
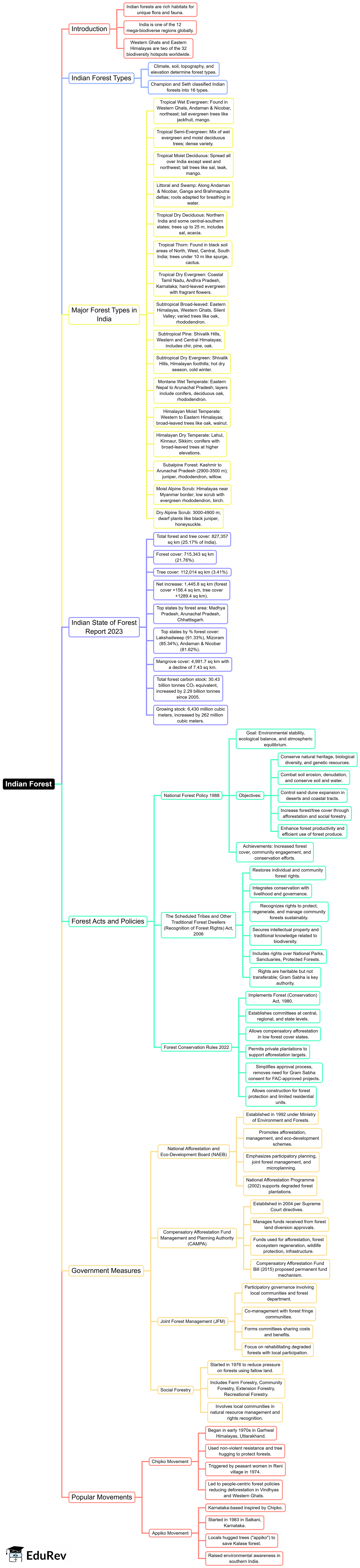
The document Mind Map: Indian Forest | Environment for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Environment for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
95 videos|230 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Indian Forest - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major types of forests found in India? |  |
Ans. India is home to a diverse range of forests, primarily categorized into four major types:
1. Tropical Evergreen Forests: These are found in regions with heavy rainfall, such as the Western Ghats and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. They are characterized by dense vegetation and high biodiversity.
2. Tropical Deciduous Forests: Also known as monsoon forests, these are found in regions with moderate rainfall and shed their leaves in the dry season. They are prevalent in states like Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
3. Temperate Forests: Found in the Himalayan region, these forests experience a cool climate and are dominated by coniferous trees such as pines and firs.
4. Mangrove Forests: Located along the coastal regions, particularly in the Sundarbans, these forests are adapted to saline conditions and play a crucial role in protecting coastal ecosystems.
| 2. What is the significance of the Forest Conservation Act in India? |  |
Ans. The Forest Conservation Act, enacted in 1980, is significant as it aims to prevent deforestation and promote the conservation of forest resources in India. The Act mandates that any diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes requires prior approval from the central government. This legislation is crucial for protecting biodiversity, maintaining ecological balance, and ensuring sustainable development. It also emphasizes the need for afforestation and reforestation in degraded areas.
| 3. How does deforestation impact biodiversity in Indian forests? |  |
Ans. Deforestation significantly impacts biodiversity in Indian forests by leading to habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation of ecosystems. As forests are cleared for agriculture, urbanization, or industrial purposes, many species lose their natural habitats, which can result in population decline or extinction. Additionally, the loss of tree cover disrupts the food chain and ecological interactions among species, leading to a decrease in overall biodiversity. This loss of biodiversity can also affect ecosystem services that forests provide, such as carbon sequestration, water regulation, and soil preservation.
| 4. What measures are taken to conserve wildlife in Indian forests? |  |
Ans. Various measures are implemented to conserve wildlife in Indian forests, including:
1. Establishment of National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries: Protected areas are created to conserve habitats and protect endangered species.
2. Wildlife Protection Act: Implemented in 1972, this act provides legal protection to wildlife and regulates hunting and trade of wildlife products.
3. Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts through eco-development programs helps in sustainable resource management.
4. Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the importance of wildlife conservation and promoting responsible tourism to minimize human-wildlife conflict.
| 5. What role do forests play in the economy of India? |  |
Ans. Forests play a vital role in the economy of India by providing a wide range of resources and services. They contribute to the economy through:
1. Timber and Non-Timber Forest Products: Forests supply timber for construction and various non-timber products such as medicinal herbs, fruits, and nuts, which support livelihoods.
2. Employment: The forestry sector provides jobs to millions, especially in rural areas, in activities like logging, forest management, and eco-tourism.
3. Ecosystem Services: Forests contribute to ecosystem services, including carbon sequestration, soil conservation, and water regulation, which are essential for agriculture and overall environmental health.
4. Tourism: Forests attract tourists for wildlife viewing and adventure activities, contributing to the growth of the tourism industry.
Related Searches
















