UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Tax Structure in India
Mind Map: Tax Structure in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Tax Structure in India - 1
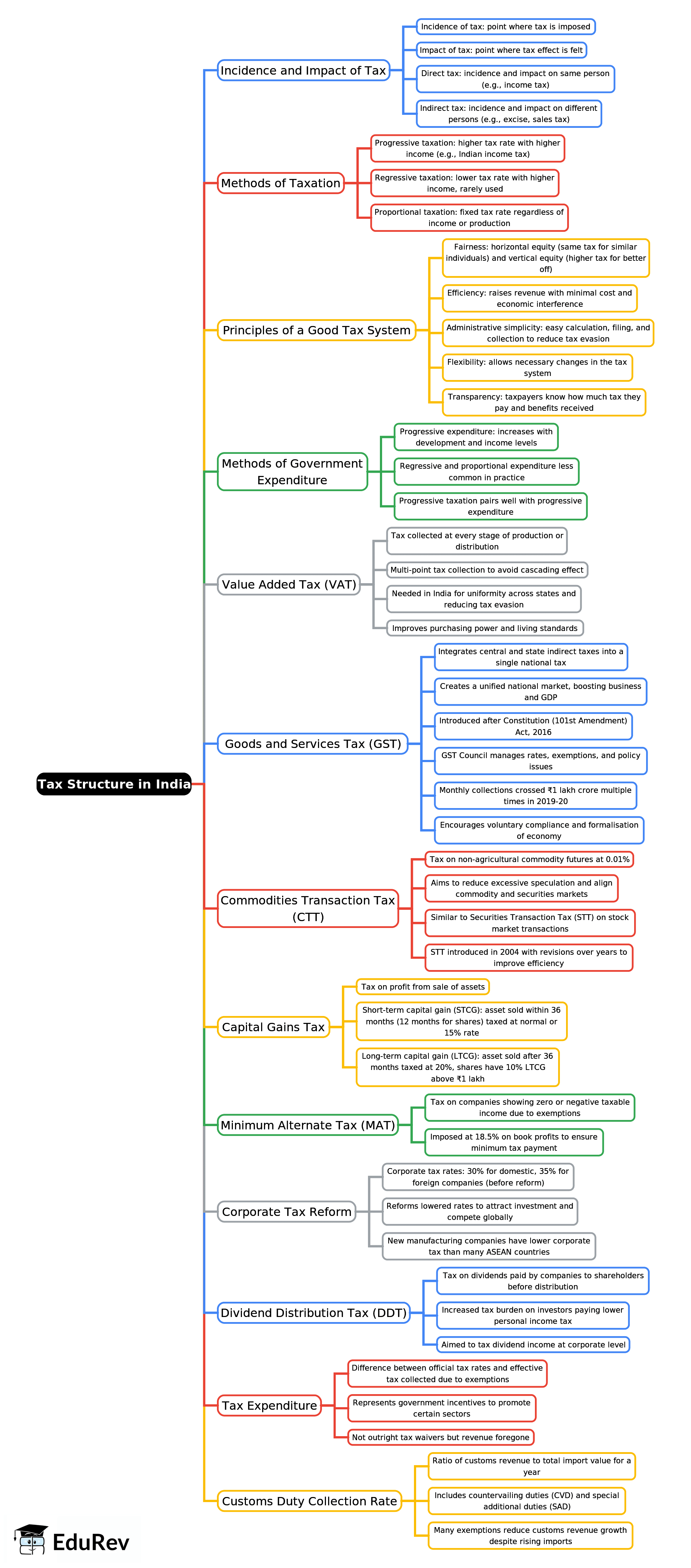
Tax Structure in India - 2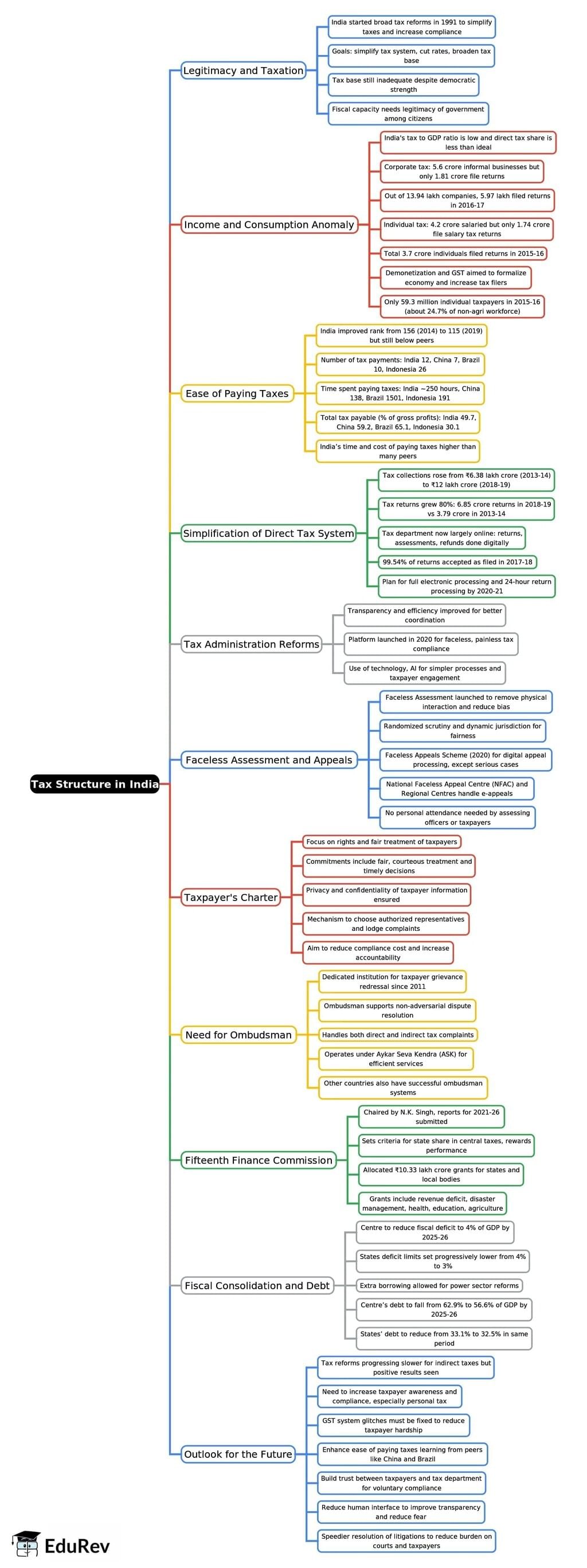
The document Mind Map: Tax Structure in India | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Tax Structure in India - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main components of the tax structure in India? |  |
Ans. The tax structure in India comprises two main categories: direct taxes and indirect taxes. Direct taxes are levied directly on the income of individuals and corporations, including income tax, corporate tax, and wealth tax. Indirect taxes are applied to the sale of goods and services, including goods and services tax (GST), customs duty, and excise duty. These taxes are collected by the government and play a crucial role in revenue generation.
| 2. How does the Goods and Services Tax (GST) impact the tax structure in India? |  |
Ans. The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a significant reform in the Indian tax structure, introduced to simplify the indirect tax system. It replaces multiple indirect taxes with a single tax regime, ensuring seamless flow of input tax credit across state boundaries. GST aims to enhance compliance, reduce tax evasion, and ultimately increase tax revenue for the government. Its implementation has led to a more organized tax system and improved ease of doing business.
| 3. What are the different income tax slabs for individual taxpayers in India? |  |
Ans. In India, individual taxpayers are categorized into different income tax slabs based on their annual income. The tax slabs vary for individuals below 60 years, senior citizens (aged 60 years and above), and super senior citizens (aged 80 years and above). Each slab dictates the percentage of tax applicable to income ranges. This tiered structure is designed to impose higher tax rates on higher income levels while providing relief to lower-income earners.
| 4. What is the role of the Income Tax Department in India? |  |
Ans. The Income Tax Department in India is responsible for the administration of direct taxes. Its primary roles include the assessment and collection of income tax, enforcing tax laws, conducting audits, and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. The department also handles taxpayer grievances and implements measures to curtail tax evasion. Through these functions, it plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the tax system and ensuring fair tax practices.
| 5. How are taxes used for public expenditure in India? |  |
Ans. Taxes collected by the government are utilized for various public expenditures, including infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and social welfare programs. The revenue generated from taxes is crucial for funding government initiatives and public services, which are essential for economic growth and development. Effective use of tax revenue contributes to improving the quality of life for citizens and promotes overall national progress.
Related Searches





















