UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Other Constitutional Dimensions
Mind Map: Other Constitutional Dimensions | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
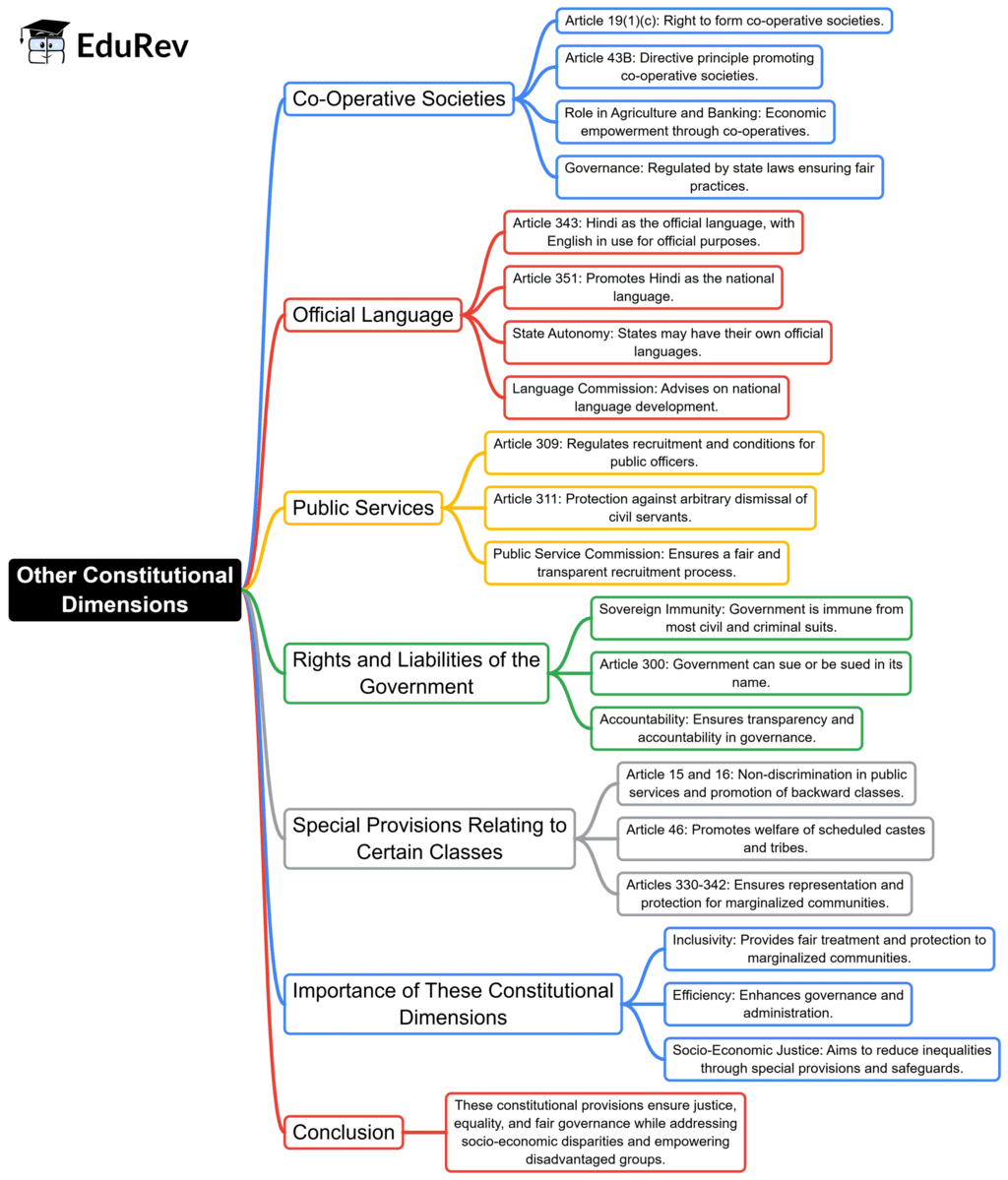
The document Mind Map: Other Constitutional Dimensions | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Other Constitutional Dimensions - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key features of the Constitution of India that reflect its federal structure? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India exhibits a federal structure through several key features. Firstly, it establishes a clear division of powers between the central and state governments, as outlined in the Union List, State List, and Concurrent List. Secondly, it provides for a strong central authority while allowing states to exercise their own powers, ensuring a balance of governance. Additionally, the Constitution includes provisions for the distribution of financial resources between the center and states, which further enhances its federal character. Finally, the presence of an independent judiciary serves to adjudicate disputes between different levels of government, maintaining the federal framework.
| 2. How does the Constitution of India protect fundamental rights? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India safeguards fundamental rights through Part III, which enumerates a series of rights that are guaranteed to all citizens. These rights include the right to equality, right to freedom, right against exploitation, right to freedom of religion, cultural and educational rights, and the right to constitutional remedies. The Constitution empowers individuals to approach the Supreme Court or High Courts for enforcement of these rights, thus ensuring protection against any infringement by the state or individuals. Furthermore, any law that violates these rights can be declared unconstitutional by the judiciary.
| 3. What role does the Directive Principles of State Policy play in the Indian Constitution? |  |
Ans. The Directive Principles of State Policy, enshrined in Part IV of the Constitution, serve as guidelines for the state in formulating policies aimed at promoting social and economic welfare. While these principles are not justiciable, meaning they cannot be enforced by the courts, they are fundamental in the governance of the country. They aim to ensure justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity among citizens. The Directive Principles complement the Fundamental Rights by providing a framework for achieving socio-economic justice and reducing inequalities in the society.
| 4. What is the significance of the basic structure doctrine in Indian constitutional law? |  |
Ans. The basic structure doctrine is a landmark principle established by the Supreme Court of India, asserting that certain fundamental features of the Constitution cannot be altered or destroyed by amendments. This doctrine emerged from the Kesavananda Bharati case, emphasizing the supremacy of the Constitution and the need to protect its core values, such as the rule of law, separation of powers, and the independence of the judiciary. The significance of this doctrine lies in its role as a safeguard against arbitrary changes to the Constitution that could undermine democracy and the fundamental rights of citizens.
| 5. How does the Constitution of India address the rights of minorities? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India addresses the rights of minorities through several provisions that ensure their protection and promote their interests. Articles 29 and 30 specifically protect the cultural and educational rights of minorities, allowing them to preserve their distinct language, script, and culture, as well as the establishment of educational institutions. Additionally, the Constitution prohibits discrimination on the basis of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth, thereby ensuring that minorities can enjoy equal rights and opportunities. This framework aims to foster social harmony and protect the interests of minority communities in the nation.
Related Searches





















