UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Pressure Groups
Mind Map: Pressure Groups | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
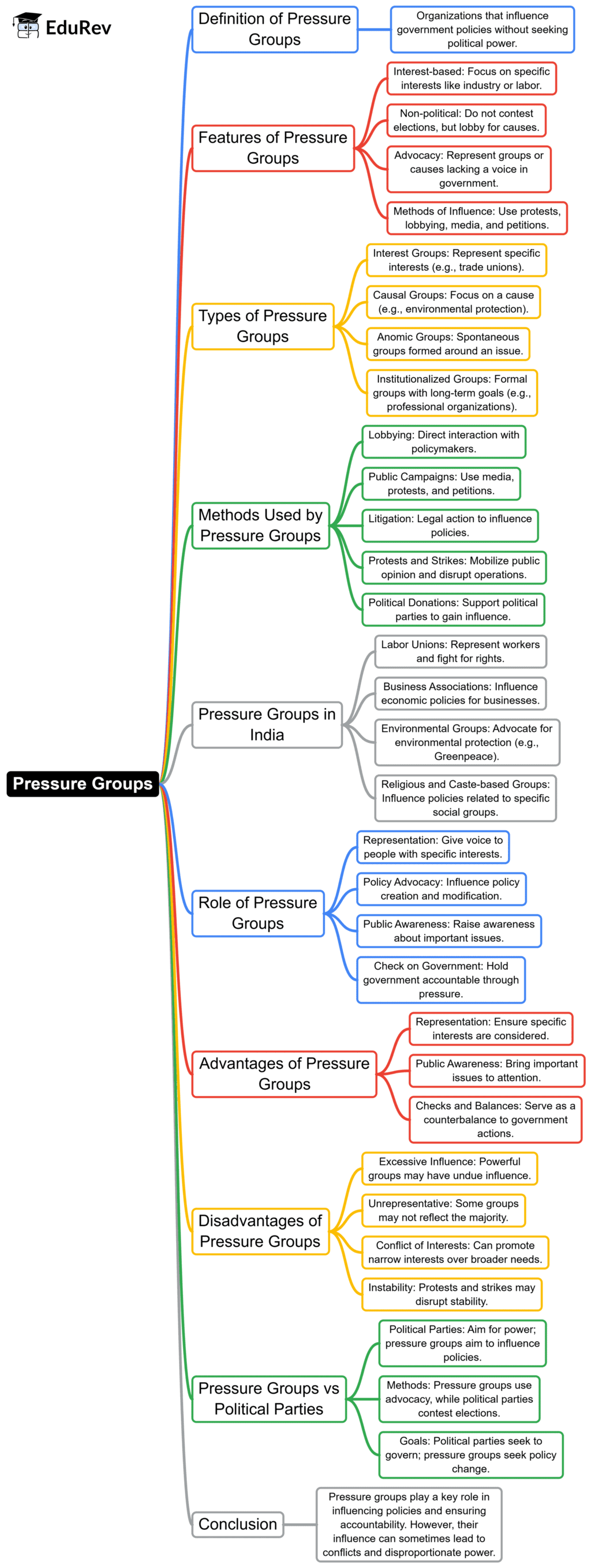
The document Mind Map: Pressure Groups | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Pressure Groups - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are pressure groups and how do they influence policy-making? |  |
Ans. Pressure groups are organized groups of individuals who share common interests and actively seek to influence public policy and decision-makers to achieve specific goals. They operate by lobbying government officials, conducting campaigns, and raising public awareness on issues. Their influence on policy-making can be significant, as they can mobilize public opinion, provide expertise and data to policymakers, and contribute to the political discourse.
| 2. What are the different types of pressure groups? |  |
Ans. Pressure groups can be categorized into several types:
1. Promotional or interest groups, which aim to promote a particular cause (e.g., environmental groups).
2. Sectional or professional groups, representing specific professions or sectors (e.g., trade unions).
3. Political pressure groups, which align closely with political parties and seek to influence their policies (e.g., party-affiliated organizations).
4. Single-issue groups, focusing on one specific issue (e.g., anti-abortion groups).
| 3. What role do pressure groups play in a democratic society? |  |
Ans. In a democratic society, pressure groups play a crucial role by representing diverse interests and viewpoints. They enhance democratic participation by allowing citizens to engage in the political process, advocate for change, and hold government accountable. They contribute to public debate, educate the public on various issues, and can lead to more informed policymaking by providing specialized knowledge and perspectives.
| 4. How do pressure groups differ from political parties? |  |
Ans. Pressure groups and political parties serve different functions within the political system. Political parties aim to gain control of government and implement a broad policy agenda, often by contesting elections. In contrast, pressure groups focus on specific issues or interests and do not seek to govern. While both seek to influence policy, their methods, objectives, and organizational structures differ significantly.
| 5. What are some challenges faced by pressure groups in their activities? |  |
Ans. Pressure groups face several challenges, including:
1. Competition from other groups with opposing interests, which can dilute their influence.
2. Limited resources, as many rely on donations and volunteer support.
3. Public apathy or skepticism towards their causes, which can hinder their campaigns.
4. Regulatory constraints, such as laws governing lobbying and campaign financing, which can restrict their activities and funding sources.
Related Searches
















