UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Coalition Government
Mind Map: Coalition Government | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
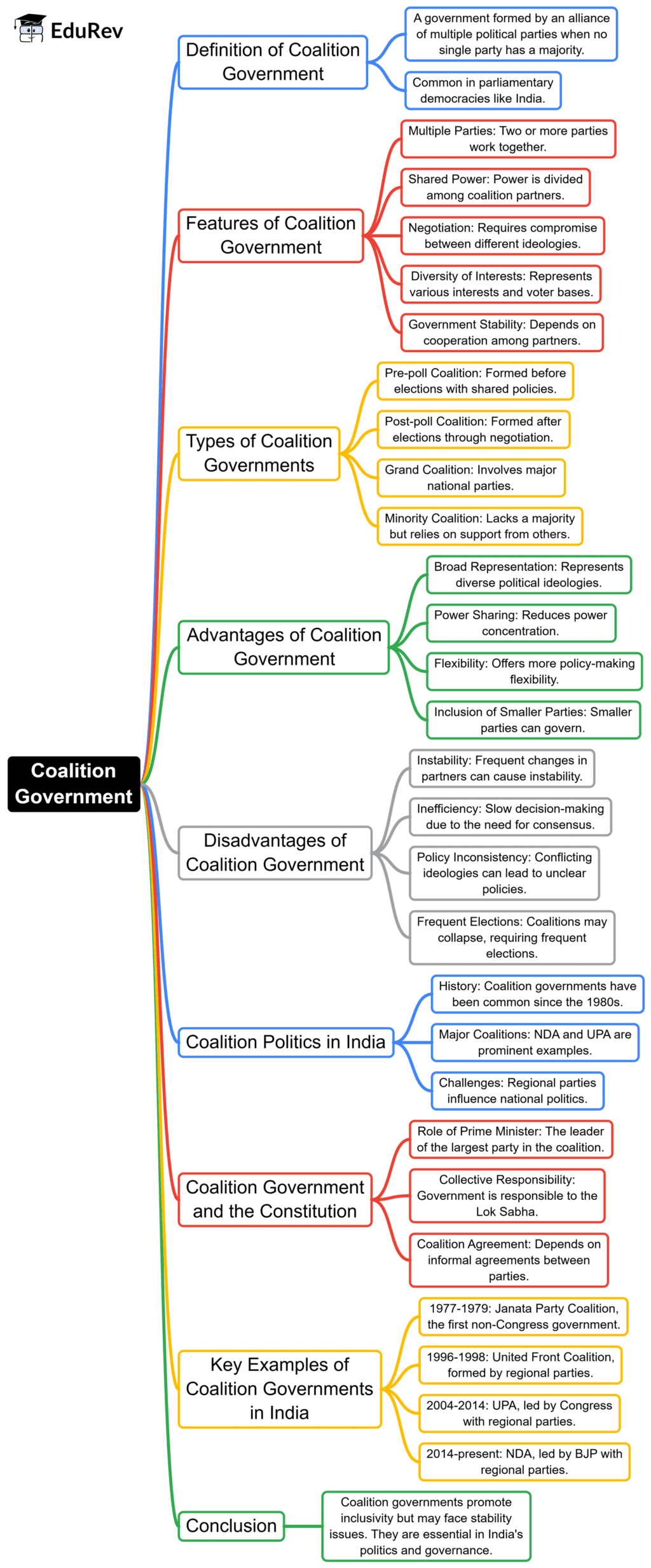
The document Mind Map: Coalition Government | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Coalition Government - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is a coalition government and how does it function? |  |
Ans. A coalition government is formed when multiple political parties come together to create a government, typically because no single party has achieved an outright majority in the legislature. This arrangement requires negotiation and compromise among the parties involved, leading to the establishment of a unified agenda and shared policy goals. Coalition governments often rely on agreements known as "coalition pacts" that outline the terms of cooperation, division of ministerial roles, and policy priorities.
| 2. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a coalition government? |  |
Ans. The advantages of a coalition government include enhanced representation of diverse views and interests, as smaller parties can have a voice in governance. It can also lead to more stable policies through consensus-building. However, disadvantages include potential instability, as coalitions may struggle to maintain unity and could collapse over disagreements. Additionally, the need for compromise might dilute policy effectiveness, leading to slower decision-making processes.
| 3. How have coalition governments influenced Indian politics historically? |  |
Ans. Coalition governments have played a significant role in Indian politics, particularly since the 1980s. The rise of regional parties and the inability of any single party to secure a majority in the Lok Sabha led to various coalition formations. Notable examples include the National Front government in the late 1980s and the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) in the 2000s. These coalitions have shaped policy decisions, electoral strategies, and party dynamics, reflecting India's diverse political landscape.
| 4. What are some key examples of coalition governments around the world? |  |
Ans. Coalition governments are common in many countries, particularly those with proportional representation systems. Examples include the German government, led by a coalition of multiple parties, often referred to as "the grand coalition." In the United Kingdom, coalition governments have emerged, such as the coalition between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Democrats. These examples illustrate how coalition governance can vary in structure and effectiveness based on the political context.
| 5. What role do coalition agreements play in the stability of a coalition government? |  |
Ans. Coalition agreements are crucial for the stability of a coalition government, as they outline the terms of cooperation among the involved parties. These agreements typically specify policy priorities, divisions of cabinet positions, and mechanisms for conflict resolution. A well-structured coalition agreement can help mitigate disputes and foster collaboration, while a poorly negotiated agreement may lead to tensions and potential collapse, emphasizing the importance of clear communication and mutual understanding among coalition partners.
Related Searches




















