UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Comparison of the Constitutions
Mind Map: Comparison of the Constitutions | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
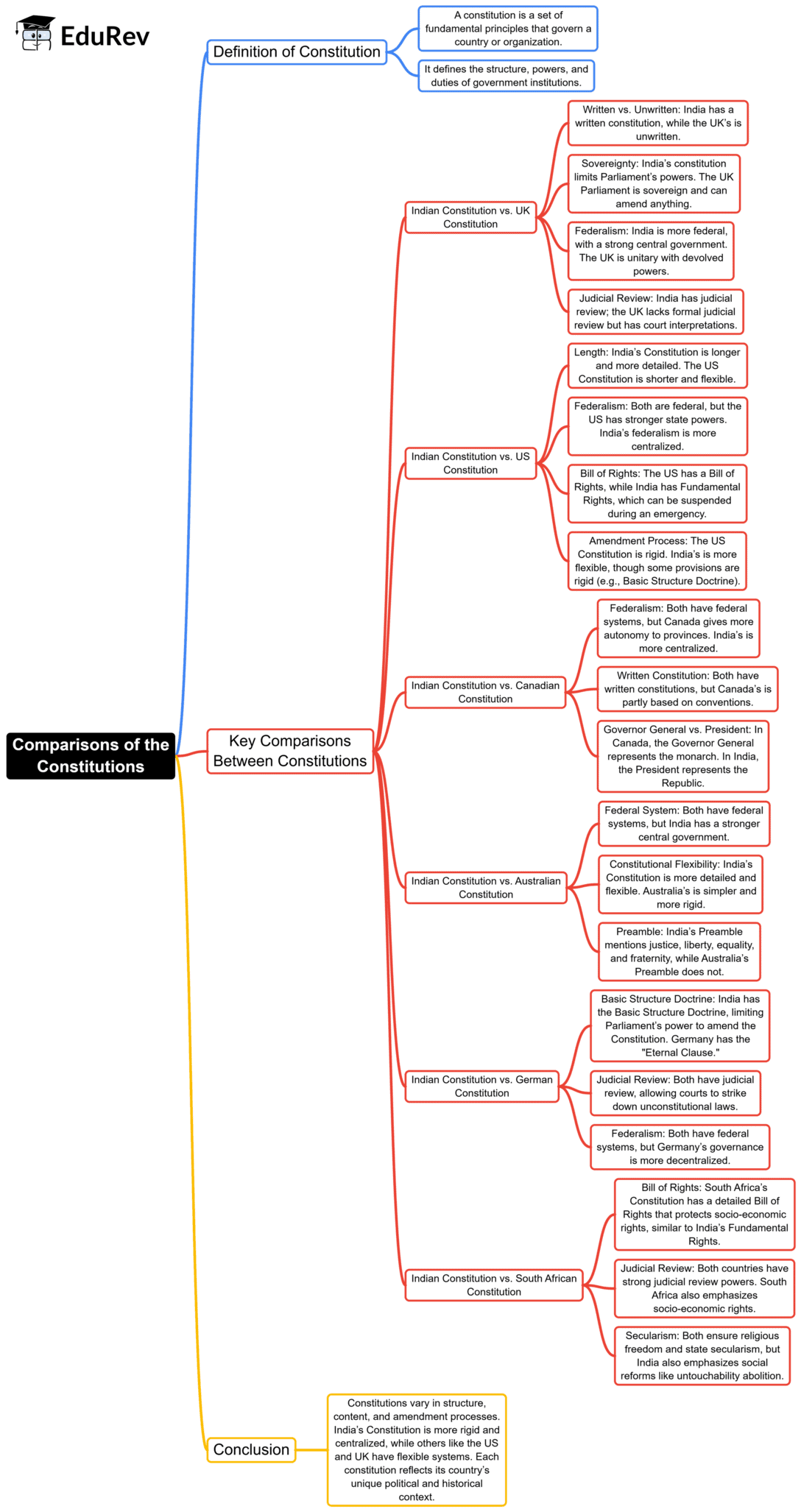
The document Mind Map: Comparison of the Constitutions | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Comparison of the Constitutions - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key differences between the Indian Constitution and the United States Constitution? |  |
Ans.The Indian Constitution is the longest written constitution in the world and incorporates a federal structure with a strong central government, while the US Constitution emphasizes states' rights and is comparatively shorter. India has a parliamentary system, whereas the US operates under a presidential system. Additionally, the Indian Constitution includes provisions for fundamental rights and duties, whereas the US Constitution outlines individual rights through the Bill of Rights.
| 2. How does the process of amendment differ in the Indian Constitution compared to the US Constitution? |  |
Ans.In India, the Constitution can be amended through a simple majority in Parliament or a two-thirds majority in both houses, depending on the type of amendment. In contrast, the US Constitution requires a two-thirds majority in both houses of Congress or a convention called for by two-thirds of state legislatures, followed by ratification from three-fourths of the states. This makes amending the US Constitution more challenging than in India.
| 3. What role do fundamental rights play in the Indian Constitution as compared to the US Constitution? |  |
Ans.Fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution guarantee individual liberties and are justiciable, meaning individuals can approach courts for their enforcement. The US Constitution's Bill of Rights similarly protects individual freedoms but has a historical context tied to the states' rights debate. While both documents emphasize freedom of speech and religion, the Indian Constitution also includes the right to equality and the right against exploitation, which are not explicitly stated in the US Bill of Rights.
| 4. How does the concept of secularism differ in the Indian and US Constitutions? |  |
Ans.The Indian Constitution explicitly defines secularism in its Preamble, ensuring equal treatment of all religions and the separation of religion from the State. It allows for some state intervention in religious matters to maintain equality among different faiths. In contrast, the US Constitution mandates the separation of church and state, meaning the government cannot favor or interfere with religion, which reflects a more individualistic approach to religious freedom.
| 5. What are the similarities in the fundamental duties outlined in the Indian Constitution and the responsibilities of citizens in the US? |  |
Ans.Both the Indian Constitution and the US Constitution emphasize the importance of civic responsibility. The Indian Constitution enumerates specific fundamental duties for its citizens, such as promoting harmony and protecting the environment. Similarly, while the US Constitution does not explicitly list duties, it implies responsibilities through democratic participation, such as voting and serving on juries, highlighting the shared value of civic engagement in both nations.
Related Searches





















