Cheat Sheet: State Legislature | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains India’s state legislatures.. They’re like mini-parliaments for each state, making laws and policies for local needs. We’ll cover their structure, members, duration, officers, sessions, law-making process, and privileges.
Introduction
State legislatures are part of India’s federal system, letting elected people make laws for their state. They ensure local voices are heard in a democratic way.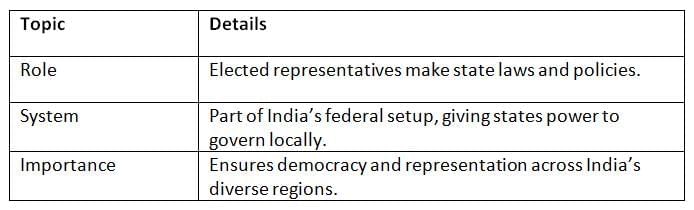 State legislatures are key to local governance, making laws that fit each state’s needs in India’s democracy.
State legislatures are key to local governance, making laws that fit each state’s needs in India’s democracy.
Organization of State Legislature
Most states have one house (unicameral), but six have two (bicameral). The structure includes the Governor and one or two houses.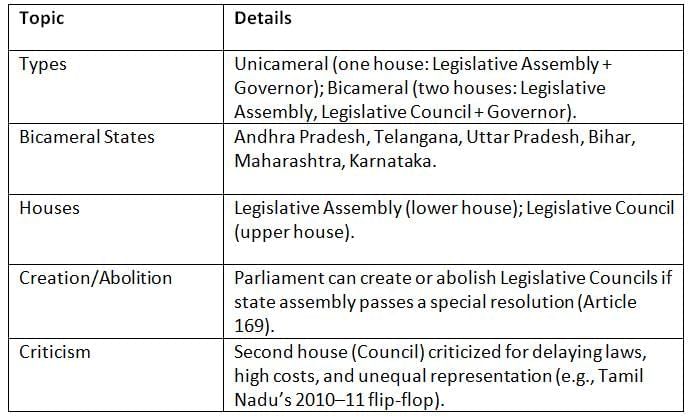 Most states have one house, but six have two. Councils can be added or removed, but they’re debated for being costly and slow.
Most states have one house, but six have two. Councils can be added or removed, but they’re debated for being costly and slow.
Composition of Two Houses
The Legislative Assembly has elected members, while the Council has elected and nominated members, each with specific roles.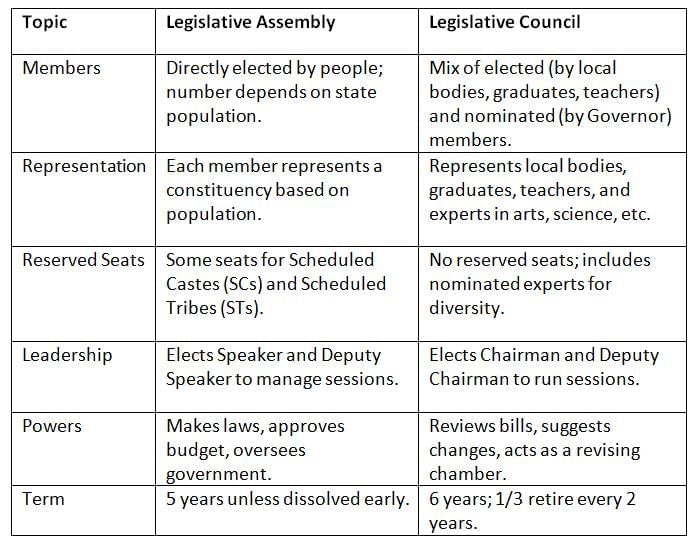
The Assembly is elected and powerful; the Council mixes elected and expert members, reviewing laws for better quality.
Duration of Two Houses
The Assembly lasts five years, while the Council is permanent with rotating members.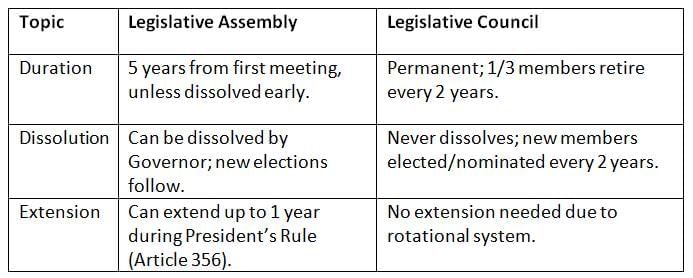
The Assembly has a fixed term but can end early; the Council stays ongoing with regular member changes.
Membership of State Legislature
Members of the legislature must meet qualifications, take an oath, and can lose their seat for specific reasons.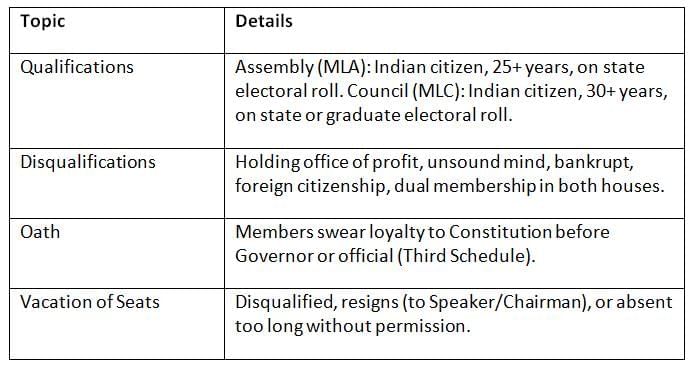
Members need to be qualified, loyal, and active, or they risk losing their seat.
Presiding Officers of State Legislature
Each house has leaders to run sessions fairly and keep order.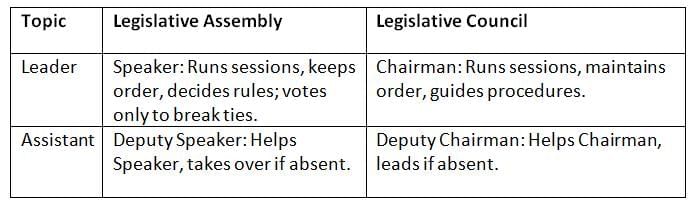
Speakers and Chairmen ensure smooth, fair sessions in their houses, with deputies as backups.
Sessions of State Legislature
The legislature meets in sessions, managed by the Governor and Chief Minister, with rules for starting, pausing, or ending.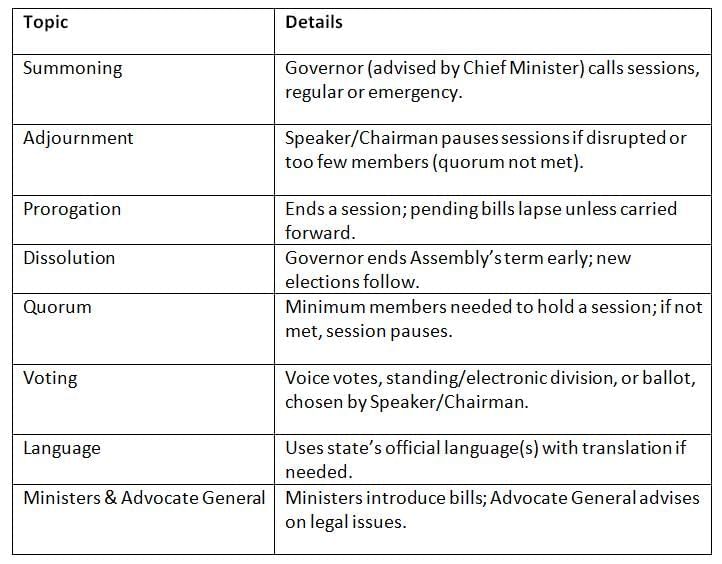 Sessions are planned and run carefully, with clear rules to ensure fair and effective work.
Sessions are planned and run carefully, with clear rules to ensure fair and effective work.
Legislative Procedure in State Legislature
Making laws involves introducing bills, debating, passing them in both houses (if bicameral), and getting Governor’s approval.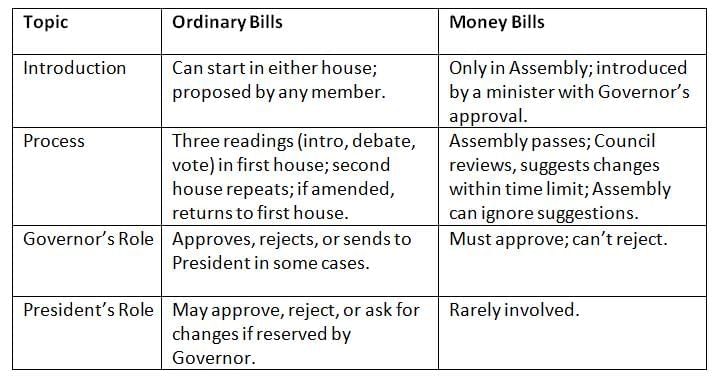 Ordinary bills need both houses’ approval; money bills are Assembly-driven, with Council’s role limited.
Ordinary bills need both houses’ approval; money bills are Assembly-driven, with Council’s role limited.
Bills Reserved for President’s Consideration
Some bills must or can be sent to the President by the Governor for approval.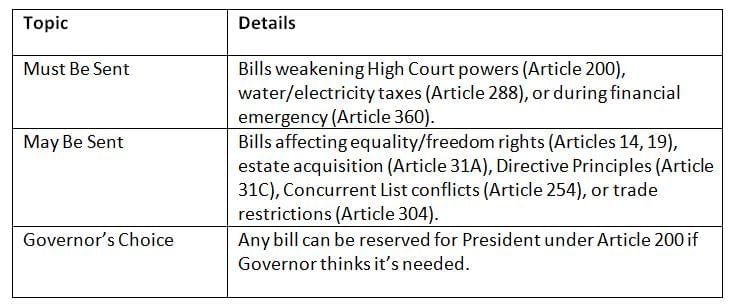 Certain bills need President’s approval to protect national or constitutional interests; Governors decide for others.
Certain bills need President’s approval to protect national or constitutional interests; Governors decide for others.
Legislative Procedure Compared: Parliament vs. State Legislature
State legislatures and Parliament have similar roles but differ in scope and focus.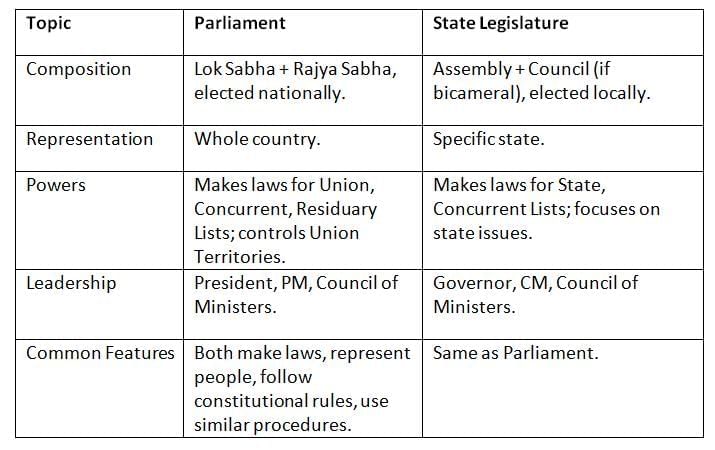 Parliament handles national laws; state legislatures focus on local needs, but both follow similar democratic processes.
Parliament handles national laws; state legislatures focus on local needs, but both follow similar democratic processes.
Position of Legislative Council
In bicameral states, the Council’s power compared to the Assembly varies—equal in some, weaker in others.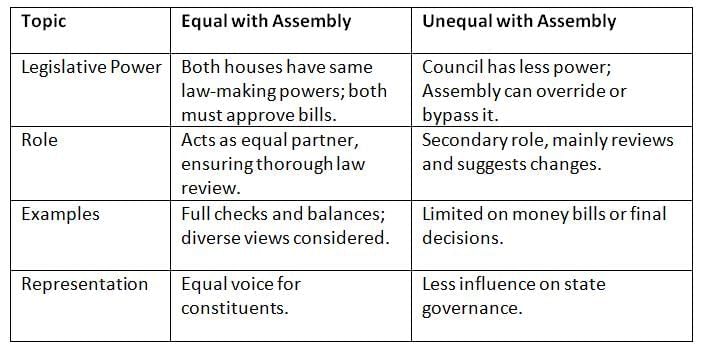
Councils can be equal partners or weaker reviewers, depending on the state, affecting how laws are made.
Privileges of State Legislature
Legislatures and their members have special rights to work freely and effectively.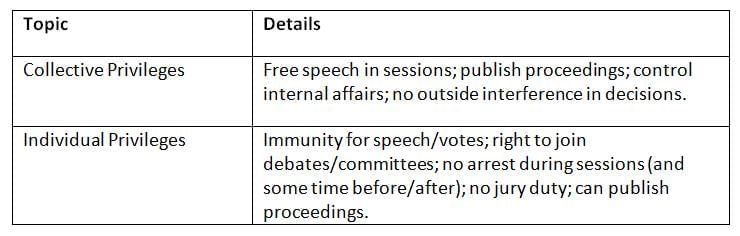
Privileges protect free speech and action, ensuring legislators can focus on their duties without fear.
Conclusion
This chapter shows how state legislatures are vital for local governance in India’s federal system. With one or two houses, they make laws, represent people, and keep the government in check. Their structure, processes, and privileges ensure democracy works at the state level. By balancing local needs with national unity, state legislatures drive progress and strengthen India’s democratic framework.
|
154 videos|998 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: State Legislature - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key features of the organization of a state legislature in India? |  |
| 2. What is the duration and term of the two houses of the state legislature? |  |
| 3. Who are the presiding officers of the state legislature, and what are their roles? |  |
| 4. What are the typical sessions of a state legislature, and how are they structured? |  |
| 5. How does the legislative procedure in a state legislature compare to that in the Parliament of India? |  |





















