Cheat Sheet: Union Territories | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains how India’s territories are organized, focusing on union territories, which are directly governed by the Central government. It covers their creation, administration, reasons for their establishment, and special provisions, like those for Delhi. The chapter shows how union territories differ from states and their role in India’s governance system.
Territory of India
Article 1 of the Indian Constitution defines India’s territory, dividing it into states, union territories, and areas that may be acquired. Union territories are centrally administered, unlike states, which share power with the Centre in a federal setup.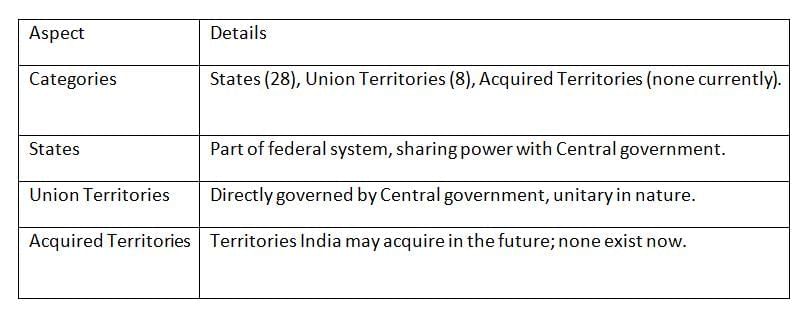
Key Points: India’s territory includes states with shared powers and union territories under direct Central control, reflecting a mix of federal and unitary governance.
Creation of Union Territories
Union territories evolved from British-era scheduled districts and were formalized after independence through constitutional and legislative changes, with some later becoming states.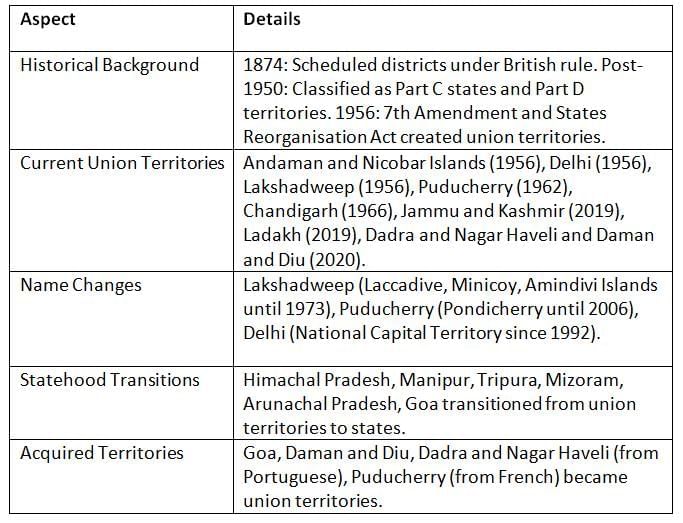
Key Points: Union territories were established post-independence, with some gaining statehood and others created or merged for administrative efficiency.
Reasons for Creating Union Territories
Union territories were created for specific political, cultural, strategic, or administrative reasons to address unique regional needs.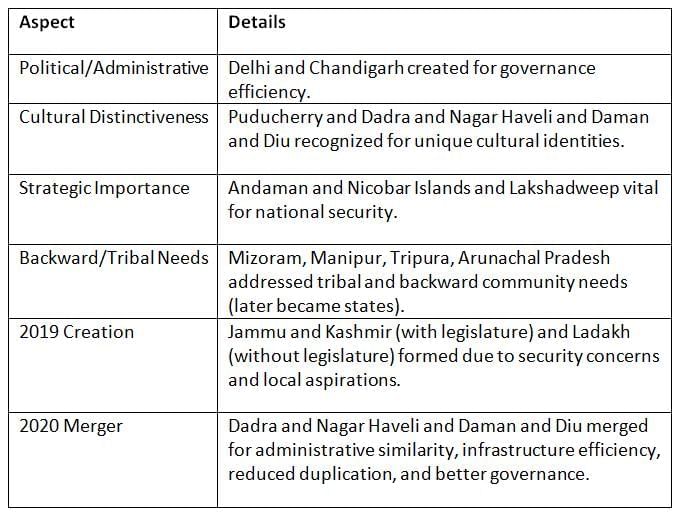
Key Points: Union territories were formed to address diverse needs like security, culture, and efficient administration, with recent changes reflecting local and strategic priorities.
Administration of Union Territories
Articles 239-241 of the Constitution outline how union territories are governed, with variations in administrative setups, including some with legislative assemblies.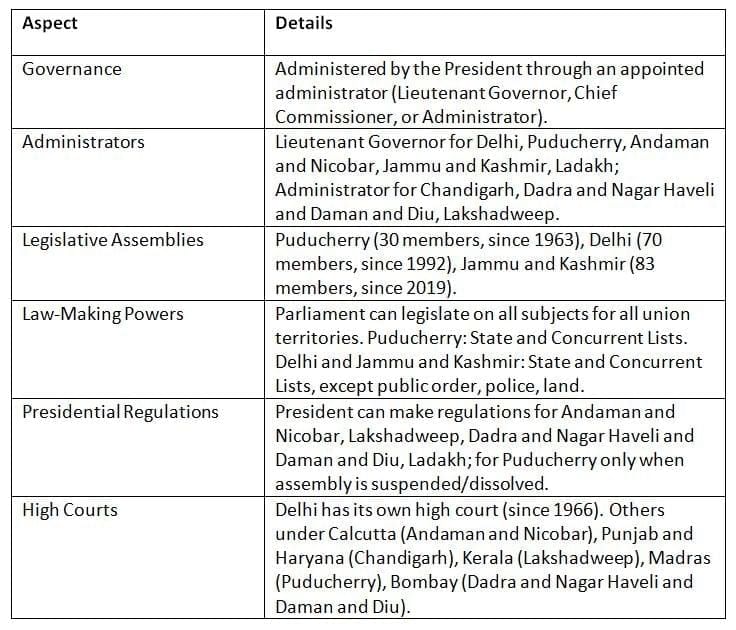
Key Points: Union territories are centrally administered with varying setups; some have legislatures, but Parliament retains supreme legislative power.
Special Provisions for Delhi
The 69th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1991 gave Delhi special status as the National Capital Territory, with a legislative assembly and unique governance arrangements.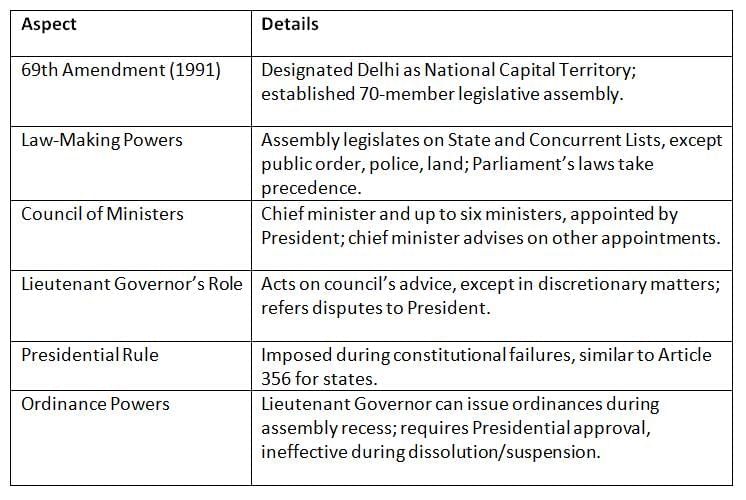
Key Points: Delhi’s special status includes a legislative assembly and council of ministers, but the Lieutenant Governor and Parliament hold significant authority.
Advisory Committees of Union Territories
Union territories without legislatures have advisory committees to support governance and address developmental needs, managed by the Ministry of Home Affairs.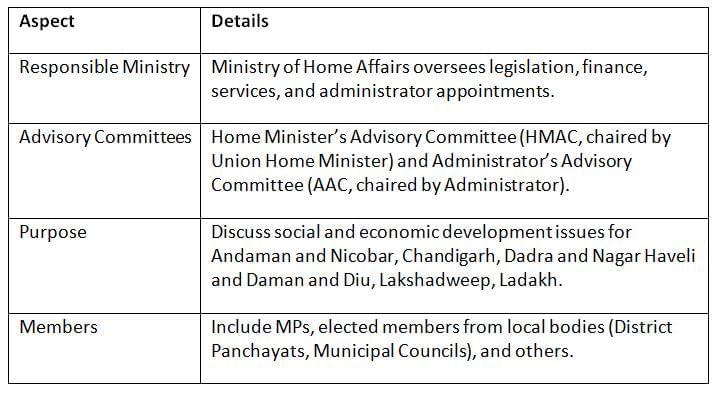
Key Points: Advisory committees provide a platform for local input in non-legislative union territories, enhancing governance and development planning.
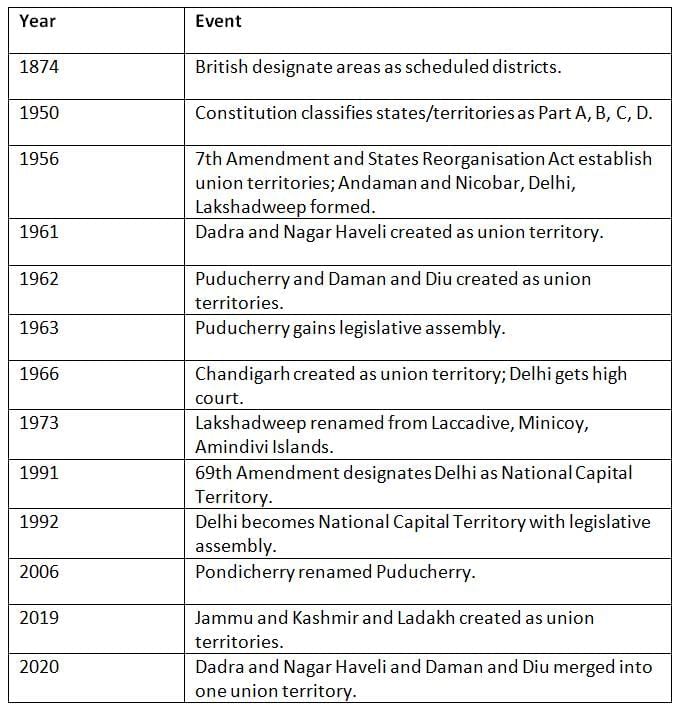
Chronology for Quick Revision
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the unique role of union territories in India’s governance, distinct from states due to their direct Central administration. Created for political, cultural, strategic, or administrative reasons, they ensure tailored governance for diverse regions. With varied setups—some with legislatures like Delhi and Puducherry, others with advisory committees—union territories balance local needs with national oversight. Strengthening their administration is key to effective governance and addressing regional aspirations.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Union Territories - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the definition and significance of Union Territories in India? |  |
| 2. What are the main reasons for the creation of Union Territories in India? |  |
| 3. How are Union Territories administered in India? |  |
| 4. What are the special provisions for the Union Territory of Delhi? |  |
| 5. What role do advisory committees play in the governance of Union Territories? |  |





















