Cheat Sheet: Coalition Government | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
Coalition politics in India involves alliances of political parties to form governments when no single party secures a parliamentary majority. Derived from the Latin term ‘coalitio’ (to grow together), it reflects a collaborative approach to governance. This chapter explores the features, history, reasons for growth, and merits and demerits of coalition governments, providing a clear reference for understanding their role in India’s democratic framework.
Features of Coalition Government
Coalition governments arise when parties unite to form a government based on a shared agenda, often necessitated by fragmented electoral mandates or national crises.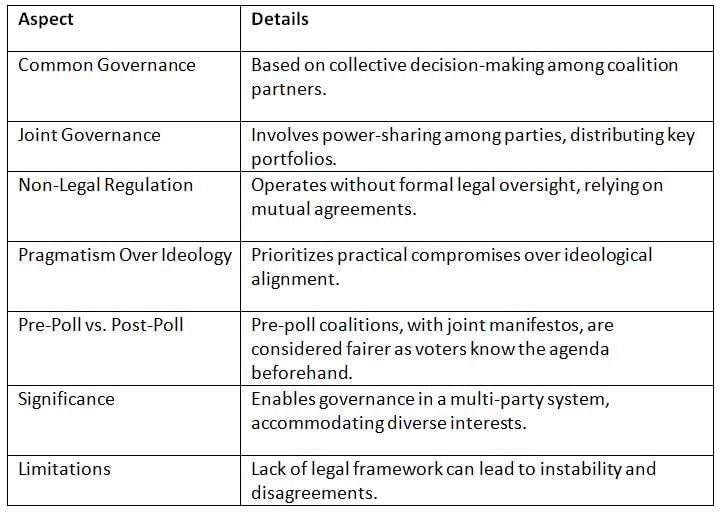
Key Points: Coalition governments emphasize shared decision-making and pragmatism but face challenges due to informal arrangements and ideological differences.
History of Coalition Governments in India
Coalition politics in India emerged post-independence, particularly after the decline of Congress’s dominance, with significant coalitions forming since the 1970s.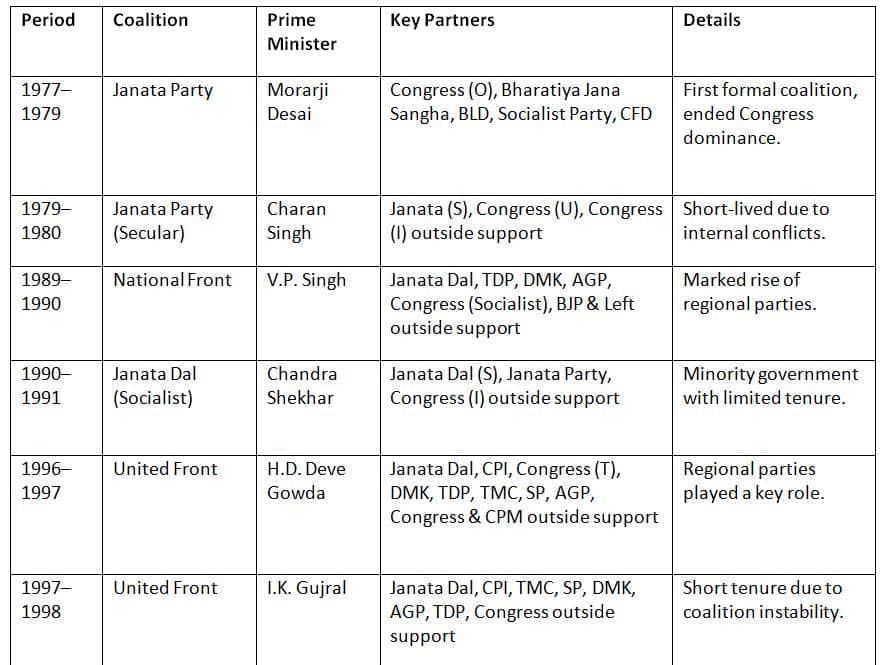
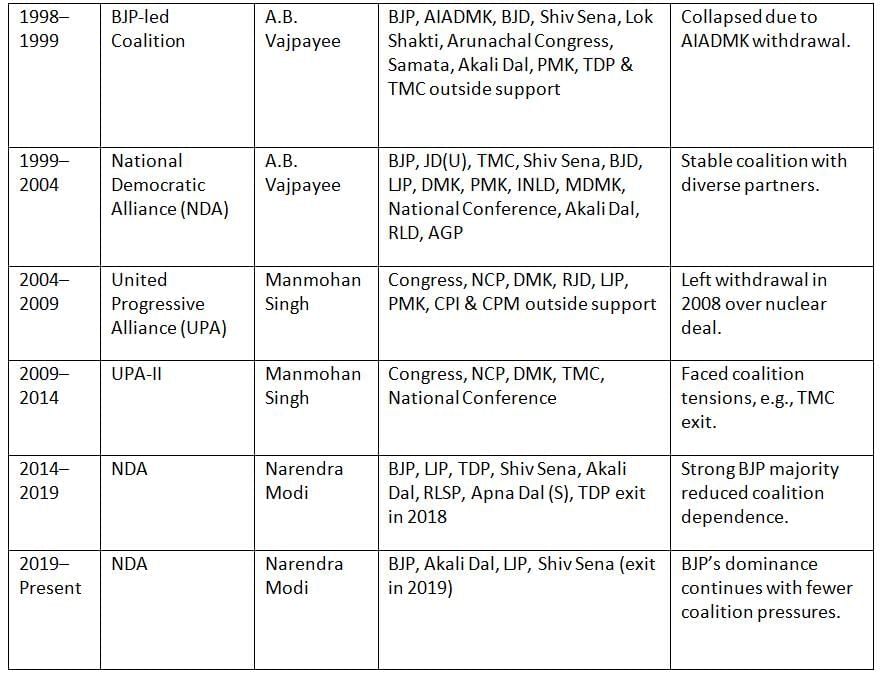 Key Points: Coalition governments became prominent after 1969, with the Janata Party’s 1977 coalition marking a shift from Congress dominance. Regional parties have since played a significant role in coalitions.
Key Points: Coalition governments became prominent after 1969, with the Janata Party’s 1977 coalition marking a shift from Congress dominance. Regional parties have since played a significant role in coalitions.
Reasons for Growth of Coalition Politics
The rise of coalition politics in India reflects the country’s diverse political landscape and the decline of single-party dominance.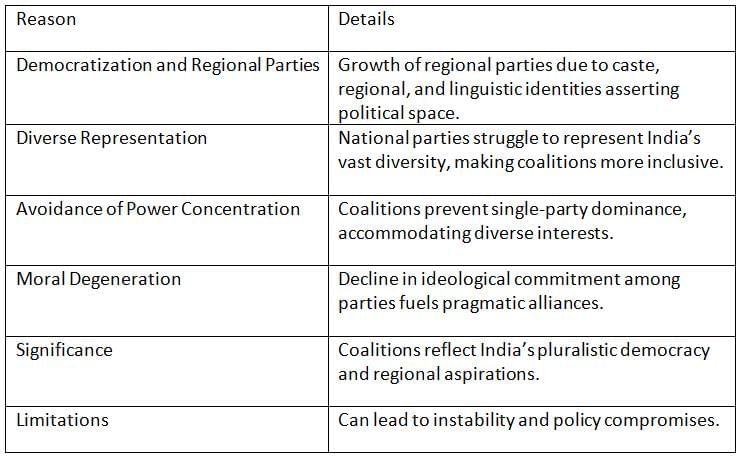
Key Points: Coalition politics thrives due to India’s diversity, regional party growth, and the need for inclusive governance, but it risks instability.
Merits of Coalition Government
Coalition governments offer several advantages by promoting inclusive and consensus-driven governance in a diverse democracy.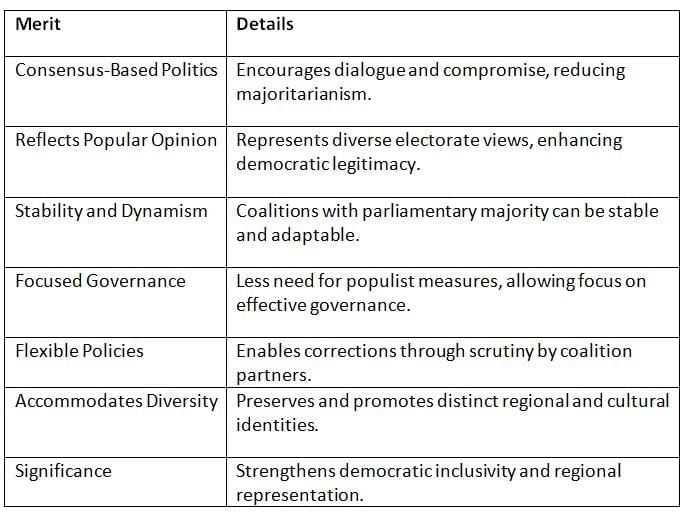
Key Points: Coalition governments foster inclusive, flexible, and democratic governance, accommodating India’s diverse identities.
Demerits of Coalition Government
Despite their advantages, coalition governments face challenges that can hinder effective governance and policy coherence.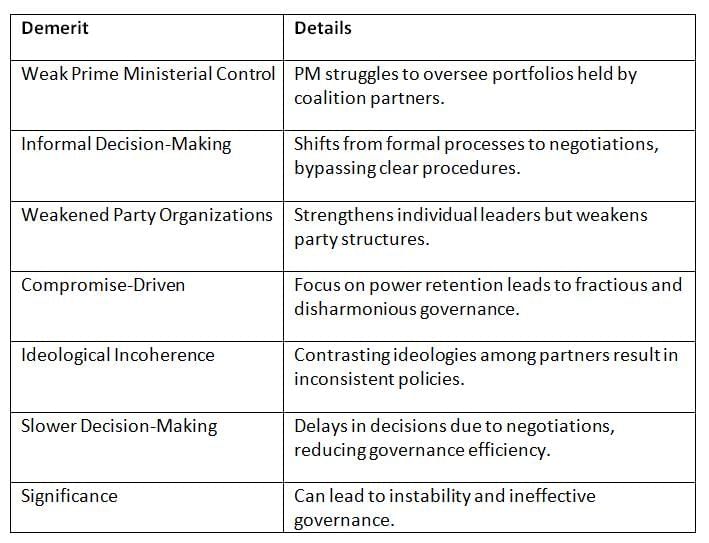
Key Points: Coalition governments often face instability, policy incoherence, and delayed decision-making due to competing interests.
Chronology of Key Coalition Governments
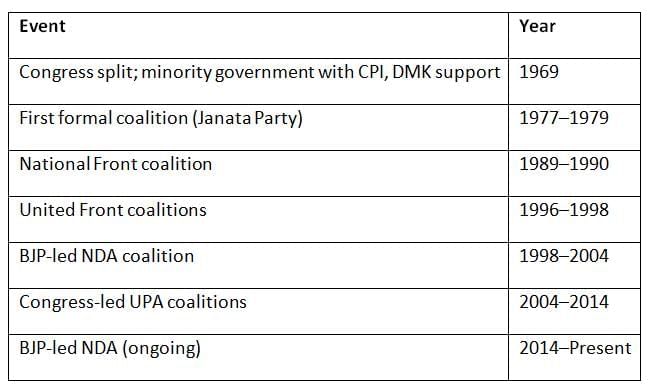
Conclusion
Coalition politics in India reflects the country’s diverse democratic fabric, enabling governance through alliances when no single party secures a majority. While coalitions promote consensus, inclusivity, and regional representation, they face challenges like instability, ideological incoherence, and slower decision-making. Understanding their features, history, and dynamics is crucial for appreciating India’s multi-party democracy and its evolving political landscape.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Coalition Government - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is a coalition government and what are its main features? |  |
| 2. What has been the historical context of coalition governments in India? |  |
| 3. What are the reasons for the growth of coalition politics in India? |  |
| 4. What are the merits and demerits of coalition governments? |  |
| 5. Can you provide a chronology of key coalition governments in India? |  |




















