Class 3 Exam > Class 3 Notes > Science for Class 3 > Mind Map: Measurement
Mind Map: Measurement | Science for Class 3 PDF Download
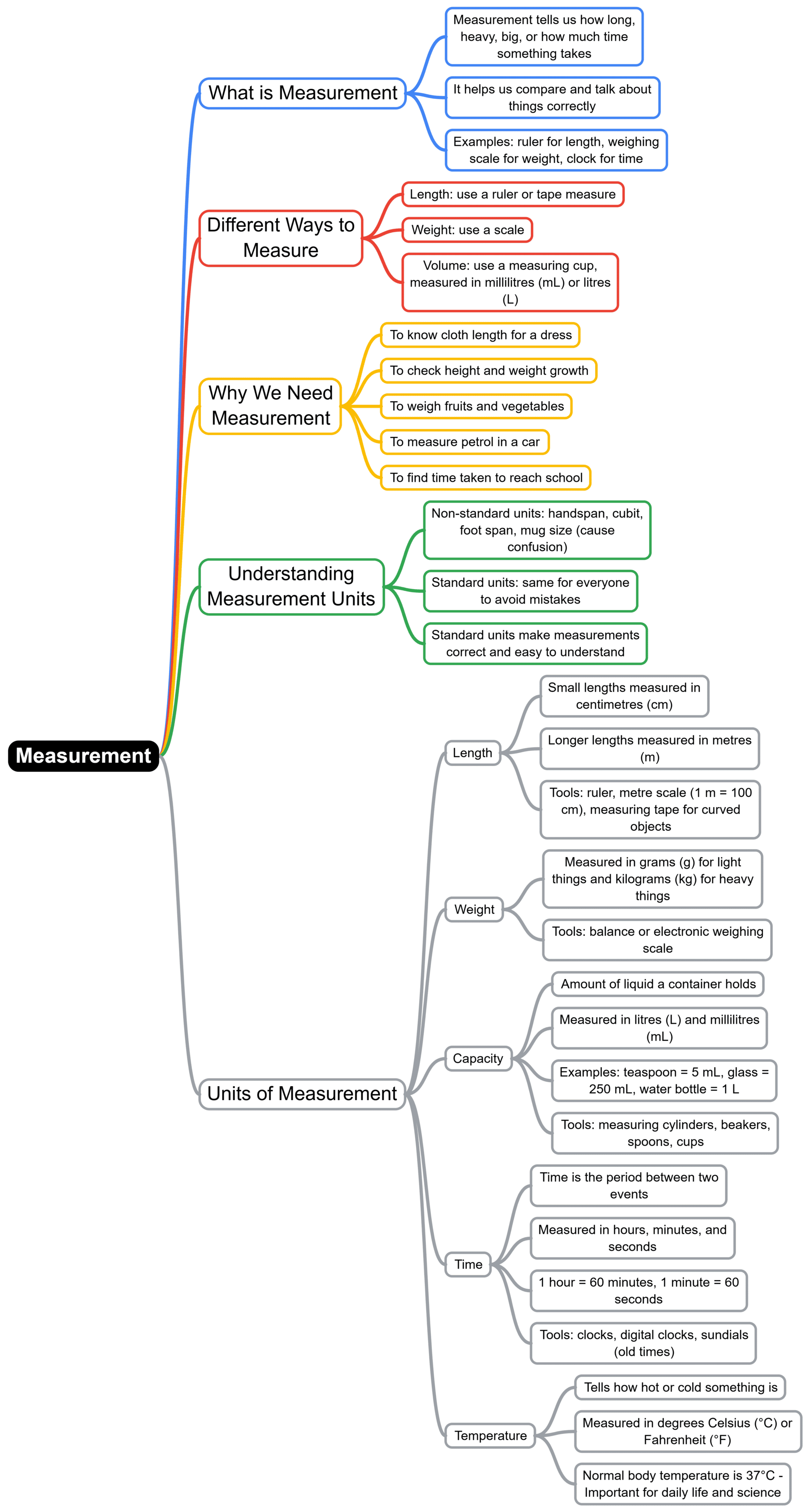
The document Mind Map: Measurement | Science for Class 3 is a part of the Class 3 Course Science for Class 3.
All you need of Class 3 at this link: Class 3
|
20 videos|121 docs|32 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Measurement - Science for Class 3
| 1. What is measurement and why is it important in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Measurement is the process of determining the size, quantity, or degree of something using established units or standards. It is important in everyday life because it allows individuals to understand and compare physical quantities, make informed decisions, and communicate effectively about dimensions and amounts. Whether cooking, building, or budgeting, accurate measurement ensures that tasks are completed correctly and efficiently.
| 2. What are the basic units of measurement in the metric system? |  |
Ans. The metric system is based on a set of standard units. The basic units include the meter (m) for length, the kilogram (kg) for mass, the liter (L) for volume, and the second (s) for time. These units can be modified using prefixes such as kilo- (1,000 times), centi- (1/100), and milli- (1/1,000) to express larger or smaller quantities.
| 3. How do you convert between different units of measurement? |  |
Ans. Converting between different units of measurement involves multiplying or dividing by conversion factors. For example, to convert meters to centimeters, one would multiply by 100 (since 1 m = 100 cm). Conversely, to convert centimeters to meters, one would divide by 100. It is crucial to know the appropriate conversion factors for accurate results.
| 4. What role do significant figures play in measurement? |  |
Ans. Significant figures are the digits in a measurement that carry meaning contributing to its precision. They are important because they indicate the accuracy of a measurement and help avoid overstatement of precision. When performing calculations, the result should be reported with the same number of significant figures as the measurement with the least number of significant figures to maintain accuracy.
| 5. What are common sources of error in measurement? |  |
Ans. Common sources of error in measurement include instrument limitations, human error, environmental factors, and improper techniques. For instance, using a ruler that is not calibrated correctly can lead to inaccurate measurements. Additionally, factors such as temperature or pressure can affect the results of certain measurements, making it essential to account for these variables to ensure accuracy.
Related Searches
















