Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Cheat Sheet: Life Processes
Cheat Sheet: Life Processes | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Overview of Life Processes |

|
| Nutrition |

|
| Respiration |

|
| Transportation |

|
| Excretion |

|
| Reproduction |

|
| Control and Coordination |

|
| Key Characteristics of Life Processes |

|
Introduction
Life processes are essential biological functions that sustain living organisms, enabling survival, growth, and adaptation. Key processes include nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, reproduction, and control and coordination, each vital for maintaining homeostasis.
Overview of Life Processes
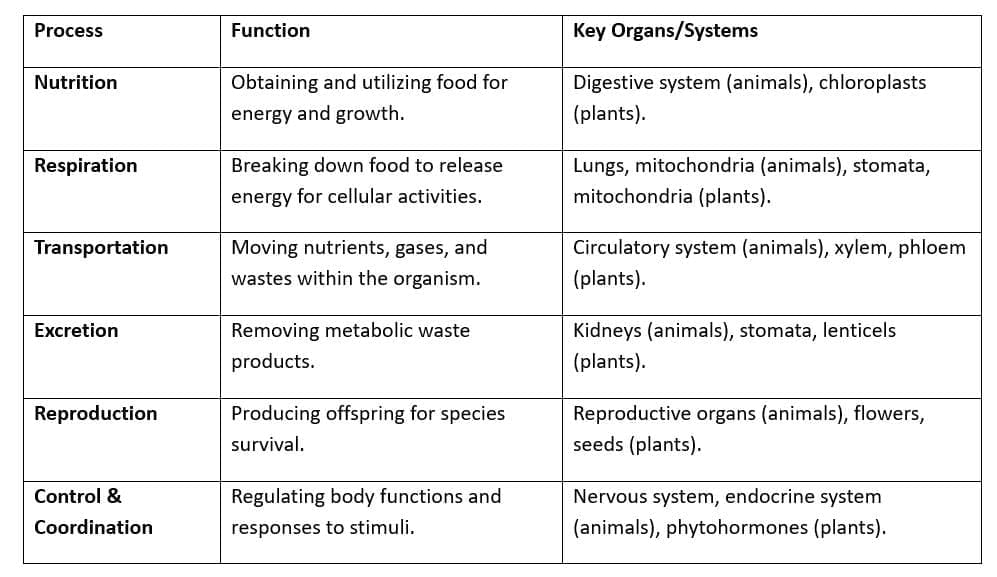
Nutrition
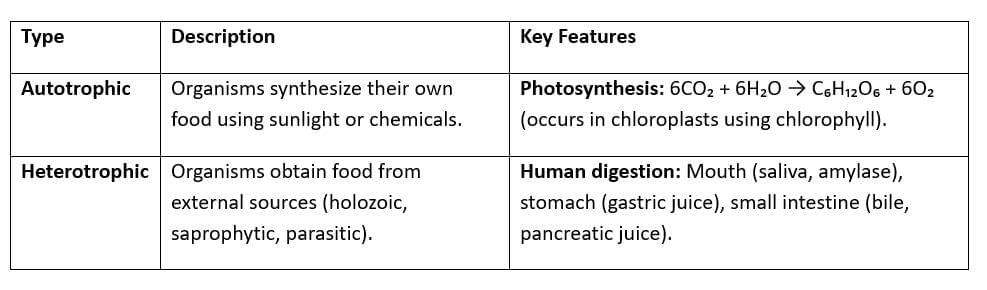
- Photosynthesis: Occurs in plant chloroplasts; produces glucose, oxygen; factors include light, CO₂, water.
- Human Digestive System: Breaks down carbohydrates (amylase), proteins (pepsin, trypsin), fats (lipase); small intestine absorbs nutrients.
- Nutritional Disorders: Malnutrition, obesity due to imbalanced diet.
Respiration
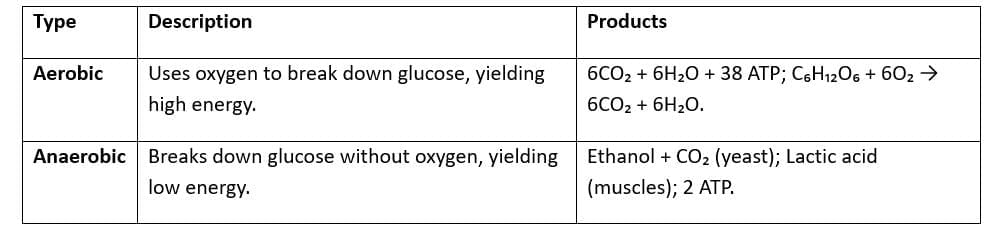
- Human Respiration: Involves nasal cavity, trachea, lungs; alveoli facilitate gas exchange (O₂ in, CO₂ out).
- Plant Respiration: Occurs in mitochondria; uses glucose, releases CO₂; occurs day and night.
- Energy Role: ATP powers cellular processes (e.g., muscle contraction, active transport).
Transportation

- Human Circulation: Double circulation; pulmonary (lungs for oxygenation), systemic (body); heart has four chambers.
- Plant Transport: Xylem moves water via transpiration pull; phloem translocates sugars via pressure flow.
- Blood Components: Plasma (water, proteins), hemoglobin in RBCs binds O₂.
Excretion
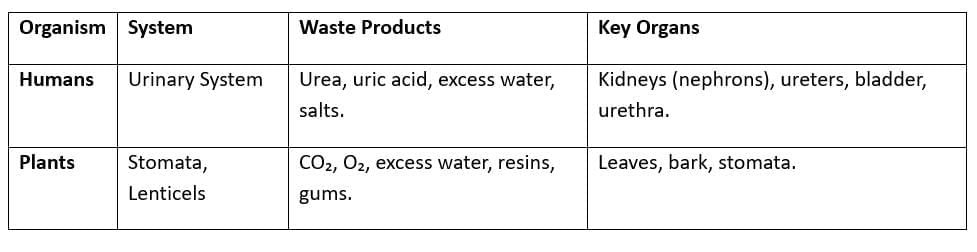
- Human Excretion: Nephrons filter blood, reabsorb water/nutrients, form urine; kidneys regulate water, electrolyte balance.
- Plant Excretion: CO₂, O₂ via stomata; wastes stored in leaves, shed as litter.
- Excretory Disorders: Kidney stones, uremia due to kidney failure.
Reproduction
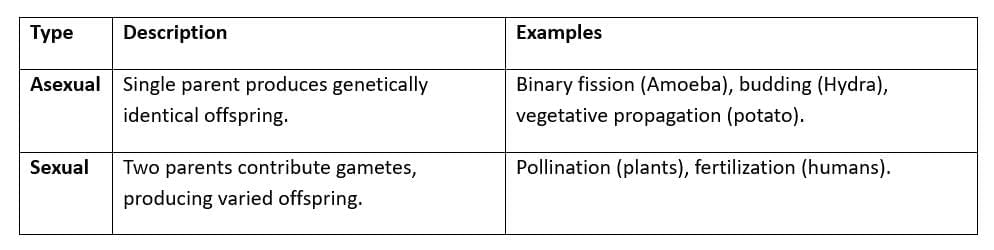
- Human Reproduction: Male (sperm) and female (egg) gametes; fertilization in fallopian tube forms zygote.
- Plant Reproduction: Sexual via pollination (pollen to stigma), seed formation; asexual via runners, cuttings.
- Significance: Ensures genetic diversity (sexual), rapid multiplication (asexual).
Control and Coordination
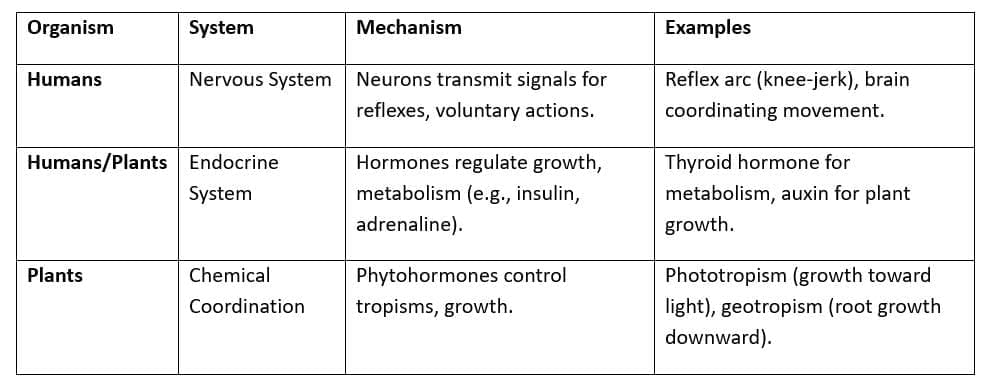
- Human Nervous System: Central (brain, spinal cord) and peripheral; synapses transmit nerve impulses.
- Plant Responses: Tropisms (e.g., phototropism, hydrotropism); phytohormones like gibberellins promote flowering.
- Hormonal Disorders: Diabetes (insulin deficiency), goiter (thyroid dysfunction).
Key Characteristics of Life Processes
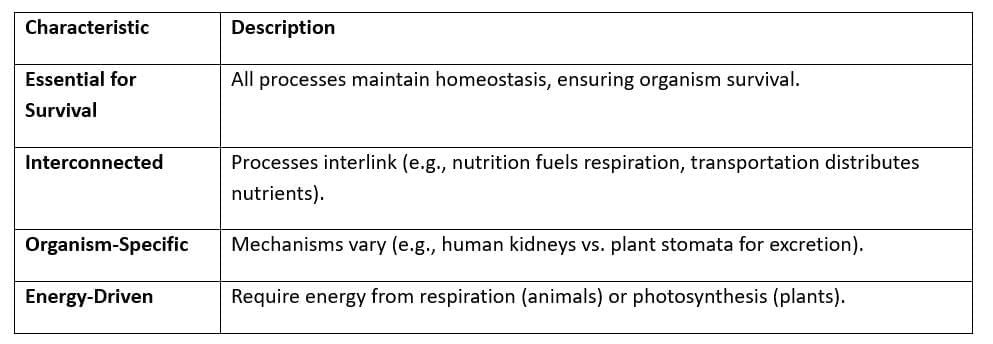
The document Cheat Sheet: Life Processes | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Life Processes - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the essential characteristics that define life? |  |
Ans.The essential characteristics that define life include organization (being made up of cells), metabolism (the ability to convert energy), homeostasis (maintaining stable internal conditions), growth and development, reproduction (the ability to produce offspring), response to stimuli (reacting to environmental changes), and adaptation through evolution over time.
| 2. What are the main life processes that organisms perform? |  |
Ans.The main life processes that organisms perform include nutrition (obtaining and utilizing food), respiration (converting food into energy), transportation (moving substances within the organism), excretion (removing waste), growth (increasing in size), reproduction (creating new individuals), and regulation (controlling internal processes).
| 3. What is autotrophic nutrition, and how does it differ from heterotrophic nutrition? |  |
Ans.Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms, such as plants, produce their own food from inorganic substances, primarily through photosynthesis, using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. In contrast, heterotrophic nutrition involves organisms that cannot synthesize their own food and must consume other organisms or organic matter for energy and nutrients.
| 4. How does photosynthesis occur, and what are its main stages? |  |
Ans.Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle). During the light-dependent reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts, sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll, leading to the production of energy carriers (ATP and NADPH) and oxygen from water. In the Calvin cycle, which occurs in the stroma, carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose using the energy from ATP and NADPH produced in the first stage.
| 5. What experiments can demonstrate the process of photosynthesis? |  |
Ans.Experiments that can demonstrate photosynthesis include the use of aquatic plants like Elodea, where oxygen bubbles can be observed when the plant is exposed to light, indicating photosynthesis. Another common experiment involves using a variegated leaf (green and white) of a plant, testing the green parts for starch after exposure to light, which shows that only the green areas that contain chlorophyll can perform photosynthesis.
Related Searches




















